Acid buffer
advertisement

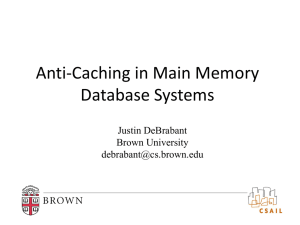
Mechanism of buffer action and buffer preparation Maintaining the optimum pH during the biological sample processing is to maintain the proper functional and structural aspects of the sample. It is important to understand the theory behind the buffering action Related LOs: Buffer composition > Prior Viewing – IDD-1. Extraction of bacterial protein, IDD-17. SDS-PAGE > Future Viewing – IDD-32. Buffer preparation for western analysis Course Name: Mechanism of buffer action and buffer preparation Level(UG/PG): UG Author(s): Dinesh Raghu, Vinayak Pachapur Mentor: Dr.Sanjeeva Srivastava *The contents in this ppt are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 India license 1 Learning objectives • 2 3 4 5 After interacting with this Learning Object, the learner will be able to: 1. Define buffer preparation and the mechanism involved 2. Operate to optimize the pH of the buffer 3. Assess the troubleshooting steps involved in the experiments. 1 Master Layout Mechanism of buffer action (Slide: 5-10) 2 3 Buffer Preparation (Slide: 11-12) pH meter standarization (Slide: 13) pH instrument working mechanism (Slide: 14-15) T4: pH measurement (Slide: 16) 4 5 1 2 Definitions and Keywords 1) Buffer : A aqueous solution mixture made in weak base with conjugate acid or weak acid with conjugate base. 2) Acid buffer: solution mixture containing acid and salt of same acid with strong base 3) Basic buffer: solution mixture containing base and salt of the same base with strong acid. 3 4 5 4) pH meter: An instrument that measures the differences in ionic strength between the sample and the standard and display it . Mostly hydrogen ions are detected to calculate the pH 1 Step 1: T1:Mechanism of buffer action 2 Acidic buffer 3 Hcl 1)CH3COONa (aq) ————-> CH3COO- (aq) + Na+ (aq) 2) CH3COOH (acetic acid) B)After Hcl addition 4 CH3COO- (aq) + H+ (aq) ⇌ CH3COOH Dissociated sodium acetate 5 From Hcl 1 Step 1: T1: Mechanism of buffer action Description of the action 2 3 4 5 Show a bottle labeled as “ acidic buffer”, instruct user to click on the bottle and show a tab as shown in figure (previous slide). Now show a bottle labeled as Hcl and the user should click on the bottle open the lid and take a filler and add drops of the Hcl to the acidic buffer bottle . Then the user should see the reactions as in the figure simultaneously while adding the HCl to the solution. Show like H+ ion in reaction (B) moving towards the CH3COO- ion and bind to it. Audio Narration Acidic buffer containing weak acid with the salt of the weak acid and strong base for eg sodium acetate and acetic acid. Sodium acetate will be in the dissociated form as sodium ions and acetate ions. , acetic acid will be in non dissociated form, when an strong acid like Hcl was added the H+ ions from the acid will react with the dissociated form acetate ion and form the acetic acid thereby constantly maintaining the pH of the buffer. 1 2 3 Step 2: T1:Mechanism of buffer action NaOH Acidic buffer 1)CH3COONa (aq) ————-> CH3COO- (aq) + Na+ (aq) 2) CH3COOH (acetic acid) B)After NaOH addition 4 5 1)CH3COOH (aq) ————-> CH3COO- (aq) + H+ (aq) 2) H+ + OH- --------------->H2O From acetic acid From NaOH 1 Step 2: T1:Mechanism of buffer action Description of the action 2 3 4 5 Show a bottle labeled as “ acidic buffer”, let the user to click on the bottle and show a tab as shown in figure (previous slide). Now show a bottle labeled as NaOH and the user should click on the bottle open the lid and take a filler and add drops of the NaOH to the acidic buffer bottle. Then the user should see the reactions as in the figure simultaneously while adding the NaOH to the solution. Show like OH- ion in reaction (B) moving towards the H+ ion and bind to it. Audio Narration Acidic buffer containing weak acid with the salt of the weak acid and strong base for eg sodium acetate and acetic acid. Sodium acetate will be in the dissociated form as sodium ions and acetate ions. acetic acid will be in non dissociated form, when an strong acid like NaOH was added the H+ ions from the acetic acid dissociate and will react with the hydoxide ion from the sodium hydroxide and form water, thereby constantly maintaining the pH of the buffer. 1 Step 2: T1:Mechanism of buffer action Calculating the pKa, [H+] and pH 2 3 4 1) if we know the value for Ka , hydrogen ion concentration and pH of the buffer can be calculated Ka for acetic acid is 1.74 x 10-5 mol dm-3. 2) to calculate the pH of a buffer solution containing 0.20 mol dm-3 of acetic acid and 0.50 mol dm-3 of sodium acetate. Substitute in the equation as follows Ka= [CH3COO-][H+]/[CH3COOH] 1.74 x 10-5 =0.50 *[H+]/0.20 [H+]=6.9 * 10-6 mol dm-3. 3) To calculate pH, substitute the [H+] value in the equation below pH = -log10 [H+] pH=log10 6.9 * 10-6 mol dm-3 \ pH = 5.1 4) To calculate ka value Ka=[H+][A-]/[HA] 5 1 Step 3: T1: Mechanism of buffer action Description of the action 2 3 4 5 Instruct the user to go through the calculation and the formulas as in the previous slide with the audio narration accompanying it. Animate like user performing the calculation Audio Narration The ka value can be found by the formula 4 and for the acetate buffer the Ka is already known, substitute the values like concentration of sodium acetate, acetic acid, ka to find the pH, go through the calculation thoroughly along with the mechanism of buffer action to understand the importance of pH calculation and constant maintenance of the pH. Following example will illustrate the buffer preparation methodology. 1 Step 4: T2: Buffer Preparation Tween 20 2 Tris base Nacl Kcl 3 4 5 Description of the action Pop-up note “ Preapare TBST buffer”. Let user takes out Nacl, Kcl, Tris Base, tween 20 from the rack and keep it next to balance. Instruct user to weigh 8g of Nacl, 0.2g of Kcl, 3g of tris base and 600ul of tween 20. let user pick the bottle, uncap it, weigh the required amount with help of spatula on a paper over the balance. Display a gradual increase in reading with quantity addition. if the gram exceeds user should remove some quantity or if it less add to get the required amount. After weighing transfer the quantity to beaker. Now take out 1000ul pipette, set it for 600ul, take out tween20 bottle, uncap it, pipette and transfer 600ul into the beaker. All events must happen when the user clicks on the hand. Audio Narration Prepare TBST buffer can be used as distain solution and also can be used for washing the membrane. 1 Step 5: T2: Buffer Preparation Tween 20 2 Tris base Nacl Kcl 3 4 5 Description of the action Now instruct the user to take methanol bottle, open the cap, take 1000ml measuring cylinder, measure 900ml. Let user remove the excess methanol if level crosses 900ml mark. Transfer it to beaker. Now take the beaker, shake it to make a proper mix as shown in slide 11. Animate the powder getting into the solution. Now set the pH to 7.6 by using pH meter. Audio Narration The pH of the TBST buffer need to set to 7.6 . 1 Step 6: T3: pH meter standarization 2 STD 1 3 4 5 Description of the action Display standard pH bottles and pH instrument and deionized water, discard placed on a table. Instruct user to caliberate the instrument. Let user ON the instrument. Initially for the pH rod is dipped in water, when user clicks on read button, display must show a reading “7”. Now show like taking out the rod and washing it with deionized-water, let user cleans the rod with tissue. Now pick the STD 1 , uncap it, dip the cleaned rod into the solution, user must click read button with display showing “4”. now clean the rod and repeat the step to note down the reading for STD 2 and now the display should show “9” STD 2 Audio Narration Before the pH reading, pH instrument need to be calibrated with standards. Once with STD 1 at pH 4 and with STD 2 at pH 9. the pH meter senses the hydrogen ion concentration with the standard inside the electrode and the differences are displayed as pH 1 Step : T4:pH instrument mechanism working 2 3 Glass electrode 4 5 Nernst equation 1 Step : T4:pH instrument mechanism working Description of the action 2 3 4 5 Show the figures one by one so that the user can understand the principle of working of pH electrode and audio narration should go simultaneously. Audio Narration Glass electrode consists of internal reference electrode (silver/silver chloride electrode) and the glass bulb at the end which is sensitive to the hydrogen ion concentration. This is actually a galvanic cell Both sides of the bulb will be protonated during the pH measurement which causes the potential difference, this protonation occurs till the equilibration is achieved. The potential difference is governed by the nernst equation and the difference the measure of pH . 1 Step 7: T4: pH measurement 2 NaOH 3 4 5 Description of the action Instruct user to set the pH for TBST pH at 7.6. Now take the TBST bottle, uncap it, dip the cleaned pH rod into the solution. User need to click on read button. Initially display must show a reading 6. now instruct user to add NaOH to adjust the pH. Now allow the user to click on NaOH bottle so that drops of NaOH should be added with filler, user need to mix the solution with glass rod, click on read button and the reading should anywhere near 6.1- 6.3. let user keeps adding the NaOH drop till the pH display shows 7.6 and later transfer the beaker solution to 1000ml measuring cylinder to makeup the volume to 1000ml by clicking on methanol and adding it to that. All action should happen when the user clicks the hand. HCl Audio Narration Prepare TBST buffer of pH 7.6. Slide 510 Tab 01 Slide 11-12 Tab 02 Slide 14-15 Slide 13 Tab 03 Tab 04 Slide 16 Tab 05 Tab 06 Tab 07 Name of the section/stage Interactivity area Animation area Slide 16: Button 01 Show like the user added excess NaOH and the pH reaching to 9 instead of 7.6 Instruction Button 02 Button 03 Instruct the user to take Hcl and add to the solution show like the pH decreasing in 8.6,8.4,8.1, 7.8 and 7.6 Instructions/ Working area Credits APPENDIX 1 Questionnaire: Question1: What is a buffer? a) Solution that maintains ionic strength b) Solution that helps to store two different sample together c) Solution that maintains pH d) Solution that has acid/base Question 2: Acidic buffer contains a) Salt of strong base and acid along with the acid b) Acid with strong base c) Salt of the acid with water d) Water and acid Question 3: Acetate buffer has a) Sodium acetate and acetic acid b) Acetic acid and water c) Water and sodium acetate d) Sodium acetate and sample APPENDIX 1 Questionnaire: Question 4: Formula to find pH of the buffer a) –log[H+] b) log[H+] c) 1/[H+] d) 1/[H-] Question 5: pH is measured using a)Ammeter b)Voltmeter c)Litmus paper d) electrodes APPENDIX 2 Links for further reading Reference websites: http://www.chemguide.co.uk/physical/acidbaseeq ia/buffers.html APPENDIX 3 Summary Buffers need to be prepared with required amount of reagents that can maintain the ionic strength of the solution. pH is important for a buffer preparation. All the reagents prepared is to be properly labeled, prepared fresh for the analysis purpose