DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis
advertisement

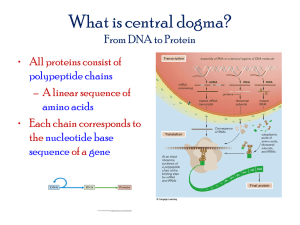
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis Chapter 11 DNA Structure • DNA is a chain of Nucleotides – 3 parts of a Nucleotide: • sugar (deoxyribose) • Phosphate • nitrogen base 4 possible bases: – Adenine – Guanine – Thymine – Cytosine Structure of DNA (continued) • The DOUBLE HELIX (looks like a twisted ladder) – Double Stranded– – 2 sugar/ phosphate backbones – rungs = nitrogen base pairs • hydrogen bonds between complementary nitrogen bases • complementary= will bond together – A is complementary to T, – G is complementary to C – Base-pairing rules (see above) • The number and sequence of the nitrogen bases determines the CODE of the genes in the DNA! Video • http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/body/publicgenomes.html Personal DNA Testing! • http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/genome/program_a dv.html Very Good! Show toward end of unit (discusses genome, mutations etc.) • S:\Biology\Protein Synthesis\Videos\Genetics Bill Nye Greatest Genetic Discoveries. Can be started around here (about 1 hr.) DNA Replication • DNA making copies of itself is called DNA REPLICATION • Steps of DNA replication are controlled by enzymes. • Animation C:\Documents and Settings\BBAUGHMAN\Desktop\bio powerpoints\Chapter 11 BDOL IC Enzymes of Replication • 3 of the main enzymes are: – Helicase: untwists the DNA – DNA polymerase: adds new nucleotides and connects them to build up a new strand (follows base-pairing rules!) – Ligase: Joins DNA fragments together Background info for Protein Synthesis… • DNA is important because it is the instructions for how to make proteins! • But… – DNA can’t make proteins by itself! – RNA is needed! Function of RNA • accomplish protein synthesis • Why?--DNA is trapped in the nucleus but protein synthesis happens at ribosomes located in cytoplasm. RNA RNA • Structure of RNA – nucleotide • sugar= ribose • phosphate • nitrogen base (instead of thymine, RNA has Uracil). – Uracil is complementary to Adenine (it replaces Thymine) – Single stranded Three Types of RNA – Messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to take the message from DNA to the ribosome – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) attaches to mRNA and helps assemble proteins – Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers (brings) amino acids to mRNA so that they can be attached to make a protein Compare and Contrast DNA and RNA in the following table DNA # strands RNA 2 1 sugar Deoxyribose Ribose Nitrogen bases A, C, G, T function Code for proteins A, C, G, U Protein Synthesis Self Check Quiz 1. Describe the relationship between DNA and RNA. - DNA codes for RNA (i.e. recipes). RNA makes proteins. 2. List three ways RNA different from DNA. 1) RNA sugar: Ribose 2) RNA single stranded 3) Uracil replaces Thymine (A= U) 3. What would happen if mRNA could not function? - No mRNA = no message (recipe) from DNA to make protein - = No protein Protein Synthesis 11.2 From DNA to PROTEIN • I. The Purpose of DNA: DNA is used to make RNA which is used to make proteins!! • DNA--> RNA--> Proteins – A. One DNA molecule has many GENES on it! – B. Gene—segment of DNA molecule that codes for a specific protein. Protein Synthesis Step 1: Transcription III. TRANSCRIPTION •Transcription Animation http://highered.mcgraw-hi – A. Transcription is the synthesis of mRNA using the code of a gene (DNA) as a template (pattern). – B. Steps 1. An enzyme (RNA Polymerase) unzips DNA 2. RNA Polymerase attaches RNA nucleotides following base pairing rules. – This makes single stranded mRNA 3. Single stranded mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome. Protein Synthesis Step 2: Translation • IV. Translation (Converting the “language” of mRNA to the language of proteins.) Codon= triplet of nitrogen bases on mRNA • – Each codon codes for one specific amino acid • • Note: amino acids are the building blocks of proteins This code is universal- it applies to all organisms! Translation continued… – The order of codons determines the order of amino acids found in the protein. – mRNA from nucleus is ‘read’ along its codons • this occurs at the ribosome • tRNA has anticodons that are complementary to specific codons • Each tRNA can only bind one amino acid • tRNA transfers or transports the amino acids to the ribosome where they are attached (in order) to make a polypeptide chain. Translation Animation http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter3/animation __how_translation_works.html Analogy of Transcription through translation (RNAi explained) http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/teachers/body/rnaidiscovered.html http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/sciencenow/3210/02.html MUTATIONS! • Any CHANGE in the DNA sequence is a mutation! • Mutations are caused by mutagens! • Types of mutations – Point mutation—change in a single base pair of DNA • May change one amino acid in protein Animation: http://www.dnalc.org/view/15532-Sickle-cell-anemia-3D-animation-with-narration.html – frameshift mutation—deletion or addition of a single base pair.—Causes every codon after the mutation to be different!! Great Video (also good intro to human genome project) • http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/genome/prog ram_adv.html Very Good! Show toward end of unit (discusses genome, mutations etc.)