chylomicron remnant
advertisement

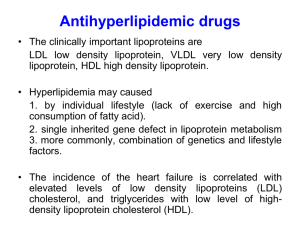
Lipoprotein metabolism Patarabutr Masaratana Outline Structure & Function Classification Metabolism Atherosclerosis Abnormalities Blood protein Plasma Erythrocytes Plasma protein Lipoprotein Hemoglobin Lipoproteins conjugated protein: protein + lipid apolipoprotein + lipid main function: lipid transport transport of fat-soluble vitamins Components of lipoprotein particles lipid transport - lipid: triglyceride cholesterol phospholipid cholesteryl ester (CE) - protein: apolipoprotein (apo) enzymes Components of lipoprotein particles Structure of lipoproteins most lipoprotein particles: spherical shape core: hydrophobic molecules triglyceride (TG) CE surface (shell): hydrophilic/amphipathic molecules cholesterol phospholipid apo Structure of lipoproteins Classification of lipoproteins diversity in size, density, lipid & protein components and electrophoretic movement high TG content bigger particle core larger particle size increased lipid content relative to protein lower density Classification of lipoproteins diversity in size, density, lipid & protein components and electrophoretic movement low TG content higher density Classification of lipoproteins high density lipoprotein (HDL) low density lipoprotein (LDL) intermediate density lipoprotein (IDL) very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) chylomicron Classification of lipoproteins highest lowest TG content Rader DJ, Hobbs HH. Disorders of lipoprotein metabolism. In: Longo DL, et al., eds. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 18th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2012:3145-3161. Classification of lipoproteins Agarose gel electrophoresis VLDL (pre-β) HDL LDL chylomicron (origin) Classification of lipoproteins chylomicron VLDL LDL HDL TG (from diet) TG (endogenous) CE Protein B48 B100 B100 AI % Lipid 98 89-96 77 50 - TG 84 44-60 11 3 - cholesterol 7 16-22 62 19 2 4-11 23 50 Main components Main apo % Protein General functions of apolipoproteins scaffold for lipation ligands for lipoprotein receptors activators/inhibitors of enzymes involving in lipoprotein metabolism Overview of lipoprotein metabolism 1. Exogenous pathway 2. Endogenous pathway 3. Reverse cholesterol transport Overview of lipoprotein metabolism Exogenous pathway - ขนส่ง TG ในอาหารไปยัง muscle, adipose tissue - chylomicron apo B-48 ลาไส้เล็ก - fatty acid ถูกสังเคราะห์กลับเป็ น TG อีกครัง้ - cholesterol ถูก esterify เป็ น CE - TG รวมกับ CE, apo B-48 และ phospholipid เป็ น chylomicron - direction of major lipid transport เข้าสู่ร่างกายทาง lacteal thoracic duct Overview of lipoprotein metabolism Endogenous pathway - ขนส่ง endogenous TG จากตับไป ยัง muscle, adipose tissue - TG ในตับรวมกับ CE, apo B-100 และ phospholipid เป็ น VLDL แล้วหลังเข้ ่ าสู่ circulation VLDL-IDL-LDL apo B-100 - TG ถูกสลายได้ fatty acid เข้าสู่ peripheral cells - CE บางส่วนอาจเข้าสู่ peripheral cells direction of major lipid transport - VLDL เสีย TG จึงมีขนาดเล็กลง Overview of lipoprotein metabolism Reverse cholesterol transport - ขนส่งไขมันในทิศทางตรงข้ามกับ exogenous และ endogenous pathway - ตับสังเคราะห์ apo A-I - apo A-I รวมกับ phospholipid เกิดเป็ น HDL apo A-I nascent HDL (discoidal shape) - nascent HDL ได้รบ ั cholesterol จาก peripheral cells - cholesterol ที่ nascent HDL ได้รบ ั ถูก direction of major lipid transport esterify เป็ น CE ซึ่งจะย้ายไปอยู่ใน Overview of lipoprotein metabolism apolipoprotein - nontransferable - transferable Exogenous pathway (chylomicron; apo B-48) Endogenous pathway (VLDL-IDL-LDL; apo B-100) apo C, apo E Reverse cholesterol transport (HDL; apo A-I) Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) - - อยู่บนผิว endothelium ของ หลอดเลือดฝอยในอวัยวะต่างๆ เช่น กล้ามเนื้ อลาย, หัวใจ, เนื้ อเยื่อไขมัน ถูกกระตุ้นการทางานโดย apo CII - LPL สลาย TG ที่ core ของ chylomicron, VLDL ได้ free fatty acid เข้าสู่เซลล์กล้ามเนื้ อ - Rader DJ, Hobbs HH. Disorders of lipoprotein metabolism. In: Longo DL, et al., eds. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 18th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2012:3145-3161. และ adipocyte chylomicron และ VLDL สูญเสีย TG ที่ core ของอณู ทาให้มีขนาด เล็กลง กลายเป็ น chylomicron remnant, IDL ตามลาดับ Lipid absorption lipid digestion: pancreatic lipase, bile acid medium-chain fatty acid: directly enter the blood and transported by albumin long-chain fatty acid: resynthesised to TG packaged into chylomicron (apo B-48) & released into lymphatic system Exogenous pathway chylomicron acquires apo C & apo E from HDL in the blood apo C-II activates LPL hydrolysis of TG in chylomicron free fatty acid (FFA) FFA enters myocyte or adipocyte β-oxidation or lipogenesis chylomicron loses core TG becomes smaller (chylomicron remnant) exposure of apo E on particle surface (release apo C back to HDL) apo E-mediated chylomicron uptake into liver through LDL receptor or LRP (LDL receptor-related protein) Exogenous pathway Lipolysis of core TG apo C-II LPL chylomicron apo C apo E β-oxidation FFA lipogenesis HDL chylomicron remnant apo E LDL receptor LDL receptor-related protein (LRP) Exogenous pathway chylomicron: half life = 10 minutes not normally found in serum after 12-hour fasting chylomicron: large particle light reflection milky serum (lipemia) (also caused by VLDL in serum) postprandial lipemia OR patients with abnormal chylomicron metabolism chylomicron apo C-II LPL apo E chylomicron remnant Endogenous pathway Sources of endogenous TG 1. de novo lipogenesis (e.g. from excess dietary carbohydrate) 2. cytosolic TG storage in hepatocytes 3. fatty acids acquired from lipoproteins delivered to the liver 4. FFA delivered to the liver depend on metabolic states Tamura S. and Shimomura I. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(5):1139–1142. Endogenous pathway endogenous TG + CE + phospholipid + apo B-100 VLDL released into circulation acquires apo C & apo E from circulating HDL apo C-II activates LPL hydrolysis of TG in VLDL free fatty acid (FFA) FFA enters myocyte or adipocyte β-oxidation or lipogenesis VLDL loses core TG becomes smaller (IDL) release apo C, phospholipid to HDL Endogenous pathway endogenous TG CE phospholipid apo B-100 HDL VLDL apo C phospholipid Lipolysis of core TG LPL FFA lipogenesis IDL β-oxidation apo C-II Endogenous pathway IDL IDL Further lipolysis by hepatic TG lipase (HTGL) apo E HDL apo C apo E LDL LDL receptor/LRP apo B-100 Scavenger receptor B type I (SR-BI) Receptor-mediated endocytosis of LDL VLDL apo C-II LPL apo E IDL chylomicron remnant apo-B100 LDL LDL receptor Reverse cholesterol transport nascent HDL apo A-I apo C, apo E phospholipid chylomicron, VLDL, IDL (through lipolysis) cholesterol LCAT ABCA1 aqueous SR-BI diffusion apo A-I CE mature HDL (HDL3) VLDL chylomicron TG CETP CE apo C, apo E mature HDL (HDL2) LCAT: lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase CETP: cholesteryl ester transfer protein ABCA1: ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 Reverse cholesterol transport mature HDL (HDL2) lipolysis by hepatic TG lipase (HTGL) SR-BI (liver) FFA nascent HDL another cycle of reverse cholesterol transport CE LDL receptor (apo E) LRP (apo E) other unknown receptors Reverse cholesterol transport HDL chylomicron VLDL apo C-II LPL HDL apo E IDL chylomicron remnant apo-B100 LDL LDL receptor Cholesterol & Atherosclerosis endothelial dysfunction (functional structural) increased endothelial permeability to lipoproteins smoking, hypertension, diabetes, etc lipid deposition in intima esp. small lipoproteins LDL inflammatory processes ROS oxidized LDL scavenger receptor foam cells macrophages No feedback regulation Cholesterol & Atherosclerosis Cholesterol & Atherosclerosis Cholesterol & Atherosclerosis antiathergonic properties of HDL: reverse cholesterol transport antioxidant- prevent LDL oxidation Adult reference ranges for lipids Reference range (mg/dL) LDL + HDL + VLDL Total cholesterol 140-200 HDL cholesterol 40-75 LDL cholesterol 50-130 TG 60-150 LDL cholesterol calculation (Friedewald formula) LDL-C = Total cholesterol – HDL-C – (TG/5) not valid if TG > 400 The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) NCEP Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) ATP III, ATP IV (due 2012) Abnormalities of lipid metabolism dyslipidemia: abnormal lipid levels causes: defective synthesis/transport/catabolism of lipoproteins hyperlipoproteinemia: elevated lipoprotein levels - hypercholesterolemia - hypertriglyceridemia - combined hyperlipidemia hypolipoproteinemia: decreased lipoprotein levels Hyperlipoproteinemia Monogenic disorders Polygenic disorders Multifactorial: Genetics + Environment Hypercholesterolemia isolated high plasma cholesterol concentration Common hypercholesterolaemia - most frequent dyslipidemia, multifactorial Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) - LDL receptor gene mutations Familial defective apo B-100 - apo B-100 gene mutations defective LDL receptor binding Autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia - mutations defective LDL receptor-mediated endocytosis Familial hypercholesterolemia monogenic disorder, autosomal dominant, rare LDL receptor gene mutations very high plasma cholesterol & LDL-C levels premature CHD (teenage years) lipid deposits at eyelids, tendon, hand, cornea heterozygotes: also symptomatic, develop CHD at the age of 20s-50s chylomicron VLDL apo C-II LPL IDL apo E chylomicron remnant apo-B100 LDL LDL receptor Hypertriglyceridemia isolated high plasma TG concentration borderline high: 150-200 mg/dL high: 200-500 mg/dL very high: >500 mg/dL genetic abnormalities or secondary causes (e.g. some hormonal abnormalities) imbalance between VLDL synthesis vs clearance Hypertriglyceridemia Familial chylomiconemia - very rare; LPL or apo C-II deficiency - chylomicron & VLDL accumulation very high TG - fasting chylomicronaemia Familial hypertriglyceridemia - relatively common - isolated VLDL elevation - excess VLDL production - still largely unknown molecular basis but likely polygenic & requires secondary factor for expression chylomicron VLDL apo C-II LPL IDL apo E chylomicron remnant apo-B100 LDL LDL receptor Fig. 1: Clinical manifestations of primary hypertriglyceridemia. Yuan G et al. CMAJ 2007;176:1113-1120 ©2007 by Canadian Medical Association Combined hyperlipidemia elevated total cholesterol & TG levels Familial combined hyperlipidemia (FCH) - autosomal dominant with variable penetrance - overproduction of apo B-100 - increased VLDL production & subsequent LDL generation - variable lipid profiles Combined hyperlipidemia Familial dysbetaipoproteinemia - apo E gene mutations apo E isoforms with low affinity to LDL receptor - IDL & chylomicron remnant accumulation - defective catabolism - phenotypic expression usually requires accompanying factors e.g. obesity, type 2 DM chylomicron VLDL apo C-II LPL IDL apo E chylomicron remnant apo-B100 LDL LDL receptor Classification of Primary hyperlipoproteinemia Molecular basis Clinical descriptive names Fredrickson system (old literatures) Fredrickson classification for Primary hyperlipoproteinemia Type I Prevalence Serum analysis - Cholesterol - Triglyceride very rare Type II A Type II B most common Type III Type IV Type V very rare very common rare N or N or N LP pattern -Chylomicron -VLDL -LDL chylomicron remnant IDL Serum appearance - Cream layer - Turbidity ++++ 0 0 0 Cause 1 2 3 4 5 6 LPL defect no or abn. LDL receptor 0 ± 0 or + + LDL cat. abn. apo E VLDL syn. 0 ++ ++ +++ CHO intake severe degree of type V 57 Chylomicronemia & Lipemia? high TG lipemia high chylomicron or chylomicron remnant or VLDL levels plasma protein electrophoresis Standing plasma test (refrigeration test) Stored at 4° overnight cream layer chylomicron, VLDL chylomicron remnant (unchanged) Standing plasma test Secondary hypertriglyceridemia Obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes - DM: increased glucose shunt into PPP increased fatty acid synthesis - increased VLDL concentrations - deficient LPL activity, increased CETP activity - increased FFA flux to the liver - fatty liver Alcohol - increased VLDL concentrations - impaired lipolysis Epinephrine Norepinephrine Growth hormone ACTH Thyrotropin Hormone-sensitive lipase increased serum TG levels triglyceride Mechanisms of dyslipidemia: General concept chylomicron DM obesity alcohol FCH VLDL apo C-II LPL DM IDL apo E chylomicron remnant apo-B100 LDL LDL receptor Transport and storage of fat in response to feeding Downloaded from: StudentConsult (on 14 August 2012 02:37 PM) © 2005 Elsevier Metabolism in the fed (postprandial) state Metabolism in postabsorptive state Metabolism in prolonged fasting state Hypolipoproteinaemia decreased lipoprotien concentrations 1. hypoalphalipoproteinaemia - isolated decrease in HDL levels (<40 mg/dL) - without hypertriglyceridaemia - often caused by genetic defects (e.g. apo A-I or LCAT deficiency, ABCA1 mutations) - increased risk of premature CHD - severe physiological stress acute transient change 2. hypobetalipoproteinaemia - isolated low levels of LDL (apo B-100 mutations) - no accompanying lipoprotein disorders 3. abetalipoproteinaemia: very rare, caused by defective VLDL assembly Main lipid-lowering medications Statins - HMG-Co A reductase inhibitor - suppress cholesterol synthesis - increase LDL receptor expression Fibrates - LPL stimulation