Gross Techniques In Surgical Pathology
advertisement

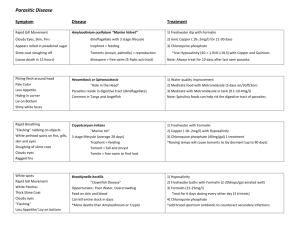
Gross Techniques In Surgical Pathology Introduction The routine work associated with a surgical pathology specimen includes gross & microscopic examinations. Gross examinations give an idea about size ,shape of specimen &any gross abnormality like ulceration, nodularity. The dissection, gross description &selection of sections for microscopic study is a crucial part of pathologic examinations Preparations of sections for histopathology 1- paraffin embedding method ( the routine & widely used procedure). 2- frozen section (intra-operative). 3- cytological diagnosis (exfoliative & fine needle aspiration cytology. 4- digital pathology & telepathology. Paraffin embedding method Include the following principle steps: 1- fixation:- to preserve the tissue, fixatives include formaldehyde, Zenker’s solution, picric acid, Bouin’s solution, The best fixative is 10% buffered formalin Advantages of Formalin 1- cheep. 2- always available. 3- good penetration into tissue. 4- cause little shrinkage. 5- preserve RBCs & fatty tissue. 6- special stains can be used on tissues fixed with it. 7- preserve color of the tissue. 8- good hardening. Disadvantages of Formalin 1- if tissue preserved in formalin for long time, formic acid will be formed which affect stainability of tissue with different stains, so it should be changed every 3-6 months. 2- when formalin solution is stored for long period a white precipitate of para formaldehyde which will not affect the efficiency of formalin as a fixative & can be removed by alcohol. 3- cannot preserve glycogen. 2- Dehydration:- by using different concentrations of alcohol. 3- Clearing:- by using xyline. 4- Paraffin impregnation. 5- Embedding:- to make the tissue as a block of hard paraffin 6- Sectioning:- by using a microtome, the tissue is sliced into very thin sections ranging from 4-6 micrometer in thickness. 7- Attaching sections to the slides. 8- Deparaffinization:- by using xylol & alcohol until the paraffin is dissolved. 9- Staining:- the standard staining method is H & E which stain the nucleus blue (basophilic) & the cytoplasm pink-red (acidophilic). 10- Mounting:- by using DPX &cover slip. Special Techniques In Surgical Pathology 1- Special stains like PAS (periodic acid schiff) stain, Gram, Giemsa, Ziel-Neelson. 2- Enzyme histochemistry. 3- Tissue culturing. 4- Histometry. 5- X-ray microanalysis. 6- Electron microscopy. 7- Immunohistochemistry, sensitive &specific. 8- Flow cytometry. 9- Cytogenetics. 10- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).




![Anti-ACTH antibody [AH26] ab76554 Product datasheet 1 Image Overview](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/011958133_1-2fddf93bd1f9ebdfc4e3a5012697c672-300x300.png)