
Warm-Up
September 29, 2014
1. What causes fingerprints? Can they be
altered?
2. What makes fingerprints unique?
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
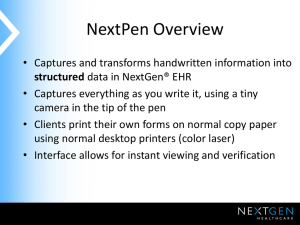
Objective
• SWBAT compare fingerprint detection
techniques.
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Agenda
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Crime 360
Types of Fingerprints
Fingerprint Detection
Fingerprint Detection Videos
Henry Classification System
AFIS/FBI Article
Frontline Real CSI
Exit Slip
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Anderson Cooper
CSI Effect – Hairs & Fibers
T. Trimpe 2008 http://sciencespot.net/
Watch the video and then answer the questions.
Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fGc4PaLB-ek
1. What crime lab did the reporter visit?
A. Chicago
B. New York
C. Las Vegas
2. How many hairs did the investigator use to help in getting a conviction in
the kidnapping/homicide case?
A. 3
B. 30
C. 300
3. True or False?
Real crime labs tend to be darker to make it easier to see evidence.
4. True or False?
It is easy to match any hair found at a crime scene to a specific person.
5. What must be present in a hair sample to test for nuclear DNA?
A. Shaft
B. Cuticle
C. Root
The answers are …
1. What crime lab did the reporter visit?
A. Chicago
B. New York
C. Las Vegas
2. How many hairs did the investigator use to help in getting a conviction in
the kidnapping/homicide case?
A. 3
B. 30
C. 300
3. True or False?
Real crime labs tend to be darker to make it easier to see evidence.
4. True or False?
It is easy to match any hair found at a crime scene to a specific person.
5. What must be present in a hair sample to test for nuclear DNA?
A. Shaft
B. Cuticle
C. Root
Types of Fingerprint Patterns
There are 3
basic fingerprint
patterns
– loops
(60-65% of
population)
– whorls
(30-35%)
– arches
(5%)
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
• Have ridges entering from
one side of the print,
turning, and leaving from
the same side.
Loops
• The pattern area of the
loop is surrounded by two
diverging ridges known as
type lines.
• The approximate center is
called the core.
• The ridge point nearest
the type line divergence is
known as the delta
(capital greek letter Δ).
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Loops
• 65% of the population have loops.
• All loops must have one delta.
• If the loop opens toward the little
finger then it is a ulnar loop.
• If the loop opens towards the
thumb then it is a radial loop.
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Arches
• In an arch, ridges
enter from one side
of the print and exit
on the opposite side.
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Arches
• Arches are divided
into two distinct
groups:
– plain arches
– tetrarches or tented
arches
• The tetrarch consists
of an upthrusted
ridge in the center of
the arch.
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Whorls
• All whorl patterns must have a core and at
least two deltas
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Special Loops
• The double loop is
made up of two
loops combined
into one fingerprint.
• The pocked loop
has a small circle at
the core.
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Other Patterns
• An accidental pattern contains two or
more patterns, but not the plain arch, and
is not covered by other categories.
• It may consist of a combination loop and
plain whorl or loop and tented arch.
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
It’s time to make
some prints!
Avoid
Partial
Prints
GOOD PRINT
Get as much of the top part
of your finger as possible!
Directions
1st – Roll the “pad” portion of your thumb over the
ink pad from the left side of your thumb to the
right. You do not have to push down really hard!
2nd – Roll the “pad” portion of your thumb from the left side of
your thumb to the right in the correct box on your paper to make a
thumbprint.
3rd – Continue this process to make a fingerprint of all ten fingers
on the “My Prints” worksheet.
4th –Use your notes to help you figure out what type of pattern is
found in each of your fingerprints. Label each one with the
pattern’s name.
A Closer Look at Fingerprints
Image from ftp://sequoyah.nist.gov/pub/nist_internal_reports/ir_6534.pdf
T. Trimpe 2007 http://sciencespot.net/
Ridgeology: The study of the uniqueness of friction ridge structures
and their use for personal identification.1
As we have learned in our first lesson, a
fingerprint is made of a series of ridges and
valleys on the surface of the finger. The
uniqueness of a fingerprint can be determined by
the pattern of ridges and valleys as well as the
minutiae points, which are points where the ridge
structure changes.
The koala is one of the few mammals (other than primates) that
has fingerprints. In fact, koala fingerprints are remarkably
similar to human fingerprints; even with an electron microscope,
it can be quite difficult to distinguish between the two.
1Introduction
to Basic Ridgeology by David Ashbaugh, May 1999
Image from http://www.cs.usyd.edu.au/~irena/minutia.gif
Fingerprint Identification
When minutiae on two different prints match, these are called
points of similarity or points of identification. At this point there
is no international standard for the number of points of
identification required for a match between two fingerprints.
However, the United Kingdom requires a minimum sixteen points
while Australia requires twelve.
Automated Fingerprint Identification System (AFIS)
AFIS is a computerized system capable of
reading, classifying, matching, and storing
fingerprints for criminal justice agencies. Quality
latent fingerprints are entered into the AFIS for a
search for possible matches against the state
maintained databases for fingerprint records to
help establish the identity of unknown deceased
persons or suspects in a criminal case.
http://www.fdle.state.fl.us/CrimeLab/images/fingerrint%20comparison%20for%20afis.jpg
Ridge Characteristics
Use these characteristics as points of identification when comparing fingerprint
samples. The more points you can find in common, the better the match!
Ridge Characteristics
Crossover
Core
Bifurcation (fork)
Ridge ending
Scar
Island
Delta
Pore
http://cnx.org/content/m12574/latest/properties.jpg
How many ridge characteristics can you identify in this fingerprint?
http://www.dkfz.de/tbi/projects/bmcv/images/iu_it246_04s_fingerprint1.jpg
Try It!
1 – Blow up your balloon about halfway and twist the end to keep the
air from coming out. Do not tie it off!
2 – Use an ink pad to make a print with all of your fingers and label each
one with a permanent marker. Write your name on the balloon as well.
3 – Blow up the balloon to full size and tie the end.
4 – Analyze the fingerprints to find several ridge structures that we have
discussed. Use a highlighter to mark these structures on your “My
Prints” worksheet.
Think About It!
Which ridge structures were most common in your fingerprints?
Which ridge structures were most common in your group?
Were there any structures that were not found in any of the fingerprints?
Balloon Fingerprint Activity: http://www.msichicago.org/fileadmin/Education/learninglabs/lab_downloads/fingerprint_analysis.pdf
Identify each fingerprint pattern.
Right Hand
Left Hand
Right Hand
Right Hand
Left Hand
• Latent: hidden or invisible
Types of Prints
– Made by natural body secretions of the hands and
fingers (perspiration & grease)
– Requires dusting or other method to make visible
• Patent: visible to the naked eye
– Blood, ink, dirt, glass
• Plastic: a 3-D fingerprint
– Wet paint
– Soft material like clay
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Impressions and Prints
• Impression
– 3-D
– in soft surface
– often visible
• Print
– 2-D
– transfer of skin perspiration, oils, or a foreign
substance
– usually latent
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Powder Techniques
• Used on non-absorbent surfaces
• Tipped or very softly brushed on
• Various types
• Black powder (carbon)
• Grey powder (Aluminum dust)
• Magnetic-Sensitive Powder (Magnabrush)
• Fluorescent Powder (seen in UV light)
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Using Powder with a Brush
• Powder is brushed on carefully with a twirling
motion.
• The excess powder is removed with the brush or
a puffer bulb.
• Prints are photographed in place before lifting.
• Lift the print with broad adhesive tape.
• Transfer the print by sticking tape onto a card or
lifter.
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Chemical Techniques
•
•
•
•
•
•
Iodine Fuming
Ninhydrin
DFO
Silver Nitrate
Physical developer
Super Glue Fuming
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Iodine Fuming
• Oldest technique for latent prints
• Iodine crystal sublimes in Fuming Cabinet
• Iodine reacts with fatty oils or perspiration
(salts)
• Print fades rapidly
• Fixed by spraying with starch solution (blue)
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
• Ninhydrin (triketohydrindene hydrate)
Ninhydrin
• For latent prints on paper & porous surfaces
• Interacts with amino acids in proteins in
fingerprints
• Easy to use & sensitive
• Sprayed on
• Prints appear in 1-2 hours, weak prints in up to 48
hours, hastened by heat.
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Frontline Real CSI
1. What is the Real CSI?
2. Who did the fingerprint match that was
found in Madrid?
3. What is the scientific premise for
fingerprints?
4. What is the standard for points of
comparison for fingerprints?
5. What unique characteristics are looked at
in a fingerprint?
6. Who did the fingerprint really belong to?
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Homework
• Fingerprinting Pre-Lab Questions due
Tuesday
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com
Exit Slip
September 29, 2014
1. Get out a mobile device or use one of
the computers and go to
m.socrative.com. You can also use one
of the iPads that has the Socrative app.
2. When prompted, enter 417101 for the
room number.
QUESTION: How does a crime scene
specialist detect latent prints and decide
how to process them?
Copyright © 2013 Crosscutting Concepts, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
www.CrosscuttingConcepts.com






![Your_Solutions_LLC_-_New_Business3[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005544494_1-444a738d95c4d66d28ef7ef4e25c86f0-300x300.png)

