Class 1A preassembled inorganic phase
advertisement

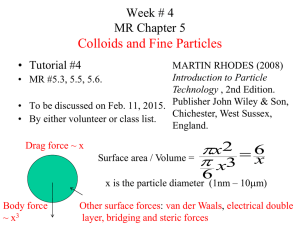
Hybrid Materials & POSS Lecture 5: : Class 1A preassembled inorganic phase (particles, fibers) dispersed in organic phase Class 1A hybrids are a composite material based on an inorganic particle & an organic polymer Silica particle (130 nm in diameter) 5 weight percent silica in Nafion Polymer is the continuous phase or matrix The inorganic particles is the dispersed phase or filler Preparation by melting polymer and mixing Preparation by dissolving polymer and mixing Solid Inorganic particles Solid Inorganic particles dispersed in same solvent Particle dispersion in solid polymer Reasons for making a particle-filled polymer • Fillers (CaCO3, Silica, Talc, wood powder) are cheaper than some plastics-cut cost. • Reduce Coefficient of thermal expansion of polymer • Reduce shrinkage during thermoset curing • Improve abrasion resistance and hardness • Increase modulus • Make melt more viscous or gel (thixotrope) • Make Flame resistant • Aesthetics – pearlesence or opalescence Organic polymers that have been used: • Thermoplastics: polystyrene, poly(methyl methacrylate), HDPE, polypropylene, Nylon’s, polycarbonate, polyimides, poly(ethylene oxide), polyurethanes, polyesters…. • Elastomers: silicones, polyisoprene,… • Thermosets: epoxies, • Polyelectrolytes: Nafion practically every commercial polymer known. Class 1 Hybrids: No covalent bonds between organic & inorganic phases Physically dispersed particles in polymer POSS in polypropylene Generally meta-stable: particles will segregate if given the opportunity Just as the colloid made from blending oil and water will return back to two continuous phases With time Which is the lower energy state? Aggregation of particles in polymer • • • Silica in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Silica and PDMS in toluene were mixed, then cast and dried. Aggregation occurs during drying stage before viscosity gets too high. Polymer 205, 46, 41270 Sedimentation of particles during mixing and drying (a) (b) Sedimentation of particles during mixing and drying (a) (b) •Solution viscosity was too low •Particles floated to the top of the membrane as the solvent dried •Solved problem by evaporating solvent while mixing until viscosity was 65 cP. Particles in polymers: thixotropes Particles are used to stop liquids from flowing until subject to shear. Used in “non-running” or “no-drip” liquid adhesives, paints, and lubricants. Silicone sealant with NO silica Silicone sealant with silica How to make inorganic particles • Sol-gel “wet” synthesis • Emulsion polymerizations (sol-gel in oil & water) • Aerosols/flame syntheses (will not make silsesquioxanes) Sol-gel: Stober synthesis All particles round and same size TEOS Concentrations 0.011M (0.03736g) to 0.28M (0.934g) NH4OH Concentrations 0.1M to 1.2M Reaction Scale = 15mL and 60mL TEOS distilled NH4OH titrated ( 9M) Anhydrous ethanol J. Colloid Interface Sci., 26 (1968), pp. 62–69 Control of particle size by changing the concentration of ammonium hydroxide with 0.28M TEOS Rayleigh scattering Light scattering from particle/polymer composites Other ways to make particles: Synthesis of T8 POSS “particle” Yields are not always so good Synthesis of Phenyl T8 POSS Also works from the polymer!!!! Best way to make POSS “Two-step” method to prepare silsesquioxane particles Typical recipe: 1) PhSi(OEt)3 (2.4 grams) in 12 mL anethol is mixed with aq. HCl (0.0027 M, 3.6 mL) for 7 h. 2) This sol was added to aq. NH3 (1M, 32.4 mL) and stirred for 20 h. Loy, D. A. Macromole Mater Eng. 2012, in press. 3) Particles isolated and washed with centrifugation. A. Matsuda et al. J. Ceram. Soc. Jap. 2007, 115, 131-135. Flame synthesis of inorganic particles Langmuir 2004, 20, 5933 Other inorganic fillers include • Clays (2-D aluminosilicates)* • Fullerene, nanotubes, and graphene* • other aluminosilicates • Main group metal oxides • Transition metal oxide particles • Alkali earth carbonates and sulfates • Quantum dots • Metals *included in this lecture POSS physically dispersed in polypropylene How do you characterize a hybrid: XRD of POSS XRD of POSS in HDPE Macromolecules, 2006, 39 (5), pp 1839–1849 Influence of nanoparticles on melt viscosity Micrographs of the PA-05-S composite (left) and the PA-05-L system (right) (MET) Silica particles mixed into Nylon while melted “Nanofillers in polymeric matrix: a study on silica reinforced PA6,” E. Reynaud, Polymer 2001, 42, 8759 Influence of nanoparticles on melt viscosity Smaller the size particle, the greater the viscosity “Nanofillers in polymeric matrix: a study on silica reinforced PA6,” E. Reynaud, Polymer 2001, 42, 8759 Tensile modulus (stiffness) of nylon 6 nanocomposites as a function of SiO2 content . Modulus increases as inorganic content increases Composites Part B: Engineering Volume 39, Issue 6 2008 933 - 961 Tensile strength of nylon 6 nanocomposites as a function of SiO2 content & surface modification using coupling agent With surface modification Without surface modification Summary for Class 1: particles in organic polymer • Made by solvent or melt mixing • Particle aggregation will ruin any positive influence from the inorganic particles • Nature of non-bonding interactions will affect strength & modulus trends • But generally, modulus and strength increases with decreasing particle size • Modulus and strength increases with increasing weight percent particle Polymer-clay composites (Class 1A) montmorillonite Exfoliated montmorillonite clay Polymer-clay composites (Class 1A) • Clay: 2-D sheets of alumino-silicate with metal cations in between • Replace metal cations with cationic surfactants • Replace surfactants with polymers (melted or in solution)-intercalation • Heat and apply shear – exfoliation • Stronger, fire resistant, less permeable Process for forming clay polymer composites intercalated exfloliated Detecting intercalation and exfoliation X-ray diffraction From Giannelis et al., Adv. Polym. Sci., 118 (1999) Tensile strength of non-covalently integrated clay-polystyrene-co-acrylate nanocomposites + Mechanics of Composite Materials 2006, 42, 45. Carbon Spheres (Buckyballs) & Nanotubes & graphene as inorganic fillers Macromolecules, 2006, 39 (16), pp 5194–5205 Nature Materials 9, 868–871 (2010) Fullerenes as inorganic particles in polymers The curves of uniaxial deformation of the LDPE films with different fullerene content: 0 (1), 1 (2), 3 (3), 5 (4) and 10 wt% (5) J. Mater. Chem., 1997,7, 1097-1109 Summary • Class 1A materials rely on non-bonding interactions and so it can be difficult finding optimum conditions to match the surfaces of filler and polymer to give good interactions. • Spherical particles are not as good as linear or 2-D fillers in improving mechanical strength. Next we look at in-situ formation of particles where we add the precursor to the polymer and the particle forms in place.