17.1.1 Nephron Functioning

Maintaining a Balance
Topic 17: Nephron Functioning
Biology in Focus, HSC Course
Glenda Childrawi, Margaret Robson and Stephanie Hollis
DOT POINT
Explain how the process of filtration and reabsorption in the mammalian nephron regulate the body fluid composition
Introduction
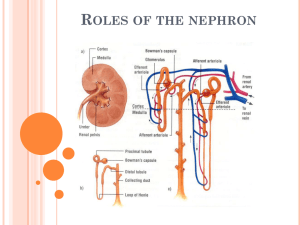
The basic functional unit within the kidney is a microscopic tubule called the nephron , the smallest structural part of the kidney that is capable of producing urine. Each kidney contains millions of these tiny units, which coil and twist across both the cortex and medulla. legacy.owensboro.kctcs.edu
Introduction
A nephron consists of four functional parts:
1.
Bowman’s capsule
2.
3.
4.
Proximal (first) convoluted tubule
Loop of Henle
Distal (second) convoluted tubule which leads into a collecting duct beltina.org
Bowman’s Capsule
Bowman’s capsule occurs at one end and is an enlarged part of the nephron tubule. It is a double-walled sac, indented on one side to accommodate a spherical network of blood capillaries called the glomerulus. kidney-hypertension.com
Bowman’s Capsule
A useful analogy is to think of the Bowman’s capsule as a baseball mitt – double-walled, hollow (where your hand fits inside) and curved around to accommodate a baseball – in close contact with and partly surrounded by the Bowman’s capsule. analytical.wikia.com
Bowman’s Capsule
The hollow part of the
Bowman’s capsule is filled with fluid called glomerular filtrate.
This fluid continues its flow along the length of the nephron. As it flows along the nephron, the chemical composition of the fluid is adjusted. Various substances are removed or added to obtain the final product – urine. click4biology.info
Nephron Functioning
Three main processes that lead to urine formation occur in the nephron. These are:
Filtration reabsorption secretion auburn.edu
Filtration
The renal artery that enters the kidney branches into numerous smaller and smaller vessels, each terminating in a globular network of capillaries – the glomerulus. The filtration of blood takes place at the surface between the glomerulus and the inner lining of each Bowman’s capsule. cumbavac.org
Filtration
A high pressure system exists in the blood flowing through the glomerulus, created partly by size of the blood vessels entering and leaving – the vessel entering the capillary network is slightly larger than that existing. Substances within the blood that are small enough are squeezed through the capillary wall under pressure.
They pass through the cellular layer lining the Bowman’s capsule and move into the lumen. robbwolf.com
Filtration
Blood cells and proteins are retained in the blood, while large volumes of water pass through, carrying dissolved substances including amino acids, glucose, salts (ions), nitrogenous wastes and other toxic molecules . Once inside the Bowman’s capsule, this fluid is termed glomerular filtrate. click4biology.info
Filtration
The process of filtration separates substances from the blood based on their size. It does not take into account whether they are wastes to be excreted or nutrients that are still required in the body. Glomerular filtrate is therefore not the final fluid excreted – its composition is adjusted as it flows along the remainder of the nephron by two processes.
nsbri.org
Filtration
Tubular Reabsorption:
Substances that the body need are reabsorbed from the filtrate into the kidney cells or bloodstream so that they are not lost with urine. cumbavac.org
Filtration
Tubular secretion:
Additional wastes that may still be in the bloodstream (those that were not squeezed out of the blood under the high pressure of filtration) must be added (secreted) into the fluid. cumbavac.org
Reabsorption
The chemical composition of body fluids is precisely regulated by selective reabsorption of certain solutes from the glomerular filtrate at various points along the nephron – the proximal tubule, loop of Henle and distal tubule. i3dlearning.pbworks.com
Reabsorption
The filtrate contains molecules that the body needs (eg: amino acids, glucose, certain ions and some water) and so they are actively reabsorbed from the nephron and passed back into the interstitial fluid and blood capillaries surrounding the nephron, a process called tubular reabsorption. physioweb.org
Reabsorption
These capillaries join up to form larger vessels which drain into the renal vein, where they are carried from the kidney back into the general circulation. legacy.owensboro.kctcs.edu
Reabsorption
All nutrients are reabsorbed from the filtrate and varying quantities of inorganic ions are reabsorbed, depending on the particular requirements of the body at that time. asknature.org
Solute Reabsorption
All amino acids, glucose and varying quantities of ions such as Na ⁺ , K ⁺ , Cl ⁻ , Ca ²⁺ , and
HCO ₃⁻ and some vitamins are reabsorbed. The differing rate of reabsorption of particular ions depend on feedback from the body. All solutes that are reabsorbed from the nephron move by means of active transport and facilitated diffusion. beltina.org
Solute Reabsorption
Glomerular filtrate also contains a relatively high concentration of dissolved urea and other wastes, most of which are not reabsorbed. cumbavac.orinquisitr.comg
Water Reabsorption
As the solutes are actively reabsorbed, water follows by the passive process of osmosis.
An enormous quantity of water is reabsorbed by osmosis – approximately 99% of the huge volume of filtrate that passes into the Bowman’s capsule is reabsorbed along the length of the nephron and only 1% is actually excreted as urine. cumbavac.org
Water Reabsorption
The membranes of the cells lining the nephron can change their permeability to water and ions, thus regulating the amount of these substances that are reabsorbed. Hormones control these changes in membrane permeability. embryology.med.unsw.edu.au
Parts of the Nephron Involved
The loop of Henle descends into the medulla and then ascends up towards the cortex, leading into the distal tubule. In the ascending limb of the loop of Henle, a large number of ions (Na in particular) are actively pumped out into the interstitial fluid in the medulla, since the membranes are permeable to salts but impermeable to water. unckidneycenter.org
Parts of the Nephron Involved
Some urea may move by diffusion out of the collecting tubule and into the surrounding interstitial fluid.
These solutes which accumulate in the medulla draw water by osmosis.
cumbavac.org
Parts of the Nephron Involved
Some water moves from the descending limb of the loop of
Henle and a large amount of water moves from the collecting tubules, both of which have membranes that are permeable to water, allowing it to move passively by osmosis into the surrounding tissue of the medulla.
Energy is used to ensure that urea does not return to the capillaries, so this is not true tubular reabsorption. cumbavac.org
Tubular Secretion
Tubular secretion is the third process that contributes to urine formation in the nephron. It involves the removal of toxic substances from the blood capillaries and tissues and their active secretion into the nephron. moodle.rockyview.ab.ca
Tubular Secretion
Metabolic wastes such as urea, uric acid, ammonia and hydrogen ions are secreted into the fluid within the nephron, along with drugs such as penicillin, saccharin and morphine. Movement of urea and ammonia is mainly by means of diffusion.
cumbavac.org
Tubular Secretion
Urea may be recycled in the nephron to help move water by osmosis – some urea may move from the collecting tubules into the interstitial fluid to help draw water out of the loop of Henle. It diffuses back into the descending limb of the loop of Henle so it may be continuously recycled if the body needs to reabsorb water. faculty.southwest.tn.edu
Activity
-Students to complete 17.1.7 Nephron Worksheet