Document
advertisement

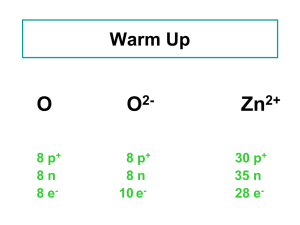
Zinc JESSICA YOUNG Structure & Properties Zn Atomic number: 30 5 Stable isotopes Zn64, Zn66, Zn67, Zn68, Zn70 Many radio isotopes Zn65, Zn72 Exists in oxidation states Zn, Zn1+, Zn2+ Also found in many compounds ZnO, ZnCl2, ZnS, and ZnSO4 Relatively long half life (4.3 X 1018 years) Uses & Applications Oxidated form (Zn2+) occurs naturally in minerals in the earth’s crust (70 mg/kg) Anthropogenic sources Smelting used to protect against corrosion Batteries Brass & Bronze manufacturing Brakes and car exhaust found to be leading cause of zinc pollution in Sao Paulo, Brazil study Uses & Applications Applications of zinc compounds Herbicides, medical and dental products, household items (makeup, shampoo, sunscreen) Zinc in Aquatic Environments How it gets there… Industrial & urban runoff Cations, zinc-inorganic coumpoudns, zinc-organic compouds Zinc ions have a low mobility in sediment and are readily taken up by plants and animals Bioconcentration factors estimated to be 1000 and 2000 for freshwater and marine fish, respectively Properties in water As a cation, it is non soluble in water and is partitioned into sediment by adsorption onto organic molecules Other common forms are much more soluble ZnCl2 ZnSO4 Other solubility factors Temperature pH Mineral composition of water Necessity & Toxicity Zinc is an essential micronutrient found in most foods; absorbed through gastrointestinal tract Necessary for enzyme function Miners exposed to acute high levels of zinc oxide in the air experienced respiratory problems Interference with absorption of copper and iron Effects on cardiovascular, respiratory, and immune systems Low leves of HDL Stimulated production of amylase and lipase by pancreas One incident of human fatality attributed to zinc overdose Zinc at the Colorado Lagoon 33.18 mg/ kg in site 5 sediment sample 35.19 mg/kg in site 8 clam tissue CO Lagoon clams contains 16 mg/ pound Recommended Daily Allowance is 8-11 mg/ day Tolerable Upper Limit is 40 mg/ day Detoxification Metallothionine (MT) Cysteine rich proteins found in Golgi Found to play key role in uptake, regulation, and distribution of zinc in organisms Zinc is efficiently regulated in mammals and excess zinc can be excreted via nephridial system References EPA; 2005; Toxicological Review of Zinc and Compounds http://www.epa.gov/iris/toxreviews/0426tr.pdf Gioia, S., Weiss, D., Coles, B., Arnold, T., Babinski, M.; 2008; Accurate and Precise Zinc Isotope Ratio Measurements in Urban Aerosols; Analytical Chemistry; v. 80 (24); p. 9776-9780 http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/ac8019587 Skidmore, J. F.; 1964; Toxicity of Zinc Compounds to Aquatic Animals, with Special Reference to Fish; The Quarterly Review of Biology; V. 39 (3); p. 227-248 http://www.jstor.org/stable/2820034 US Dept of Health and Human Services, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry; 2005; Toxicological Profile for Zinc http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/ToxProfiles/tp60.pdf National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements http://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Zinc-HealthProfessional/ Sigel, Astrid; Sigel, Helmut; Sigel, Roland K. O.; Metallothionines and Related Chelators; Metal Ions in Life Sciences; v. 5; http://www.springer.com/chemistry/inorganic+chemistry/book/978-1-84755899-2?detailsPage=reviews Zinc Hazards to Fish, Wildlife, and Invertebrates: A Synoptic Review http://www.pwrc.usgs.gov/infobase/eisler/chr_26_zinc.pdf