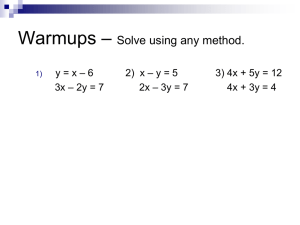
1084818Notes 10.1
advertisement

Chemical Reactions • Occur when atoms rearrange – break apart and recombine differently • Produces new substances • Same as a chemical change • Energy is absorbed or released Evidence of a Rxn • • • • • • Temperature change Heat or light Color change Odor Gas bubbles Appearance of a solid Rxn Details • • • • • Reactants = they react / on left side Products = they’re produced / on right side Arrow = yields (new products are formed) + = separates reactants &/or products s, g, l, aq = indicates state (or solution) Ways to Show a Rxn • Word equations: iron(s) + chlorine(g) iron (III) chloride(s) • Skeleton equations: Fe(s) + Cl2(g) FeCl3(s) • Balanced chemical equations: 2Fe(s) + 3Cl2 (g) 2FeCl3(s) 3 Rules of Word Equations 1. Pure metals (only 1 kind of atom) – will be monoatomic Ex: iron metal = Fe 2. Pure nonmetals or hydrogen (only 1 kind of atom) – will usually be a gas & will be diatomic unless told otherwise Ex: hydrogen gas = H2 3 Rules of Word Equations 3. Compounds (more than 1 kind of atom): A. Will reveal the name Ex: carbon dioxide = CO2 B. Use oxidation numbers to find the correct formula (criss cross & reduce) Ex: magnesium chloride = Mg+2 & Cl-1, so MgCl2 Try It • Write a skeleton equation for these: a. solid barium and oxygen gas react to produce solid barium oxide b. solid iron and aqueous hydrogen sulfate react to produce aqueous iron (III) sulfate and hydrogen gas c. calcium carbonate decomposes to produce calcium oxide and carbon dioxide Solutions a. Ba(s) + O2(g) BaO(s) b. Fe(s) + HSO4(aq) Fe(SO4)3(aq) + H2(g) c. CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g) Chemical Equations • • • • • Indicates identities of products & reactants Indicates relative amounts Must be balanced (law of conservation of mass) Balanced with coefficients only Steps to balance: – – – – Write skeleton (or this will be given to you) Atom inventory Guess & check with coefficients Double check for lowest ratio & equal # Try It • Decide if the following equations are balanced. If not, balance them. a. 2Al + 6HCl 3AlCl3 + 3H2 b. C5H12 +11O2 5CO2 + 12H2O c. Ba(ClO3) 2 BaCl2 + 2O2 Solutions a. 2Al + 6HCl 2AlCl3 + 3H2 b. C5H12 +8O2 5CO2 + 6H2O c. Ba(ClO3) 2 BaCl2 + 3O2