Definition - elsehomework
advertisement

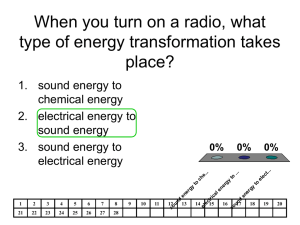
Pure substance is some thing that has to either a element or compound that has constant chemical components. Water, table salt and diamond are examples of pure substance. By: Naomi Halder Thermal Pollution Thermal Pollution is…… Thermal pollution is the degradation of water quality by any process. It is a bi-product of power plants and factories. 3 Examples…… The examples of Thermal Pollution are, when rain falls on a warm road, the rainwater warms, and runs off into a body of water which causes the body of water to warm. Thermal Pollution usually happens when the water temperature increases in lakes, streams, rivers or oceans because of the discharging of hot or heated water from industrial processes. The Cause… The cause of Thermal Pollution is the use of water as a coolant. The coolant is by power plants and manufacturers. solvent A solvent is usually a liquid that dissolves something. Examples: water and salt, water and sugar, water and baking soda. Thermal pollution Thermal pollution is when the temperature rises in a lake or river which kills things that live in the water. This is caused from heated industrial waste and water from the cooling towers in nuclear power plants. Heated industrial waste will come out of these 2 places and make thermal pollution. Cooling towers will send out polluted water out making thermal pollution Definition: Sound energy is a form of energy associated with vibration or disturbance of matter. Sound waves require some kind of materials to travel through. Examples of sound energy: Any type of sound Radio Yelling, Screaming, Laughing etc. By: Quinn Dodds A solvent dissolves other substances or solutes. Some examples of solvents are water, acid and Coca-Cola. Solubility The amount of solute can be dissolved into the solvent till it become concentrated. The solubility will rise if the temperature rises. Examples: 1ml of salt will dissolve in 100ml of water at 0 degrees. It take 43.9 grams of Aluminum chloride to concentrate 100ml of water at 0 degrees. It takes 49.7 grams of iron chloride to concentrate 100ml of water at 0 degrees. Saturated saturation is the point at which a solution of a substance can dissolve no more of that substance. Three examples are: - candy spilling out of its bowl - no more salt can be dissolved in water - no more sugar cant be dissolved in water Radiation! Definition: Energy from a source that travels through space or through a material. Some types of radiation are light, heat and sound. Examples of Radiation: The heat from a light bulb. The radio waves of a radio. The UV rays of the sun. The cosmic rays from stars. The electromagnetic radiation of an x-ray. The infrared waves of a hairdryer. Radiation: Heat transfer through waves • Radiation is caused by various things based on the kind of decay. However, radiation will not under any circumstances, give you superpowers in any way, shape or form. For the sake of simplicity I will only be covering Alpha decay and only briefly. • Alpha decay only go a few centimeters, or just through paper. Unless you swallow something that constantly emits alpha decay, you’ll be fine around them. Cockroaches cannot be harmed by alpha decay. Most of the pictures available are complicated so I have 2 pictures of alpha decay. I considered a picture of a cat, but In decided against it. Definition: Homogenous are composed of two or more components that are: equally (uniformly) distributed throughout the system, miscible (will dissolve), of a single phase, easily dispersed through a membrane, and inseparable by mechanical means. Examples: 1. Blood 2. Sugar solution when sugar is completely dissolved. 3. Mixture of alcohol & water 4. A glass of orange juice 5.salty water (where the salt is completely dissolved) 6.brewed tea or coffee 7.soapy water 8.a dilute solution of hydrochloric acid 9.hard alcohol 10.wine Whipped cream is an example of a homogeneous mixture . The melting point foe butter is 96.8 °F (28-36 °C) Ice melts at 32 ˚F and 0˚C . That is the melting point of ice. The melting point for ice cream is about a above zero Definition: The temperature at which a solid substance or melts. • The temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. It is equal to the freezing point 1. Electric iron 2. Ice melting into water 3. Rock is hard to melt because rock’s melting point is high Mechanical mixture. Mechanical mixture is When two or more different materials are mixed together but are visible, not only one. Example of mechanical mixtures are: sand and stone milk and cereal in a bowl vegetable pizza. Mechanical Mixtures • • Definition: It is a mixture whose components can be separated by mechanical means. Examples: sand, granola bar, hot dogs, pizza, relish, salads, oil, etc. • Kinetic energy is when potential energy is used. Kinetic energy is formed when something is moving. Something that is not moving is called potential energy, it also depends on the chemistry of the object. Kinetic energy and potential energy are the opposite. Three examples of kinetic energy are a rollercoaster going down the track. Another example of kinetic energy is a car racing down the highway. The last example is a boat moving fast on the water. By Kenan White What is kinetic energy? Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, when we move energy comes out and that is kinetic energy and kinetic energy is the energy of motion. Riding your bike is a example of kinetic energy When a animal runs, the animals are using kinetic energy Light is a visible energy in the form of electromagnetic waves that travels in straight lines called rays that fan outward from the source of the light, causing the growth of plants and the existence of most life forms. In theory, mechanical energy is a sum to potential energy and kinetic energy. Mechanical energy is the energy that cooperates with the physical movement and the position of the object itself. Mechanical energy is like gravitational force, it is constant. Some mechanical energy is even converted into heat. Mechanical energy is used in everyday life. • • • • • Walking and running Gravity Moving water (stream, river) Wrench, hammer Rotation and Revolution of the earth • Sound waves Heat Heat is the condition or quality of being hot The “heaTer” helps To “heaT The room You need heat to boil water Heat is used to cook this food Heat 3 examples of heat: 1. When you are heating foods or drink. (Boiling water) 2. At winter, when you use heating system. 3. Flame of any type. Definition of heat: To make or become hot. Few pictures that shows the meaning of the world. Definition • Sound energy is an energy that is made by sound vibrations. It is also the energy in a sound wave. • Examples of sound energy are a telephone, screaming and the noise from a flying airplane Noise from Plane Screaming Telephone Diagrams Convection Definition: it is heat that is moved by the vibration of particles from one place to another. The temperature of heat moving gas, liquid or solids. Examples: convection oven, hot air rising, cooling than falling and a convection cell which is an old fashioned radiator. The possibility for electric currents to produce or make light, heat, cold air or other forms of energy. By: Jennifer The stove needs the energy of heat, the plug and socket transfer electrical energy to heat the stove. Solute By: Zihang Zou Definition Solute: Solute is a substance that dissolved in solvent, usually the component of a solution present in the lesser amount. Examples Examples: 1. salt water=salt(solute)+water(solvent) 2.sugar water= sugar (solute)+ water(solvent) 3. water hot chocolate= hot chocolate(solute)+ water(solvent) An insulator is something that lines an object so that heat and energy can not escape and can spread it out to certain places and cut of the energy and heat. Some examples of insulators are windows, wood and plastic are all insulators. Insulators are useful to keep the heat in and as well as electricity in the huge power lines. This is one Example of conduction This is another Example od conduction This is the last example By: Derek Pure water is not a electric conductor however it does conduct heat. Examples: 1. Metal 2. Wire 3. Water Heat conductors like this are to test which material conducts heat the best. incapable of being dissolved; incapable of forming a solution, esp in water Diagrams Convection Definition: it is heat that is moved by the vibration of particles from one place to another. The temperature of heat moving gas, liquid or solids. Examples: convection oven, hot air rising, cooling than falling and a convection cell which is an old fashioned radiator. Convection Convection , a flow of heat, a movement of matter that goes from a hot region to a cool region. When the air heats up, the molecules expand causing the heat to become less dense. Three examples: A hot air balloon A cup of coffee Boiling water Conductor By: Dante • A electrical conductor is a material that allows the flow of electrical current. • A heat or thermal conductor is a material that can transfer thermal energy. Some examples of conductors are electrical conductors, thermal or heat conductors. Conduction is the process of which heat is transmitted through a substance. Three examples are: A fire heating a pot up. The pot will heat up because of the heat being applied to it. The dropping of the atom bomb on Hiroshima, Japan, by the United States in 1945 initiated the atomic age. Nuclear energy immediately became a military weapon of terrifying magnitude. Nuclear energy power plant In 2011 five nuclear reactors at two power plants lost cooling ability in the aftermath of the powerful earthquake (8.9) that hit Fukushima Daiichi,japan. This is bad because radiation is in the nuclear reactors and can kill you. It kills by attacking the good cells in your body and making them bad, then you get cancer because your body cant regulate the blood through your body, which kills you. A form of energy produced by an atomic reaction, capable of producing an alternative source of electrical power to that supplied by coal, gas, or oil. atomic energy: the energy released by a nuclear reaction. Spencer K Nuclear Energy Nuclear Energy – Energy that comes from splitting atoms of radioactive materials, such as uranium. Pictures: Nuclear Warning Sign Nuclear Plant Fat Man and Little Boy Nuclear Bombs Diagram: Diagram of how Nuclear Energy works 3 Examples of Nuclear Energy: 1. 2. 3. Radiation from nuclear energy helps kill cancer cells. It has become very common to expose foods to small amounts of nuclear radiation as part of the processing routine. Nuclear power plants are the most visible source of nuclear energy. There are over 400 power plants worldwide, which function off of nuclear reactors. Over 20% of the United States power is generated by power plants. Thermal pollution Thermal pollution is when the temperature rises in a lake or river which kills things that live in the water. This is caused from heated industrial waste and water from the cooling towers in nuclear power plants. Heated industrial waste will come out of these 2 places and make thermal pollution. Cooling towers will send out polluted water out making thermal pollution Definition: Sound energy is a form of energy associated with vibration or disturbance of matter. Sound waves require some kind of materials to travel through. Examples of sound energy: Any type of sound Radio Yelling, Screaming, Laughing etc. By: Quinn Dodds solvent A solvent is usually a liquid that dissolves something. Examples: water and salt, water and sugar, water and baking soda. Solubility The amount of solute can be dissolved into the solvent till it become concentrated. The solubility will rise if the temperature rises. Examples: 1ml of salt will dissolve in 100ml of water at 0 degrees. It take 43.9 grams of Aluminum chloride to concentrate 100ml of water at 0 degrees. It takes 49.7 grams of iron chloride to concentrate 100ml of water at 0 degrees. What is ‘homogeneous’ • • • 1: of the same or a similar kind 2: of uniform structure or composition throughout a culturally homogeneous neighborhood. 3: having the property that if each variable is replaced by a constant times that variable the constant can be factored out : having each term of the same degree if all variables are considered a homogeneous equation. Example: Example: Example: The strength of a solution. The amount of dissolved substance in a volume of solvent. A homogeneous •