Titration Experiment
advertisement

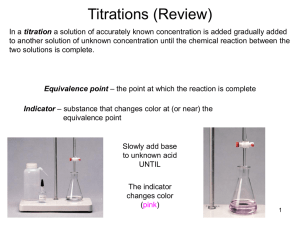
Titration Expt. Overview • Day 1: You will create a ~0.1 M NaOH solution • Day 2: You will standardize your solution of NaOH by titrating it with a solid acid, KHP • Purpose: To verify your [NaOH] up to 3 SF • It should be close to 0.100 M NaOH • Day 3: You will titrate your now known concentration of NaOH with an unknown concentration of HCl • Purpose: To determine the [HCl] Day 1: Making a NaOH solution • You and your partner will make 250 mL of a ~0.1 M NaOH solution • How will you do this? What do you need to know? What equipment do you need? • Remember, M = mol/L • Measure NaOH mass using a balance and dissolve in 250.0 mL distilled water together in a volumetric flask • Calculate and record exact [NaOH] in M (mol/L) • 3 SF • Should be close to 0.100 M, but won’t be exact Day 2: Standardization of NaOH(aq) • Purpose: To verify your [NaOH] by reacting (titrating) it with an known acid, KHP (PHTH) Buret w/ base ~0.1 M NaOH Flask w/ acid and PHTH ind. ~0.3 g KHP in ~75 mL H2O Faint pink tinge… Use white paper underneath to see better Day 2: Standardization of NaOH(aq) • Purpose: To verify your [NaOH] by reacting (titrating) it with an known acid, KHP To neutralize… mol H+ = mol OH• Acid = ~0.3 g solid KHP (potassium hydrogen phthlate) • mass g KHC8H4O4 mol KHP = mol H+ • Recall M = mol/L, so mol OH- = M OH· L OH therefore… mol H+ = M OH · L OH • Do one dry run ball park amount NaOH • Do at least two good trials, if not three • Average your [NaOH] results Day 3: Titration of HCl(aq) with NaOH(aq) • Purpose: To determine unknown [HCl] by reacting (titrating) it with known base, NaOH Buret w/ base ~0.1 M NaOH Flask w/ acid and ind. Yellow ~ 15 mL of ? M HCl Green Endpoint Use white paper underneath to see better Blue Overshoot (too basic) Day 2: Standardization of NaOH(aq) • Purpose: To verify your [NaOH] by reacting (titrating) it with an known acid, KHP To neutralize… mol H+ = mol OH• Acid = ~0.3 g solid KHP (potassium hydrogen phthlate) • mass g KHC8H4O4 mol KHP = mol H+ • Recall M = mol/L, so mol OH- = M OH· L OH therefore… mol H+ = M OH · L OH • Do one dry run ball park amount NaOH • Do at least two good trials, if not three • Average your [NaOH] results Lab Report • Typed (calculations may be hand-written) • Sections Written portions should be: • Overview (3-5 sentences) • Procedure • 3rd person • Passive voice • Past tense • Day 1: Making NaOH solution • Day 2: Titration (Standardization) with KHP • Day 3: Titration with HCl • Data Tables • Show organized data for all three days of expt. (include dry run data and label as such) • Include related data table with each day’s procedure • Calculations • Show all calculations (no need to use dry run data) • Include related calculations with each day’s procedure strong acid HCl (aq) + [H+] = 0.50 M ~ 15 -20 mL + strong base salt + HOH product pH = 7… use bromothymol blue yellow (acid), green (neutral), blue (base) NaOH (aq) [OH-] = ? M VB NaCl (aq) + HOH (l) Measure both V in expt. (to the nearest 0.00 mL) Trials 1. (Dry Run)… calculations unimportant (ball park numbers) 2. 3. 4. Calculate [OH-] for trials 2-4 and then average Strong Acid/Strong Base Titration HCl + NaOH H2O + NaCl Titrate with Bromthymol Blue pH At this point, everything is water, Na+ and Cl-, so the pH = 7 Equivalence Pt mol H+ = mol OH- Overshoot Endpoint mL of base Weak Acid/Strong Base Titration + strong base weak base + HOH product pH > 7… use phenolphthalein (PHTH) clear acid pink base HCH3COO (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCH3COO (aq) + HOH (l) (acetic acid, 0.24 M (Na+ (aq) + i.e. vinegar) VB CH3COO-(aq)) [H+] = ? ~ 3-5 mL Weak acid Trials 1. (Dry Run)… calculations unimportant (ball park numbers) 2. 3. 4. Weak Acid/Strong Base Titration HC2H3O2 + NaOH H2O + NaC2H3O2 Titrate with Phenolphthalein At this point, the solution contains water, Na+, and C2H3O2 - , so the pH > 7. pH BUFFERING REGION HC2H3O2 C2H3O2 - + H+ mL of base Equivalence Pt mol H+ = mol OH- Endpoint Overshoot Weak Base/Strong Acid Titration HCl + NH4OH H2O + NH4Cl Titrate with Methyl Orange NH3 + H+ NH4+ BUFFERING REGION pH At this point, the solution contains water, Cl-, and NH4+, so the pH < 7. Equivalence Pt mol H+ = mol OH- Endpoint Overshoot mL of acid