Chapter 1: Introduction
advertisement
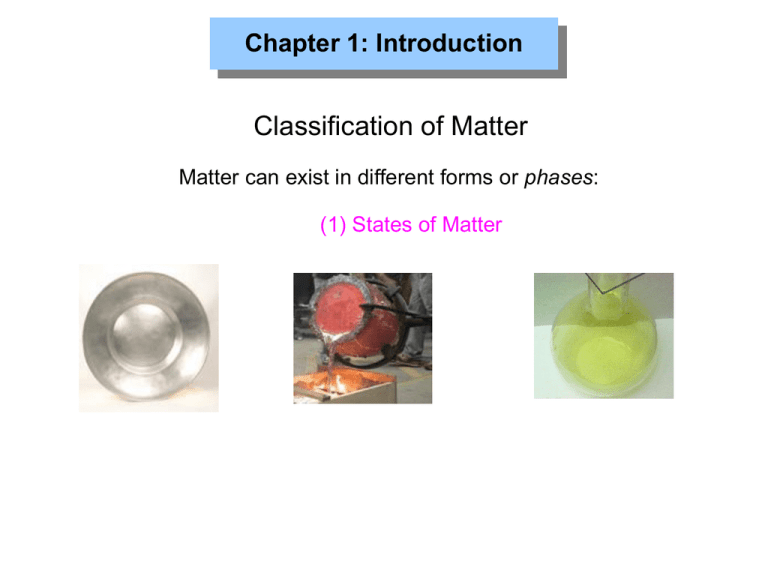
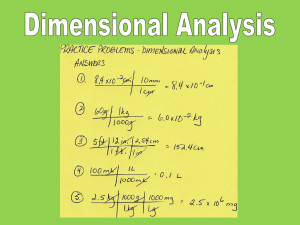
Chapter 1: Introduction Classification of Matter Matter can exist in different forms or phases: (1) States of Matter Chapter 1: Introduction Classification of Matter Chapter 1: Introduction Classification of Matter Defined shape? Solid Liquid Gas Defined volume? Distance between molecules? Compressible? Chapter 1: Introduction Classification of Matter (2) Molecules, Elements, Compounds, Pure Substances, and Mixtures Molecules: atom Chapter 1: Introduction Classification of Matter (2) Molecules, Elements, Compounds, Pure Substances, and Mixtures Elements: Chapter 1: Introduction Classification of Matter (2) Molecules, Elements, Compounds, Pure Substances, and Mixtures Compounds: Chapter 1: Introduction Classification of Matter (2) Molecules, Elements, Compounds, Pure Substances, and Mixtures Pure Substance: Chapter 1: Introduction Classification of Matter (2) Molecules, Elements, Compounds, Pure Substances, and Mixtures Mixtures: Chapter 1: Introduction Classification of Matter (2) Molecules, Elements, Compounds, Pure Substances, and Mixtures Homogeneous Mixtures <-> Heterogeneous Mixtures Oil on water Air Chapter 1: Introduction HW: 1, 2 Classification of Matter (2) Molecules, Elements, Compounds, Pure Substances, and Mixtures Phase state? Molecules or atoms? Compound? Mixture? - what kind? HW: 9, 15 Chapter 1: Introduction Homogenous or Heterogeneous Mixtures? Vinaigrette Mud Granite Coffee - a Coffee - b Brass Water and flour Chapter 1: Introduction Chapter 1: Introduction Mixtures can be separated ... for example by Filtration Chromatography Distillation Chapter 1: Introduction Properties of Matter Physical Properties & Changes → no change in identity or composition of substance Chemical Properties & Changes → how a substance reacts to form a different substance Chapter 1: Introduction Properties of Matter Burning of wood: Melting of ice: HW: 17, 19 Chapter 1: Introduction Physical of Chemical Property? Zinc (Zn): ● silver-grey metal ● melting point: 420oC reacts with oxygen to form Zinc oxide (ZnO) ● ● density (25oC) = 7.13 g/cm3 generates hydrogen when dissolved in sulfuric acid ● Chapter 1: Introduction Physical or Chemical Process? Sugar dissolving in water. The picture on the left represents a) compounds in the gas phase b) elements in the gas phase c) molecules in the gas phase d) a heterogeneous mixture of elements e) a mixture of molecules in the liquid phase Chapter 1: Introduction Intensive Properties… …are independent of the amount of substance Extensive Properties… …depend on the amount of substance Boiling/melting point (bp/mp) Mass Volume Density Chapter 1: Introduction A gold nugget (1cm x 0.5 cm x 0.7 cm) has a density of 19.3 g/cm3. A jeweler decides to use this gold nugget to make a perfect gold Sphere with a diameter of 0.4cm. What is the density of this sphere? Chapter 1: Introduction Units of Measurement: Temperature K = OC + 273 Chapter 1: Introduction Units of Measurement Système International d'Unités (SI units) Mass Length Time Temperature Amount of a substance kilogram meter second Kelvin mole kg m s K mol Chapter 1: Introduction Units of Measurement Prefixes used in the metric system: You ABSOLUTELY MUST know these (Table 1.5 page 14): Giga Mega Kilo Deci Centi Milli Micro Nano Pico Femto G M K d c m µ n p f gigameter (Gm) megameter (Mm) kilometer (Km) meter (m) decimeter (dm) centimeter (cm) millimeter (mm) micrometer (µm) nanometer (nm) picometer (pm) femtometer (fm) = 109 m = 106 m = 103 m =1m = 10-1 m = 10-2 m = 10-3 m = 10-6 m = 10-9 m = 10-12m = 10-15m Chapter 1: Introduction Units of Measurement: Derived Units Volume: 1m 1m 1m 1cm 1cm (1 m)3 = 1m3 = 1cubic meter 1cm (1 cm)3 = 1cm3 = 1cubic centimeter = 1mL Chapter 1: Introduction Units of Measurement: Derived Units mass Density = volume ● Generally expressed as g/mL or g/cm3 ● Depend on temperature HW: 24, 29 Chapter 1: Introduction Dimensional Analysis Converting inches into cm: Conversion factor: same quantity but in different units 23 . 2 in 2 . 54 cm 58 . 9 cm 1in - the units to be eliminated go on opposite sides of the fraction Converting m/min into m/s: 1.2 m 1 min m × = 0.020 min 60 s s Conversion factor HW: 49, 52 Chapter 1: Introduction Dimensional Analysis More than one conversion: A car travels 12 km per liter of gasoline. How many many miles per gallon will it go? => Convert 12 km/L into mi/gallon => first, convert length units: km into mi, second, convert volume units: L into gallons (1) km 12 × L 1 mi 1.61 km or 1.61 km 1 mi Chapter 1: Introduction Dimensional Analysis More than one conversion: A car travels 12 km per liter of gasoline. How many many miles per gallon will it go? => Convert 12 km/L into mi/gallon => first, convert length units: km into mi, second, convert volume units: L into gallons (1) (2) 1 mi mi km = 7.45 12 × 1.61 km L L mi 7.45 × L 1 gal 3.785 L or 3.785 L 1 gal Chapter 1: Introduction Dimensional Analysis More than one conversion: A car travels 12 km per liter of gasoline. How many many miles per gallon will it go? => Convert 12 km/L into mi/gallon => first, convert length units: km into mi, second, convert volume units: L into gallons (1) (2) 1 mi mi km = 7.45 12 × 1.61 km L L mi mi 3.785 L = 28.198 7.45 × gal 1 gal L = 28 mi gal Correct number of sig. figs. Chapter 1: Introduction Dimensional Analysis More than one conversion: A car travels 12 km per liter of gasoline. How many many miles per gallon will it go? => Convert 12 km/L into mi/gallon => first, convert length units: km into mi, second, convert volume units: L into gallons => with more PRACTICE you can combine steps (1) and (2): 1 mi km 3.785 L mi 12 × × = 28 1.61 km 1 gal L gal Chapter 1: Introduction Dimensional Analysis Conversions involving squared and cubic units: The volume of a container is 5.3 m3. What is the volume in cm3? => Convert m3 into cm3 5.3 m3 × 100 cm 1m Units must match in order to cancel out! Chapter 1: Introduction Dimensional Analysis Conversions involving squared and cubic units: The volume of a container is 5.3 m3. What is the volume in cm3? => Convert m3 into cm3 1003 cm3 3 5.3 m × = 53,00000 cm 13 m3 = 5.3 × 1000000 cm3 3 = 5.3 × 106 cm3 Units must match = cube both number AND unit ! Chapter 1: Introduction HW: 35 Uncertainty in Measurement Inexact Numbers Obtained by measurement Exact Numbers Value is known precisely The temperature of the asphalt on Randall Drive today? Mass of 1L of milk? The number of mm in one yd of speaker cable ? Chapter 1: Introduction Uncertainty in Measurement good accuracy good precision poor accuracy good precision poor accuracy poor precision good accuracy poor precision Accuracy: how do the measured values agree with the “true” value? Precision: how reproducible is the measurement? Chapter 1: Introduction Significant Figures Which digits count? (a) All significant digits in a number Zeros... (b) ...between nonzero digits count (c) ...in the beginning of a number never count (d) ...in the end of a number count (compare lab manual) 0.04305 4 sig figs 0.34000 5 sig figs 1.04305 6 sig figs 45,000 2 sig figs Chapter 1: Introduction Significant Figures 0.04305 4 sig figs 0.34000 5 sig figs 1.04305 6 sig figs 45,000 2 sig figs This is easiest to see when written in exponential notation: 0.04305 = 4.305 x 0.01 = 4.305 x 10-2 0.34000 = 3.4000 x 0.1 = 3.4000 x 10-1 45,000 = 4.5 x 10000 = 4.5 x 104 Chapter 1: Introduction Significant Figures ● Final result is only as accurate as the least accurate measurement ● The least accurate measurement determines the number of sig. figs. (1) Division and Multiplication: volume = 1.32cm x 1.1cm x 3.540cm = 5.14008cm3 = 5.1cm3 Answer rounded to 2 sig. figs. velocity = 342 m / 32 s = 10.6875 m/s = 11 m/s Answer rounded to 2 sig. figs. Number with fewest sig. figs. determines sig. figs. of answer Chapter 1: Introduction Significant Figures ● Final result is only as accurate as the least accurate measurement ● The least accurate measurement determines the number of sig. figs. (2) Addition and Subtraction + + - 1.234 0.124 320.13 56.1 Number with fewest decimal places (NOT sig. Figs.) determines answer = 265.388 = 265.4 answer rounded to 1 decimal point