Bio I Chp 4 Cell Structures and Functions
advertisement

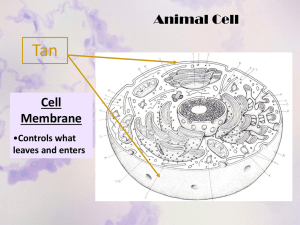
Cell Structures and Functions Unit 5 – Chapter 4 The Cell Theory Devised by Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow. 1. _______________________________ _____________. 2. _______________________________ _____________________. 3. _______________________________ _____________________.. The World of Cells Cell – basic building block of life. ______________– (1665) – observed the dead cells of cork. He likened them to cells in a prison….thus coining the name “cell”. _______________ – nutrition, digestion, excretion, secretion, absorption, biosynthesis, respiration, response, reproduction. 2 Types of Cell Organization 1. - - - ______________: Exs.) Bacteria and Cyanobacteria ONLY smaller and less complex than eukaryotes Do not have membranes enclosing cell parts, therefore NO DISTINCT NUCLEUS DNA (genetic material) is on a circular loop in center of cell 2. _________________: - includes all cells other than bacteria and cyanobacteria (prokaryotes) - Larger and more complex than prokaryotes - Have cell parts that are enclosed in membranes - HAVE A DISTINCT NUCLEUS THAT HOUSES THE DNA Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Go to Section: Cell Membrane Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 1. _____________ Nickname: “The Control Center” Function: holds the DNA Parts: 1. 2. 3. 4. _______________: dark spot in the middle of the nucleus that helps make ribosomes _______________: controls traffic in/out of nucleus _______________: all substances INSIDE the nucleus _______________: unraveled chromosomes = DNA Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function _____________ 2. Function: site where _______________ _________________ Found in all cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function _____________________(ER) 3. Nickname: “Highway system” Function: Provides a route for cell products to move throughout the cell Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum 2 Types: 1. _____________: 2. Rough appearance because it has ribosomes attached Function: helps make proteins, that’s why it has ribosomes _____________: NO ribosomes attached Function: makes fats or lipids Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Complex Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function _______________ 4. Nickname: “Shipping department” Function: packages, modifies, and transports materials to different locations inside/outside of the cell Appearance: stack of pancakes Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function _____________: circular, but bigger than ribosomes) 5. Nickname: “Clean-up Crews” Function: _________________________ ____________________ into particles the the cell can use, and to destroy old and diseased cells Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Ribosomes Cell Membrane Mitochondria Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function __________________ 6. Nickname: “The Energy Factory” Function: ______________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________ ATP: is the major fuel for all cell activities that require energy Animal Cell Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Ribosomes Cell Membrane Mitochondria Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum A Few Additional Cell Organelles ___________ – in animal cells, this is a food storage sac. ____________ – all substances OUTSIDE the nucleus. ____________– controls traffic in/out of the entire cell. Now let’s talk about structures ONLY found in PLANT Cells!! Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Section 7-2 Plant Cell Water Vacuole Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function _______________ 7. Function: stores water, sugars, waste products This is what makes lettuce crisp When there is no water, the plant wilts Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cell Section 7-2 Vacuole Chloroplasts Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Plant Cell Organelles and Function ______________ 8. Function: traps energy from the sun to produce food for the plant cell Green in color because of chlorophyll, which is the green pigment that captures the sunlight Chloroplasts 2 Other Types of Plastids ________________ – many different colors such as those found in fruit and flowers. ________________ – cloudy white or clear…they store starch such as in potatoes, rice, squash. Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cell Section 7-2 Vacuole Chloroplasts Cell Membrane Cell Wall Go to Section: Eukaryotic Plant Cell Organelles and Function ____________ 9. Function: _______________________ ______________ to the cell membrane Found outside the cell membrane in plant cells Allows the plant cell to hold high water pressures…this keeps the plant from wilting Plant Cell Cytoplasm Vacuole Smooth ER Ribosomes Chloroplasts Cell Membrane Cell Wall Nucleolus Golgi Bodies Nucleus Mitochondria Rough ER How Do Some Organisms Build from the Cell?? (Also known as the levels of organization in living things)……..see below…… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Cell – basic unit ↓ Tissue – group of CELLS that work to do the same job such as Nervous tissue ↓ Organ – group of TISSUES that work to do the same job such as the heart. ↓ System – group of ORGANS that work together to do the same job such as the digestive system ↓ Complete Organism – group of SYSTEMS that work together to do one job