The Cell - Haiku Learning for FSD
advertisement

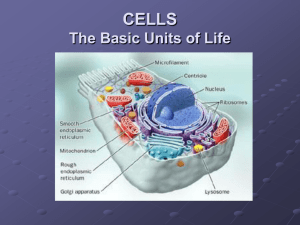
The Cell 1.1 Characteristics of Life Living things have organization Living things are able to grow and develop Living things are able to respond to their environment Living things are able to reproduce 1.1 Needs of Life All organisms need energy to carry out life’s activities The energy used by almost all organisms comes from the sun. Plants and some bacteria can capture the energy from the sun and use it to make food. Other organisms eat plants or other animals to get their energy 1.1 All living things are made of cells. The cell is the smallest unit of a living thing Some organisms are made of a single cell. These organisms are unicellular and usually are to small for you to see by yourself. Most organisms you can see like a frog are made up of many cells and are multicellular. Unicellular Algae Multicellular Frog 1.1 Unicellular vs. Multicellular Unicellular organisms have the same needs and characteristics of life as multicellular organisms. Multicellular organisms have bodies that are more complex, different body parts that perform different functions. Multicellular organisms have different types of cells. These cells work together to carry out the basic activities of life. 1.1 The Microscope Most cells are microscopic, too small to see without the aid of a microscope. A microscope is an instrument that makes an object appear bigger than it is. The invention of the microscope lead to the discovery of cells. 1.1 Microscope Robert Hooke and Anton Van Leeuwenhoek (LAY- vuhn-hook) were among the first people to describe cells. 1.1 Cell Theory Once cells were discovered people started asking, who has them, where do they come from? The observations and evidence gathered by many scientists over a long time resulted in the cell theory. 1.1 Cell Theory 1. Every living thing is made of one or more cells 2. Cells carry out the functions need to support life 3. Cells come only from other living cells. A scientific theory is a widely accepted explanation of things observed in nature. 1.1 Louis Pasteur French Scientist Discovered bacteria in spoiling milk He developed a process called pasteurization, in which heat is used to kill bacteria and therefore keep milk fresh longer. Pasteur discovered that bacteria could not be formed by spontaneous generation. They could only come from other bacteria cells. 1.1 Question: A _____organism is made of one cell. A. Frog B. Multicellular C. Unicellular D. Human E. Dog 1.1 Question: Which scientists were the first to look at cells under a microscope? A. Louis Pasteur B. Gregor Mendel C. James Watson D. Robert Hooke and Anton Van Leewenhoek E. Francis Crick 1.1 Question: Which scientist discovered bacteria? A. Francis Crick B. Gregor Mendel C. James Watson D. Robert Hooke and Anton Van Leewenhoek E. Louis Pastuer 1.1 Question: Which of the following is part of the cell theory? A. Cells carry out the functions to support life B. Cells only come from other cells. C. Every living thing is made of at least one cell. D. All of the above E. None of the Above 1.2 Cells are Diverse Cells can differ in size and shape The inside of one cell can be different from that of another cell. All Cells have this in common. 1. 2. 3. 4. Cell Membrane Cytoplasm DNA (differences) Ribosomes (differences) 2 Types of Cells Prokaryotes Single celled Simple Smaller No cell parts DNA sprinkled through out Examples= Bacteria, algae Eukaryotes Multicellular Complex Bigger Many cell parts DNA in the nucleus 2 types= Plant and animal cells Examples- Humans, plants, dogs Animal vs Plant Cell Animal cells are round and plant cells are rectangular Plant cells have 3 parts that animal cells don’t have: cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole 1.2 Parts of a Eukaryotic Cell Cell membrane- encloses the inside of each cell and protects it. Any material moving in or out the cell must pass through the cell membrane. Cytoplasm- is gelatin like substance where most of the work of the cell is carried out. 1.2 Parts of a Cell In a eukaryotic cell, most of the genetic material is stored in the nucleus, these cells are more complicated and have many more parts then a prokaryotic cell. Scientists use the word organelle to describe any part of the cell enclosed by a membrane. 1.2 Parts of a Cell The largest organelle that contains most of the genetic material is called the nucleus. The nucleus is like the control center for a eukaryotic cell. It stores the instructions the cell needs to function. Most unicellular organisms are prokaryotic, and most multicellular organisms are eukaryotic. Plants and animal cells are eukaryotes. 1.2 Cell Parts Plant cells also have cell walls. A cell wall is a tough outer covering that lies just outside the cell membrane. The cell wall supports and protects the cell. Having a cell wall is one way in which plant cells differ from animal cells. 1.2 Cell Parts No cell can live without energy. Plants absorb energy from the sun. Plant cells have chloroplasts which are organelles that use energy from the sun to make sugars. Some of the sugar is used right away and some is stored. 1.2 Cell Parts Ribosomes are tiny structures located through the cytoplasm and in the endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes use information from the nucleus to build molecules called proteins. 1.2 Cell Parts No cell can stay alive without energy! That means they/you need to eat or absorb energy from some source Plants get their food from the sun through photosynthesis and their chloroplasts Animals must eat food to get their energy Both Plant and Animal cells must process the food Cell Parts Mitochondria are the organelles that allow plants and animals to use energy. Mitochondria use oxygen to get energy from processing food. 1.2 Cell Parts The endoplasmic reticulum works with the ribosomes to build proteins but it is also a part of the cellular transport system. Pieces of endoplasmic reticulum break off to form small packages called vesicles. The vesicles carry processed materials to an organelle called the golgi apparatus. 1.2 Cell Parts The Golgi apparatus takes the materials and finishes processing them. Cells store water, sugar, and other materials. Cells must also store waste materials. Vacuoles function with the cell membrane to move materials in and out of the cell. They also can store water, waste, and other materials. The are found in plant cells. 1.2 Cell Parts Lysosomes are the animal cells version of vacuoles. Lysosomes can hold materials and contain chemicals that can break down nutrients, old cell parts, and other waste. 1.2 Question: A _____cell is simple and only has a single cell. A. Large B. Eukaryotic C. Elephant D. Prokaryotic E. Multicellular 1.2 Question: The ___holds the genetic material and is the control center for the cell. A. Mitochondria B. Cell Membrane C. Cell Wall D. Ribosomes E. Nucleus 1.2 Question: Which 3 parts do only plant cells have? A. cell wall, large vacuole, and nucleus B. chloroplasts, cell wall, and ribosomes C. cell wall, chloroplasts, and large vacuole D. cell wall, cell membrane, chloroplasts E. None of the above 1.2 Question: Which organelle uses oxygen to energy from processing food? A. Mitochondria B. Chloroplast C. Ribosome D. Endoplasmic Reticulum E. Nucleus 1.2 Question: Which organelle uses the sun to make sugar? A. Mitochondria B. Chloroplast C. Ribosome D. Endoplasmic Reticulum E. Nucleus 1.3 Cell Type Organisms can be classified by their cell type. Unicellular organisms have prokaryotic cells Multicellular organism have eukaryotic cells. 1.3 Cells can Specialize Most multicellular organisms consist of many different types of cells that do different jobs. For example most animals have blood cells, nerve cells, and muscle cells. The cells are specialized. Specialization of cells means that specific types of cells perform specific functions. 1.3 Specialization This specialization is why a single cell from a multicellular organism cannot survive on its own. All the cells in your body work together. You can think of the cells in an organism as members of a community. The size and nature of the community differ from organism to organism. 1.3 Community of Cells Cells are the smallest unit. In complex animals and plants, cells are not only specialized but grouped together in tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that are organized to do a specific job. Examples- connective, muscle, nervous, and epithelial (skin) 1.3 4 Types of Tissue Epithelial Tissue (skin)- provides protection and allows for absorption and secretion Nerve Tissue- transmits or sends electrical impulses from one part of the body to another 1.3 4 types of tissue Muscle Tissue- consists of bundles of long and narrow cells that can contract or shorten. They make all movement possible. Connective Tissue- joins body parts together providing protection and support. Tendons and ligaments are examples. Together tissues provide protection and support. 1.3 Community of Cells An organ is made of different tissues working together to perform a particular function. Organs represent another level of organization. Examples- eye, heart, and leaf So far we have cells tissue organ 1.3 Community of Cells Different organs and tissues working together form and organ system. An organism may only have a few organ systems while others have many. Humans have about 10 organ systems. The nervous system for examples includes: brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors in organs such as the eyes and ears. 1.3 Organization Cells tissues organs organ systems -> Organism Examples of organ systems: digestive system, reproductive system, respiratory system, and skeletal system 1.3 Question: Eukaryotic organisms have ____cells that each do a particular job. A. Large B. separated C. Specialized D. Colorful E. Small 1.3 Question: A ____is a group of similar cells working together. A. Organ B. Organ System C. Cell D. Tissue E. Organism 1.3 Question: An____is made of different tissues working together. A. Organism B. Organ System C. Cell D. Tissue E. Organ 1.3 Question: Our digestive system is an example of an____. A. Organ B. Organ System C. Cell D. Tissue E. Organism