2.3 Notes
advertisement

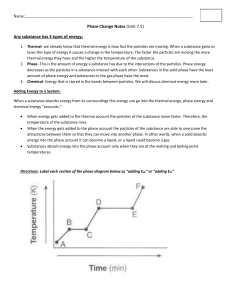
Changes in Matter Chapter 2 Section 3 • • • • • Physical Change Any change that alters the form or appearance of matter but does NOT make any substance in the matter into a different substance. Examples: Sand Castles Crushing a Can Dissolving Sugar in Water Changes of State Matter Occurs in 3 States Solid Liquid These are all physical changes Gas Physical Change • Is there a physical change when you What could you do separate dissolve a the sugar from the water? teaspoon of sugar in water? YES! Other examples of physical change: ~ Bending ~ Crushing ~ Chopping Chemical Change Change in matter that produces one or more new substances s a chemical change (reaction). Example: What happens when you pour hydrogen peroxide on a cut it breaks down into water and oxygen gas. Chemical Change Two or more substances can also combine to form different substances. A chemical change produces What do iron metal and oxygen new make when they combine? substances with properties different from those of the original substances. iron oxide (rust) • • • Law of Conservation of Mass Matter is not created or destroyed in any chemical or physical change. Mass measures the amount of matter. Atoms are not lost or gained, only rearranged. Matter and Thermal Energy Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. Every chemical or physical change in matter includes a change in energy. Temperature and Thermal Energy Temperature is a measure of the average energy of random motion of particles of matter. Warm air outside particles of gas have greater average energy of motion that the particles of air in a cool building. Thermal energy is the total energy of all the particles in an object. Thermal Energy and Changes in Matter When matter changes, the most common form of energy released or absorbed is thermal energy. Melting of Ice: Warming hands by a fire: ENDOTHERMIC CHANGE EXOTHERMIC CHANGE (energy taken in by ice) (energy released by wood fire) The End