Amino acid degradation in animals
advertisement

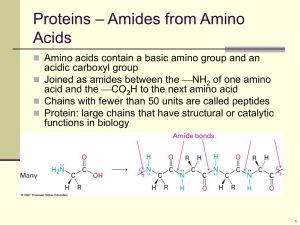
Chapter 18 Amino Acid Oxidation and The Production of Urea Amino Acid Oxidation Dependency of amino acid as energy source Carnivores> herbivores> microorganism >> plant Amino acid degradation in animals Amino acids for oxidation Extra amino acid during protein turnover Protein-rich diet (no storage) During starvation or in uncontrolled diabetes Removal of amino group (NH4+) a-keto acid (C skeleton of amino acids) Oxidation to CO2 & H2O Sources of C3 or C4 units for gluconeogenesis or fuels Pathways of amino acid catabolism 18.1 Metabolic Fates of Amino Groups Amino Group Catabolism Amino Group Catabolism Amino acid metabolism amino group (= nitrogen metabolism) Liver is a major site Recycle for biosynthetic pathways Excretion; ammnonia, urea, uric acid Glutamate & glutamine General collection point for amino group NH3 from amino acids + a-ketoglutarate glutamate into mitochondria, release of NH4+ Source of ammonia Dietary protein (major source) Muscle & other tissues NH4+ + glutamate glutamine mitochondria in hepatocytes NH4+ + pyruvate alanine hepatocytes Digestion of Dietary Protein In stomach Entry of diet secretion of gastrin from gastric mucosa secretion of HCl (parietal cells), pepsinogen (chief cells) Acidic gastric juice (pH 1.0 to 2.5) Pepsinogen : zymogen Antiseptic & denaturing agent (protein unfolding) Conversion to active pepsin by autocatalytic cleavage (at low pH) Digestion of peptide bonds at Phe, Trp, Tyr mixture of small peptides In small intestine Low pH secretion of secretin stimulation of bicarbonate secretion from pancreas neutralization Arrival in the upper part of intestine (duodenum) release of cholecystokinin into blood stimulation of pancreatic zymogens Trypsinogen : activated by enteropeptidase Chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidase A and B : activated by trypsin c.f.) Protection of pancreas from proteolytic digestion Production of zymogens Pancreatic trypsin inhibitor Protein digestion by trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase, aminopeptidase Uptake of amino acids by the epithelial cells Digestion of Dietary Protein Blood capillaries Liver Transamination 1st step of amino acid catabolism Transfer of a-amino group to a-ketoglutarate Generation of L-glutamate & a-ketoacid Aminotransferase (transaminase) Amino acid specificity (named after amino acids) Reversible reaction ; ∆G’° ≈ 0 kJ/mol Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) Bimolecular Ping-Pong reactions Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) Coenzyme form of pyridoxine (vitamin B6) Intermediate carrier of amino group Electron sink for carbanion (resonance stabilization) Transamination Racemization (L- & D-form interconversion) Decarboxylation PLP-mediated transamination at a-carbon PLP-mediated transamination: Ping-Pong mechanism amino acid pyridoxal phosphate a-ketoglutarate pyridoxamine phosphate a-keto acid pyridoxal phosphate glutamate PLP-mediated amino acid transformations at a-carbon Oxidative Deamination of Glutamate Oxidative deamination Mitochondrial matrix of hepatocytes Glutamate dehydrogenase Generation of a-ketoglutarate & ammonia NAD+ or NADP+ as electron acceptor Intersection of C and N metabolism Allosteric regulation By ADP (inhibition) By GTP (activation) Transdeamination Transamination + oxidative deamination of Glu A few amino acids undergoes direct oxidative deamination Glutamine as Ammonia Carrier in the Bloodstream Ammonia generated in extrahepatic tissues Glutamine synthetase Incorporation of ammonia into glutamate glutamine Transport of gln to the liver via blood Higher gln concentration than other amino acids in blood Glutaminase in the liver, intestine, and kidney Glutamine Glutamate + NH4+ Alanine Transports Ammonia from Skeletal Muscles to the Liver Glucose-alanine cycle In muscle Glycolysis & degradation of amino acids Alanine aminotransferase Transfer amino group of glutamate to pyruvate alanine + a-ketoglutarate Transport of alanine to the liver In the liver Alanine aminotransferase Transfer amino group of alanine to aketoglutarate glutamate + pyruvate Gluconeogenesis Pyruvate , lactate glucose Transport of glucose to muscle Ammonia is toxic to animals. Comatose state of brain (high brain’s water content) 1. NH3: alkalization of cellular fluid 2. a-ketoglutarate, NADH, ATP: citric acid cycle & ATP production 3. glutamate and GABA (g-aminobutyrate): neurotransmitter depletion