Button Text - EPHS Knowles Biology
advertisement
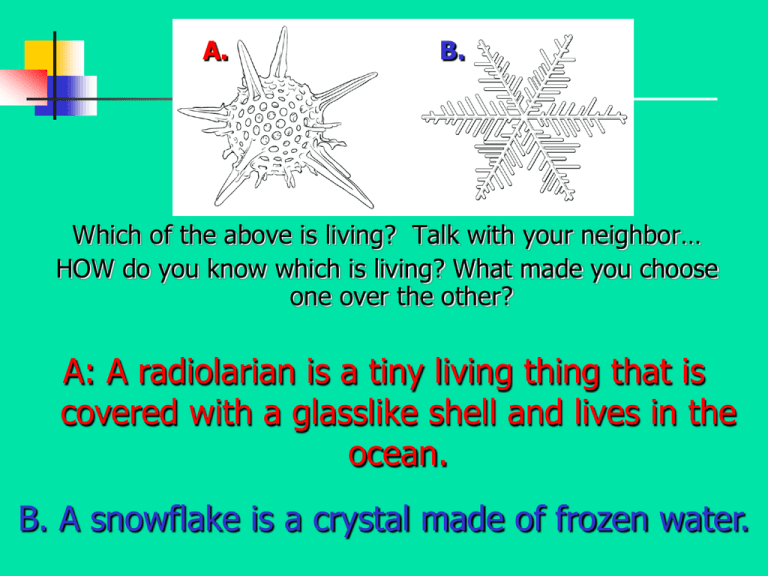
A. B. Which of the above is living? Talk with your neighbor… HOW do you know which is living? What made you choose one over the other? A: A radiolarian is a tiny living thing that is covered with a glasslike shell and lives in the ocean. B. A snowflake is a crystal made of frozen water. THE CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Biology The organized study of living things and their interactions with the environment around them In other words, The study of life! Themes in Biology Organization Cells Correlation between structure & function Interaction between organisms & their environment Unity in diversity Evolution (change over time) Scientific Processes Living things don’t exist in isolation… All living things depend on other living (and non-living) things in a variety of ways Examples: Plants and Humans Humans and water. Time to think…. On your own, think of some characteristics you would look for to determine if something is alive or not. Now, share your ideas with one neighbor. Finally, let’s share as a whole group…. WHAT IS LIFE? Living things are called ORGANISMS All organisms must have ALL of the following NINE Characteristics of Life… Remember: FRED H. GARC “FRED” F – Use and need Food Organisms need nourishment as they grow and change Organisms go through METABOLISM: R – Must be capable of Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Offspring result from and resemble TWO parents E – Must be able to transfer Energy Offspring result from and resemble ONE parent Sexual Reproduction The combination of chemical reactions through which organisms build up or breakdown materials as it carries out its life processes Different organisms obtain energy in different ways (plants vs. animals vs. bacteria) D – Develop and Grow Organisms undergo a series of stages to reach maturity Infant Toddler Young Adult Adult “H” H – Homeostasis Is a Steady internal balance H+ Blood Pressure Respiration rate Body Temperature “GARC” G – Genetic code All organisms are based on virtually the same genetic code Inheritance of traits is carried and directed by DNA A – Adapt to change and EVOLVE ADAPTATION Any structure, behavior, or internal process that enables an organism to respond to stimuli and better survive in an environment Structural – wings, arms, ect. Physiological – internal body processes Behavioral – innate, learned R – Respond to stimuli Variables (both living & nonliving) cause organisms to make internal as well as external adjustments STIMULUS RESPONSE A condition in the environment that requires an organism to change or adjust A reaction to a stimulus C – Made of at least one (1) Cell Made up of Cells Cell A collection of matter enclosed by a barrier that separates the cell from its surroundings Organisms can be unicellular (singlecelled) or multi-cellular (many-celled) Levels of Organization From smallest to largest: 1.) Atom 2.) Molecule 3.) Macromolecule 4.) Organelle 5.) Cell 6.) Tissue 7.) Organ 8.) Organ System 9.) Organism











