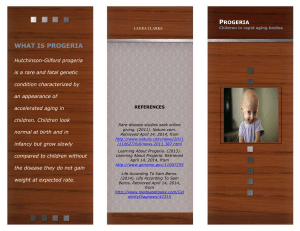
progeria
advertisement
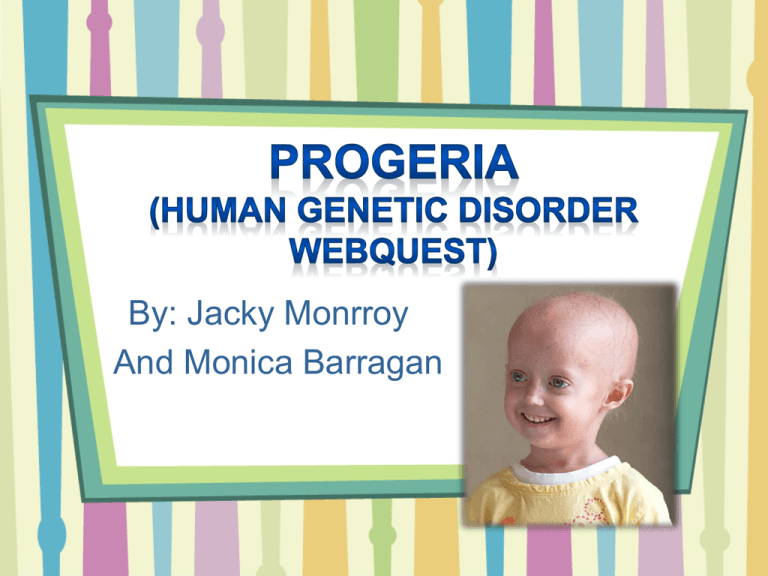
By: Jacky Monrroy And Monica Barragan What do you know about genetic disorders in general? We know that it is a disorder that is caused by a change in a gene, that causes “premature aging.” What do you want to find out about this disease? We want to know how long the child lives with this disorder, the child’s lifestyle, and if the disorder has a cure. Progeria is a rare, fatal genetic disorder that is characterized by an appearance of accelerated aging in children. About 1 in 4-8 million newborns are affected. Affects both sexes equally throughout the world. The children are usually born looking healthy, but symptoms begin to display around the age of 2. (1824 months.) The disorder is caused by a mutation in a gene called LMNA. The LMNA gene produces the Lamin A protein that holds the nucleus of a cell together The defective Lamin A protein makes the nucleus unstable How did the child get the disorder? There is an 88% survival rate for patients after six years of treatment. Children usually die within the ages of 8-21. without treatment, they can die at really young ages Genetic Counselor What is the survival rate? Is it treatable? There is presently no treatment to prevent this disorder, treatment plans are individualized. The plans can include physical therapy to minimize joint stiffness. What are the treatments, if any for this disorder? Dietary treatments tube feeding for infants and supplements to help reduce weight loss. Low-dose daily aspirin is recommended to prevent stroke and heart attacks. Genetic Counsel Besides the symptoms, which tests can be done to diagnose the disorder? Genetic testing can be carried to detect mutations in the Lamin A gene What biotechnical applications are currently being used in the fight against the disease? What is the type of disordergene or chromosomal? Is it dominant or recessive? It is a dominant gene disorder. What other names or abbreviations are used for the disorder? Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome is another name. (HGPS) What different tests could have been provided to the parent to have found out about this disorder before its birth? Genetic testing could have been done. This would have helped the parents to see earlier that their child was sick. The child could have been treated earlier. What are the signs and symptons of the disorder, including a description of how it affects the human body? Symptoms include: Early aging of the body Slow growth Poor weight gain Loss of body fat Wrinkled skin Loss of hair (includes eyebrows and eyelashes) Stiffness of joints (joint abnormalities) Abnormal Teeth Premature eruption of adult teeth Hip dislocation Head that is too large for face (Symptoms don’t usually start to appear until child is 2 years old ) What kind of lifestyle will your child live? Most children affected with progeria have to be tube-fed, given dietary treatments and supplements to help reduce the loss of weight, and aspirin to prevent heart attacks and strokes. How long will your child live? Children that are treated can live until they are 21, but can die as early as age 8. Children that are not treated can die earlier than age 8 or can live until ages 13 or 14. Will your child be able to have children? Will they be affected with the disorder? No, they cannot have children, since most of them die at an early age. If they were to have children it is not likely for their child to have progeria, since the disorder doesn’t normally run in families. What is the probability that your next child will be affected with progeria? Progeria is not usually passed down in families. The gene change is a sporadic mutation. Prenatal testing for progeria is possible using amniocentesis. However, because the disease is not passed down genetically and is extremely rare, there would be little reason to perform this testing.