File
advertisement

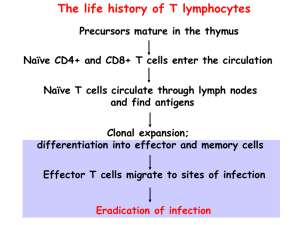
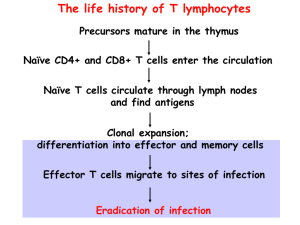
Aims • Describe T cell maturation and be able to differentiate naïve and effector T cells. • Differentiate the development and functions of Th1 and Th2 cells. • Describe the mechanism of T cell cytotoxicity. • Readings: Abbas & Lichtman, Chapters 4, 5 & 6 T Cell Maturation and Selection • Occurs in the thymus. • Positive selection – T cells must recognize a MHC molecule in order to survive. – Makes sure TCR molecule can recognize MHC + peptide. • Failure of positive selection – No recognition of MHC+ peptide. • Negative selection – T cells who strongly recognize a MHC molecule undergo apoptosis. – Eliminates self protein reacting T cells. Adapted from Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 4-13 Intracellular Microbes • Cell mediated immunity is responsible for intracellular microbial infections. • Common intracellular infections – Phagocytosed microbe that survive in phagolysosomes. – Microbe that escapes into cytoplasm. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-1A Intracellular Microbes • Microbes that bind to membrane receptors and enter a cell’s cytoplasm in order to infect a cell. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-1B Activation of T Cells • Antigen recognition – MHC-TCR • Activation – Cytokines • Clonal expansion • Differentiation – CD4+, CD8+ Cytokines Cytokines Peripheral • Effector function Adapted from Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-2 MHC-TCR Interaction • TCR recognizes antigen (peptide) within MHC molecules. • CD4 binds to MHC class II molecules (CD8 to class I). • Signaling begins with phosphorylation of the ζζ associated with _CD3_. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-4 CD4+ T Cell Activation • Activation requires two signals. – 1) MHC/peptide antigen binding to TCR. – 2) Costimulatory molecule on APC binding to specific receptors on T cell. • B7-1 (CD80) or B72 (CD86) on APC binding to CD28 on T cell. Adapted from Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-6 CD4+ T Cell Activation • Activated T cells produce cytokines and cytokine receptors. – IL-2 – High affinity IL-2 receptor. • Resulting in clonal proliferation and differentiation of that T cell. Adapted from Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-6 CD4+ T Cell Activation • If no costimulation occurs when TCR binds to MHC / Peptide, T cell becomes nonresponsive (anergy) or undergo apoptosis. • Only activated APCs express costimulatory molecules. – Thus only naïve T cells in direct contact with APC containing microbial antigen will be activated. Adapted from Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-6 CD8+ T Cell Activation • Antigen presentation by APC via MHC class I (infected APC). 10,000 fold – APC express costimulator molecules. • Phagocytosed infected cell by APC results in antigen presentation via MHC class II to CD4+ T cell and MHC class I to CD8+ T cell. – CD4+ T cells secrete cytokines to activate CD8+ T cells. Adapted from Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-7 Effector Function of CD4+ T Cells •Differentiated effector cells appear 3-4 days after exposure to microbe. • Activation of macrophages. – – – – Expression of CD40L by CD4+ T cells. CD40L bind to CD40 on Macrophages. Secretion of cytokines (IFNg) by CD4+ T cells. Results in macrophage killing of phagocytosed microbe. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-10B Effector Function of CD4+ T Cells • Activation of a B cell. – – – – Expression of CD40L by CD4+ T cells. CD40L bind to CD40 on B cells. Secretion of cytokines (IL-4) by CD4+ T cells. Results in B cell secretion of antibody. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-10B Function of Th1 CD4+ T Cells • Macrophages and dendritic cells respond to bacterial or viral infections by secreting _IL-12_ which causes naïve CD4+ T cells to differentiate into Th1 cells. Adapted from Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-11A IL-12 Function of Th1 CD4+ T Cells • Th1 cells secrete IFNg. – Macrophage activation. • Stimulates expression of MHC class II. • Stimulates the expression of B7 costimulators. – B cell production of IgG subclasses involved in phagocytosis via Fc receptors. Adapted from Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-11A IL-12 Function of Th2 CD4+ T Cells • If there is no production of IL-12 by the APC then the T cell itself secretes IL-4 inducing its differentiation into the Th2 phenotype. – This is what happens in infections by helminths which are too big to be phagocytosed. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-11B Function of Th2 CD4+ T Cells • Th2 cells secrete IL-4 – Stimulates the production of (class switch to) IgE by B cells. • Th2 cells secrete IL-5 – Activates eosinophils. • Th2 cytokines (IL-4) inhibit macrophage activation and Th1 mediated immunity. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-11B Effector Function of CD8+ Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes • CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize MHC class I with peptides on infected cells. • Differentiated cytotoxic T lymphocytes do not require costimulation or T cell help for activation. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 6-10 Effector Function of CD8+ Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes • Cytotoxic T lymphocytes kill target cells by releasing granule contents. – Perforin polymerizes resulting in pores in target cell membranes. – Granzymes enter target cell through perforin pores and activate caspases resulting in apoptosis. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 6-10 Resistance to Cell-Mediated Immunity • Inhibition of phagolysosome fusion. • Mycobacteria escapes death by avoiding enzymes in lysosome. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 6-12 Resistance to Cell-Mediated Immunity • Inhibition of class I MHC expression. – CMV & EBV Inhibit proteosomal activity. – HSV Inhibits transport of peptides into ER. – CMV Removes class I MHC from ER. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 6-12 Resistance to Cell-Mediated Immunity • Production of inhibitory cytokines – EBV secretes IL-10 (similar to IL-4) that inhibits macrophage activation. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 6-12 Resistance to Cell-Mediated Immunity • Production of soluble cytokine receptors. – Quench cytokines resulting in lack of cytokine activity. – Pox virus secretes soluble IL-1 and TNF receptors. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 6-12 Next Time • Describe the humoral immune response. • Compare and contrast the primary and secondary antibody responses. • Compare and contrast T-dependent and Tindependent antigens and the antibody response to each. • Describe effector functions of antibodies including neutralization and ADCC. • Readings: Abbas & Lichtman, Chapters 7 & 8 Objectives 1. Describe T cell maturation and be able to differentiate naïve and effector T cells. 2. Describe the process of T cell activation 3. Describe the development and functions of Th1 and Th2 cells. 4. Describe the mechanism of T cell cytotoxicity.