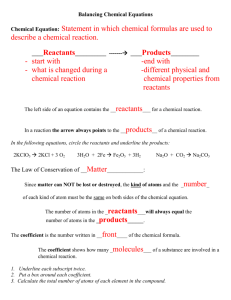
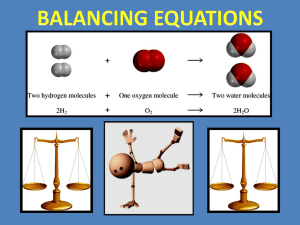
chemical reactions
advertisement

Happy FRIDAY! 11/30/2012 DO NOW! 1. Are most elements on the periodic table metals, nonmetals, or metalloids? 2. Why are metals commonly used for cookware? 3. Plastic is an insulator. Explain what this means. 4. What does ductile mean? Create a SMALL T-chart under your Do Now and write down your observations Tearing Paper Burning Paper LEQ #5 • What is the difference between a physical and chemical change? • Create another T-chart underneath. (Take up the whole page) Physical Change Chemical Change • Tearing paper and Burning paper? Physical Change (NOTES) • A change that does NOT change the identity of the substance • ex: –Tearing paper –Melting ice, Boiling water and Freezing water (change in state or phase) Chemical Change (NOTES) • Change in appearance AND chemical make-up -- a NEW substance is formed. • Irreversible • A chemical reaction occurs. • Ex: –Burning paper –Digesting Food Chemical Change (NOTES) Signs of a Chemical Change : – Color change – Light and Heat is produced – A gas forms (bubbles) – Precipitate forms • A solid forms from a chemical reaction that takes place in a solution Brainpop Video • Write down at least TWO examples of: • Physical change • Chemical Change In your T-Chart Hypothesis • I think that the difference between a physical change and a chemical change is…. • Think - Pair - Share Hot Question! Which is an example of a physical change? A. Boiling B. Burning C. Rotting D. Rusting Experiment • Tell if each example is a chemical change or a physical change. • Be ready to explain why…Ms. K will randomly pick a team member to explain for the point. • Add the correct answer to your T-chart in your notebook. Melting Ice Chopping Wood Mixing Salt and Water Breaking Glass Burning Wood Melting Iron Melting Ice Cream on a hot day Digesting an apple Boiling Water Cooking an egg Mixing Peas and Carrots Bicycle rusting LAB TIME! • Perform each station of the lab (I will lead you in the first station). • Lab: – Follow the procedure carefully!!! – Make observations of the change that is occurring – Is this an example of a physical change or a chemical change? – Explain how you know. Data Collection • • • • Discuss your answers with another group… Did you both get the same conclusions? Why or why not? Debate (respectfully)… who was right? Why? Data Analysis (NOTES) How can you tell the difference between a chemical and physical change? • Signs of a Chemical Change –Light and heat is produced –A gas forms –Color change –Precipitate forms • A solid forms from a chemical reaction that takes place in a solution Add Examples to your T-Chart • Salt water boiling • Vinegar and baking soda combining What about a Mixture? Compound? Add to your T-chart Your turn! • Read one through 10 and decide if it is a physical change (P) or Chemical Change (C) • The next blank you must explain why? What sign did you see of a chemical change • You have 7 minutes! Answer LEQ on back of EXIT TICKET • Day 1: (Hint: there are 4 signs…) • Ms. K mixes 2 substances and passes around the flask for students to observe. She tells them a chemical reaction (change) has taken place. How do the students know? Day 2 LEQ 9 Chemical Reactions • Homework: Chemistry questions due TODAY • # 23 should be C (Boron is the only metalloid) • Do Now: add these words Physical Change – draw a picture Chemical change – draw a picture Participate – draw a picture • Chemical reaction • Reactant • Product • Coefficient • Subscript 1. Which is only a physical change? souring or milk melting of ice burning of oil rusting of iron HOT Qs 2.Which process involves a chemical change? Photosynthesis freezing water boiling water melting ice 3. In the making an omelet, which process involves a chemical change? melting butter frying eggs chopping onions stirring eggs Chemical Reactions • Watch the video and watch for REACTIONS –Are they chemical or physical changes do you think? • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=90FR8mzEH4 So… What is a Reaction? Give me some examples from the video and life… • a response to something NOTES • Chemical reaction-when two or more substances interact and a chemical change occurs – Ex. Rust, when Iron (Fe) combines with Oxygen (O) in the air – NOT an ex. When water (H2O) evaporates (still H2O) • Reactant + Reactant Product – Example: Carbon + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Reaction in a Bag! • Turn in your notebooks to “Signs of a Chemical Change” from yesterday. Be on the lookout to see which of these signs occur in our experiment. • Combine: steel wool, Yeast and hydrogen peroxide • What happened? How did you know? 1. Pour the baking soda into the Ziploc 2. Put the steel wool into the Ziploc 3. Pour your hydrogen peroxide (or is it vinegar?) into the bag, then QUICKLY zip it up! 4. Shake it like a Polaroid picture. 5. Fill out the chart in your notebook and answer the question with your group. Hot Question! What type of change has occurred when a statue changes from it’s original color due to acid rain? A.The statue has been painted B.Physical change C.Physical weathering D.Chemical change Testable Question • How can we represent chemical reactions? • Brainpop video NOTES • Chemical Equations: how scientists represent chemical reactions 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2 NOTES 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Reactants Products Chemical Reaction Coefficient Subscript NOTES • Reactants: substances that take part in a chemical reaction • Chemical Reaction: process by which new substance is formed • Products: substances made during a chemical reaction NOTES • Coefficient: # of molecules of a compound in a chemical reaction • Subscript: # of atoms of an element in a compound Experiment 2 H202 2 H20 + O2 2 (H202) 2 (H20) + O2 1.Reactants? 2.Products? 3.How many molecules of H20 are in the products? 4.How many atoms of Hydrogen are in H202? 5.How many atoms of Hydrogen are in the Reactants? Experiment (Notes) C3H8 + 5 O2 C3H8 + 5 (O2 ) 4 H2O + 3 CO2 4 (H2O) + 3 (CO2 ) 1.Reactants? 2.Products? 3.How many molecules of H20 are in the products? 4.How many atoms of Hydrogen are in C3H8? 5.How many atoms of Hydrogen are in the Reactants? Experiment 4Al + 3 O2 2 Al2O3 4(A)l + 3 (O2 ) 2 (Al2O3 ) 1.Reactants? 2.Products? 3.How many molecules of Al203 are in the products? 4.How many atoms of Oxygen are in O2? 5.How many atoms of Oxygen are in the Reactants? Experiment 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2 1.Reactants? 2.Products? 3.How many molecules of C02 are in the reactants? 4.How many atoms of Hydrogen are in H20? 5.How many atoms of Hydrogen are in the Reactants? What in the world is a precipitate? • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8RmVwz2 fNGc (shorter) • OR • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JAeOP2Mf rDY&feature=related (longer) Finding the main idea and supporting details! (20 min. 4 min/paragraph) • Read the article about reaction rates. • For each paragraph, write down the main idea and 2 supporting details • 1 reader and 1 recorder • Reader reads aloud • Recorder writes down the main idea and supporting details • Switch for each paragraph Factors that affect the RATE of a chemical change (NOTES) • Rate—how quickly something happens Factors that affect the RATE of chemical change (NOTES) • Temperature • Surface area • Concentration HOT Q Which factors will increase solubility of a solute dissolving in a solvent? A.Decrease temperature and surface area B.Decrease temperature and increase surface area C.Increase temperature and surface area D.Increase temperature and decrease surface area Ms. Honeycutt will place an alka seltzer in a film canister with: 1. Water 2. Hot water 3. Tablets 4. Crushed Tablet Students will time how long it took for the reaction to take place Data Collection • Record data in the table below: Trial 1(water) 2 (hot water) 3 (2 tablets) 4 (crushed tablet) Time Reaction Rates Race! • Answer the conclusion questions about reaction rates. • It gets harder as you answer more questions • If you get stuck, use your article as your solution station (it has all the answers!) Answer the LEQ • Day 2: How could Ms. Honeycutt have increased the rate of the reaction?