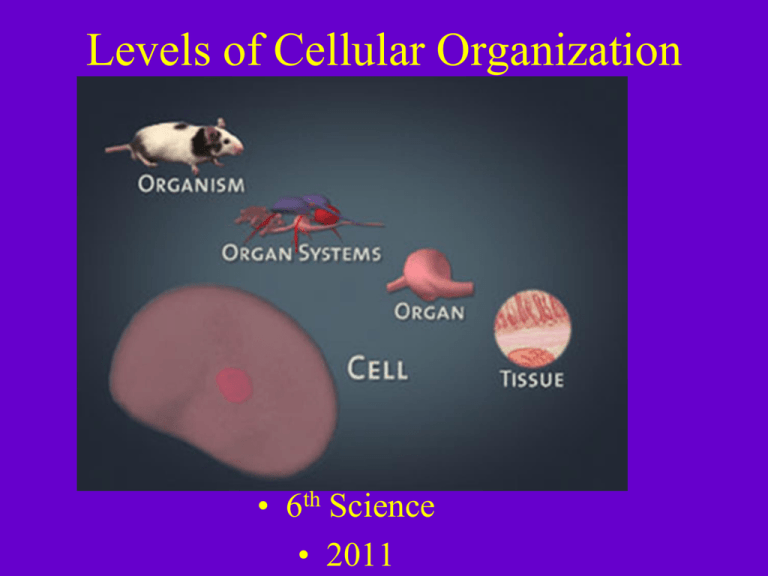
Levels of Cellular Organization
• 6th Science
• 2011
Unicellular vs. Multicellular
• Unicellular: One celled organism. They
must perform all activities within one cell.
NO TISSUES, ORGANS, OR SYSTEMS!!
Multi-cellular Organisms
• Multi-cellular – Organisms made of more
than one cell. The cells work together to
make tissues, organs, and organ systems.
Unicellular vs.
Multicellular
Similar
1. Carry on all 7 characteristics of life.
2. Have the same MAIN cell parts as multi-cellular
organisms. Mitochondria, vacuole, ER, nucleus,
ribosomes, chloroplast, golgi bodies, etc. Except
nucleus in Arachebacteria and Eubacteria
Different
1. Cells in multi-cellular organisms have a specific job.
Unicellular organism must carry on all 7
characteristics of life in one cell.
2. Multi-cellular organisms have tissues, organs, and
organ systems. Unicellular organisms DO NOT.
Levels of Cellular Organization
LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
-Cells work together to form tissues
Cardiac cells
Bone cells
Muscle tissue
epithelial tissue
Cardiac organ
Bone
Levels of Organization
• Tissue- group of
similar cells
working together
LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
• Tissues work together to form organs
Levels of
Organization
• An organ is a structure that contains at least
two different types of tissue functioning
together for a common purpose
Skin- epithelial-connective-nerve
LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
-Organs work together to form organ
systems
Arteries & veins
heart
bones
Cartilage &
tendons
Circulatory
system
Skeletal
system
LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
-Organ systems work together to form
the whole organism
Skeletal
system
Muscular
system
Whole
organism
Circulatory
system
Levels of Organization
•Cells that work together to do the
same job form tissues
•Tissues that work together to do the
same job form organs
•Organs that work together to do the
same job form systems
•Systems work together to form the
whole multi-cellular organism
4 Types of Tissues
• Epithelial – SKIN!!
• Function – Covers the outside of the body
and lines the inside of your body!!
• Your skin is the largest organ in your body!
4 Types of Tissues
• Connective – ligaments, cartilage, blood,
and bone
• Function – fills in space and connects other
tissues together; support, protects, nourishs
and insulates organs.
Bone
RBC
WBC
4 Types of Tissues
• Muscular – Smooth and skeletal muscles
• Function - contrasts and relaxes to allow
movements; makes up some organs
Smooth
Skeletal
4 Types of Tissue
• Nervous – nerves(makeup brain and spinal
cord)
• Function – transmits messages through the
body
LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
– Multicellular organisms Have specialized
cells to perform specific jobs
– The shape of the cell is designed for its
job
Red blood
cells
Liver
cells
Nerve
cells
Cardiac
cells
As you know, all living things are made of cells. We have looked at two
types of cells:
Typical LEAF Plant Cells
NOT – root, stem or
flower!!!!
Typical SKIN Cells –
not nervous, muscle,
bone, etc
But not all plant cells are rectangular and not all animal cells are
circular!!!!!!!!!
Form Fits Function
– The shape of the cell is designed for its
job
Onion skin
cells
Nerve Cells
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Function – Provide gas exchange between bloo
and environment.
Cell – Smooth muscle
Tissue – Smooth
muscle
Organ – Lungs &
nose
Digestive System
Function – Breakdown and absorb nutrients tha
necessary for cellular respiration.
Cell – smooth muscle cells
Tissue – smooth muscle tissue
Organs – stomach, liver, gall bladder, small
intestines, large intestines
Smooth MUSCLE TISSUE
Notice the Shape: Smooth
muscle cells are tube
shaped to contract
smoothly TO MAKE UP
YOUR ORGANS
(STOMACH, KIDNEYS,
INTESTINES, ETC)
These are smooth
muscle cells. Draw
it into your notes.
Why do you think these
cells need to be able to
contract smoothly?
SMOOTH MUSCLE TISSUE
Organs where
Smooth Muscle
tissue can be
found are:
Stomach,
intestines,
blood vessels,
esophagus,
trachea, other
organs.
Organ Systems
where Smooth
MuscleTissue is
found:
Digestive System
Other organ systems directly dependent on
Smooth Muscle Tissue: Respiratory,
Reproductive
NERVOUS SYSTEM
Function – carries messages back and forth
between the spinal cord and the brain and every
other part of the body.
ORGAN – Brain & spinal cord
TISSUE - NERVOUS
CELL: This is a nerve cell
called a neuron. Draw it into
your notes.
Notice the shape. It is shaped
like a wire to carry electrical
messages to and from the brain.
Nervous Cells
Nervous cells are shaped like wires to carry
electrical impulses.
NERVOUS TISSUE
Organs where nervous tissue can be found are:
Spinal cord
Brain
Neurons
Nerves
NERVOUS TISSUE
Other organ systems directly dependent on
Nervous Tissue:
Muscular
System
Circulatory
System
Red Blood Cells
• Red Blood Cells have a space or hole in the
middle to carry oxygen. Why do organisms
need oxygen?
White Blood
• Function: Shaped like a blob to engulf
foreign objects in the blood.
Why do red and
white blood cells
look different??
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Function – Circulates blood throughout your body
which carries important nutrition and oxygen for
your cells.
CELLS - These are red
blood cells called
erythrocytes. Draw one
into your notes.
Notice the shape. It has a hole
in the center because it doesn’t
have any organelles so it can hold
more oxygen. It is also very
flexible. Why do you think that
would be important?
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Both these blood
cells along with
platelets make up
BLOOD. Blood is
a tissue.
Why?????
This is a white
blood cell called a
leucocyte. Draw
it into your notes.
Notice the shape:
White blood cells are
shaped like blobs to
gobble up bacteria like
Pac-man.
RBC
WBC
Circulatory System
Cell & TISSUE: Cardiac Muscle, RBC &
WBC
These are cardiac muscle
cells in cardiac muscle
tissue . Draw it into your
notes.
Notice the shape. Banded for
strength and quickness so your
heart can pump the blood
through your body. Why do
you think these cells need to
be strong and able to contract
quickly?
CARDIAC MUSCLE TISSUE
Organs where
Cardiac tissue can
be found are:
Heart
ONLY
Organ Systems
where Cardiac
Tissue is found:
Circulatory
System
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
Organ Systems where BLOOD Tissue is found:
The Circulatory
System is responsible
for delivering oxygen
and food to all the
cells in the body.
Circulatory
System
Other organ systems directly dependent on
Blood Tissue:
ALL OTHER SYSTEMS
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
TISSUE – Connective, nervous, and muscular.
Organs – heart and blood vessels.
CIRCULATRY SYSTEM
Heart and blood vessels
Does blood support, protect or connect?
SKELETAL SYSTEM
FUNCTION – Provides support for the body
protects organs
CELL -This is a bone cell.
Draw it into your notes.
Does bone
support,
protect or
connect?
This big hole is
where tiny nerves run
through.
Notice the shape. It has tiny
holes called pores to make the
bone lightweight but strong.
Bone Cells
• Bone cells are circular and stack on each
other to make the bone strong.
Muscle Cells
• Muscle cells look like rubber bands that
contract when they get the impulse from the
nerve.
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
Other organ
systems
directly
dependent on
Bone Tissue:
Organs: Bones
Tissue: Connetcive
Bones
Skeletal
System
Muscular
System
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
Cartilage and Fat are also Connective Tissues.
What do they do?
Cartilage
Protects
Fat
Protects
MUSCLE SYSTEM
Function – moves and connect your bone
Cell – Skeletal Muscle
Tissue – Skeletal Muscle
Organs – Muscles
SKELETAL MUSCLE
Notice the Shape:Skeletal
muscle cells are banded
(striped) to contract
quickly, tube shaped to
contract smoothly TO
MOVE YOUR BONES!!!!!!!!
These are skeletal
muscle cells. Draw
it into your notes.
Why do you think these
cells need to be able to
contract quickly and
smoothly?
SKELETAL MUSCLE
Organs where
skeletal muscle
can be found are:
Muscles
Organ Systems
where Skeletal
muscle is found:
Muscular
System
Other organ systems directly dependent on
Cardiac Muscle Tissue: SKELETAL SYSTEM
Smooth MUSCLE TISSUE
Notice the Shape: Smooth
muscle cells are tube
shaped to contract
smoothly TO MAKE UP
YOUR ORGANS
(STOMACH, KIDNEYS,
INTESTINES, ETC)
These are smooth
muscle cells. Draw
it into your notes.
Why do you think these
cells need to be able to
contract smoothly?
SMOOTH MUSCLE TISSUE
Organs where
Smooth Muscle
tissue can be
found are:
Stomach,
intestines,
blood vessels,
esophagus,
trachea, other
organs.
Organ Systems
where Smooth
MuscleTissue is
found:
Digestive System
Other organ systems directly dependent on
Smooth Muscle Tissue: Respiratory,
Reproductive
Skin
• Function : Flat to stack on each other and
protect the body.
EPITHELIAL TISSUE
Function – forms a protective layer for outside
of the body (skin) and lines hollow spaces (mouth,
ear, nose, etc.) and organs.
This is a epithelial
(skin) cell. Draw it
into your notes.
Notice the shape. It
is thin and flat to fit
together like tiles on a
floor to shield the
cells underneath.
EPITHELIAL TISSUE
Organs where epithelial tissue can be found are:
Stomach lining
Mouth lining
Lining of the intestines and blood vessels
MOST IMPORTANTLY IT MAKES UP THE ORGAN SKIN. THE
ORGAN SYSTEM IS SKIN.
EPITHELIAL TISSUE
Organ Systems where Epithelial Tissue is found:
Other organ systems directly dependent on
Epithelial Tissue:
Digesti
Circulatory
PLANT TISSUES
Plants are also made up of cells. These cells
form tissues and organs just like animals.
There are three basic
organs in any plant.
These organs are the
roots, the stem and the
leaves. Each one is made
up of tissues that perform
different functions to
keep the plant alive.
Leaf
• Function : Hard brick to stack on each
other and make the plant stand up. The
vacuole pushes against the cell wall.
PLANT TISSUES AND ORGANS
Stems – support the
above ground parts of the
plant. Transports food
and water between the
leaves and the roots.
Stems help the other two types of plant
organs by holding the leaves up so they can
receive maximum sunlight. Stems also
transport water from the roots to the leaves
and transport food from the leaves to the
roots.
PLANT TISSUES AND ORGANS
Stems are made up of two (2) types of tissue:
xylem and phloem
These are xylem cells.
Draw them into your
notes.
Notice their shape.
Xylem cells are
shaped like tubes to
carry water and
minerals in an upward
direction from the
rootsand
to the leaves.
FUNCTION: Carry water
Minerals to rest of plant.
PLANT TISSUES AND ORGANS
Stems are made up of two (2) types of tissue:
xylem and phloem
These are phloem cells.
Draw them into your notes.
Notice their shape.
Cells are shaped like
straws to carry food
made in the leaves all
over the plant.
FUNCTION: Carries
food to rest of plant
from the leaves.
PLANT TISSUES AND ORGANS
ROOTS
FUNCTION– absorb water and minerals from
the soil, anchor the plant and store food made
in the leaves.
Roots provide stems and leaves with water and
minerals. Roots absorb the water and
minerals from the soil
PLANT TISSUES AND ORGANS
Roots are also made up of two (2) types of
tissue: xylem and phloem
This is a root in cross
section. Draw it into
your notes.
Root in Cross Section
Xylem are the cells
in the middle.
Phloem are the cells
around the outside.
Xylem and Phloem
have the same
function in the root.
PLANT TISSUES AND ORGAN
LEAVES
FUNCTION: Leaves trap light and make food
for the plant through the process of
photosynthesis.
This is a
leaf cell.
Draw them
into your
notes.
Notice the Shape: Leaf cells are rectangular
for strength. They are also thin and flat to
expose the chloroplasts to sunlight.
PLANT TISSUES AND ORGANS
Leaves trap light and make food for the plant
through the process of photosynthesis.
Mesophyll – the middle
layer where
photosynthesis takes
place.
Cuticle – waxy layer,
prevents water loss.
This is a leaf in
cross section.
Skeletal System
Function: Provides shape and support,
protects organs, and produces red
blood cells.
Organ: Bone
Tissue: Connective
Cell: Bone Cell
Muscular System
Function: Contracts and allows the
body to move
Organ: Muscle
Tissue: Muscle
Cell: Smooth Muscle, Cardiac Muscle, and S
Circulatory System
Function: Delivers food and oxygen to
the body cell and carries carbon
dioxide out.
Organs: Heart, veins, and arteries
Tissue: muscle and nerve
Cell: red blood cell and white blood cell
Digestive System
Function: Breaks down food for our body
to use for energy
Organs; Stomach, Small Intestines, Large
Intestines, gall bladder,
pancreas
Tissue: smooth muscle
Cell: smooth muscle cell
Skeletal System
Function: Provides shape and support,
protects organs, and produces red
blood cells.
Organ: Bone
Tissue: Connective
Cell: Bone Cell
Muscular System
Function: Contracts and allows the
body to move
Organ: Muscle
Tissue: Muscle
Cell: Smooth Muscle, Cardiac Muscle, and S
Circulatory System
Function: Delivers food and oxygen to
the body cell and carries carbon
dioxide out.
Organs: Heart, veins, and arteries
Tissue: muscle and nerve
Cell: red blood cell and white blood cell
Skin
Function: Protects the body and
your organs
Organ: Skin
Tissue: Epitheleal
Cell: Skin
Endocrine System
Function: Regulates varies body
functions(hormones)
Organs: hypothalmous
Tissue: smooth muscle
Cell: smooth muscle
Excretory System
Functions: Removes liquid and solid
wastes from the body
Organs: kidney, colon, spleen
Tissue: smooth muscle
Cell: smooth muscle
Reproductive System
Function: Produces male and females
sex cells
Organs: testes and ovaries
Tissues: smooth muscle
Cell: smooth muscle cells