MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
Cell Division
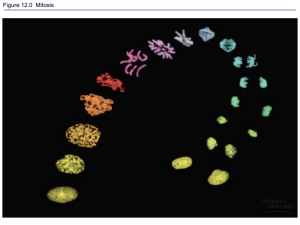
MITOSIS
ASEXUAL division of a cell
Occurs in EUKARYOTIC cells (they HAVE
a nucleus)
Makes a clone
A CLONE is a genetically identical copy
MITOSIS
Produces offspring with the full DIPLOID
number of chromosomes.
Ex. In a fruit fly, there are 8 chromosomes, so
our diploid number (2n) is 8.
2n
2n
2n
MITOSIS
“Offspring” (daughter cells) are genetically
identical to the “parent” cell.
In humans, mitosis is used for growth and
repair of body tissues.
Ex. If you have a cut, mitosis is what helps the
cut to heal.
MITOSIS
Picture
STAGES OF MITOSIS
INTERPHASE
This “stage” is where the cell spends most of
it’s “life”.
The cell prepares for division by making an
exact copy of each chromosome. (replication)
STAGES OF MITOSIS
PROPHASE
The chromosomes become visible.
The nuclear membrane begins to disappear.
The SPINDLE FIBERS form between
CENTRIOLES.
STAGES OF MITOSIS
METAPHASE
The chromosomes “line up” in the middle of
the spindle.
Spindles attach to centromere
STAGES OF MITOSIS
ANAPHASE
The chromosomes begin to separate
When they separate, each piece becomes a
CHROMATID.
STAGES OF MITOSIS
TELOPHASE (in ANIMAL cells)
Two new cells begin to form by pinching in
(cleavage) at the membrane.
CYTOKINESIS-the division of cytoplasm
STAGES OF MITOSIS
TELOPHASE (in PLANT cells)
Instead of pinching in, a CELL PLATE forms
between the two daughter cells.
3 REASONS MITOSIS OCCURS
1. As the cells divide, the organism
increases in size.
2. In humans, mitosis occurs to replace
dead red blood cells (about every 120
days).
3. Asexual cellular reproduction
Ex. Amoeba
MITOSIS PICTURES
MITOSIS PICTURES
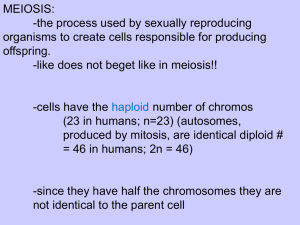
MEIOSIS
Sexual reproduction (involves 2 parents)
Makes sex cells (gametes)
These gametes are
___________________(male)
___________________(female)
The gametes are made in the gonads.
The gonads are
_______________________(males)
_______________________(females)
MEIOSIS
All meiosis occurs in the GONADS
Purpose:
To reduce the chromosome number so when
2 gametes combine (fertilization), a zygote is
formed.
MEIOSIS
Picture of GAMETOGENESIS
MEIOSIS
Oogenesis
Occurs in the _______________
Forms of 1 egg and 3 polar bodies
The egg has half the chromosome number as the
parent cell. (haploid number)
Spermatogenesis
Occurs in the _______________
Produces 4 sperm cells
Each sperm has half the chromosome number of the
parent cell. (haploid number)
MEIOSIS
Chromosome numbers are reduced during
meiosis.
Examples:
If a body cell has 46 chromosomes, the gamete will have
_______.
If a dog’s skin cell has 72 chromosomes, each sperm cell
will have _______.
If a liver cell has 32 chromosomes, how many chromosomes
does the egg cell have? _____
If an alligator has 14 chromosomes in its sperm, how many
chromosomes are in his mates egg cell? ______
If the haploid number is 23, then the diploid number is _____.
MEIOSIS
Recombination of chromosomes causes
GENETIC VARIATION.
Picture of fertilization
MEIOSIS
Meiosis is called reduction-division of
chromosomes because the chromosome
number is reduced and replicated before
the cell divides.
Diploid Haploid
2N N
MEIOSIS
Steps of meiosis: Meiosis I and Meiosis II
During Meiosis IInterphase
Chromosomes pair up to form homologous pairs.
Prophase
Spindle forms and nuclear membrane disappears
Metaphase
Homologous Pairs line up in the middle of the spindle
This is called SYNAPSIS
A TETRAD is formed (sister chromatids)
Anaphase
Homologous Pairs are separated from one another
This is called DISJUNCTION
Telophase
Cytoplasm divides
Each cell has the monoploid (haploid) number of chromosomes
MEIOSIS
Steps of meiosis: Meiosis I and Meiosis II
During Meiosis IIProphase II
Spindle forms and nuclear membrane disappears
Metaphase II
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the spindle.
Anaphase II
Chromosomes are pulled apart by spindles.
Telophase II
Cytokinesis (cytoplasm divides) and four DAUGHTER CELLS
are formed (in males).*
*In females, only ONE viable monoploid cell is produced.
MEIOISIS
MEIOSIS
MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS