Introduction to Human Body Systems
advertisement
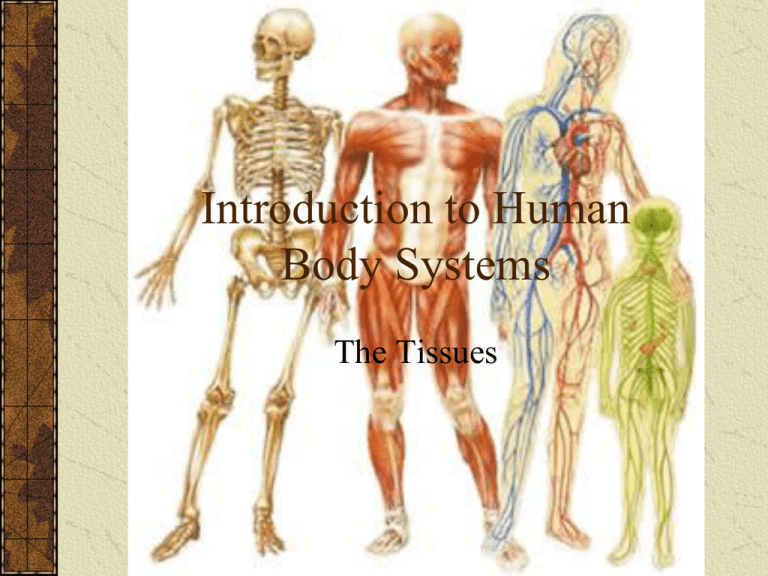
Introduction to Human Body Systems The Tissues Levels of Organization Molecules (like DNA and proteins) Organelles Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Populations Communities Levels of Organization A bunch of cells make up tissues (like muscular tissue) Tissues come together to form organs (like a heart) Organs work together in organ systems (like the circulatory system) Organ systems work together to make organisms (like humans) Guess the Organ Systems… What are some organ systems that you can think of? Tissues All of the organ systems are made up of just four TYPES of tissues Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Each tissue type contains many different tissues Epithelial Tissue Function: cover, protect, secrete and absorb makes up various surfaces. Cuboidal: Single layer of cube like cells. Columnar: Single layer of tall slender cells; may have microvilli at free surface. Connective Tissue Properties: living cells are separated by a nonliving matrix, which is usually secreted by the cells themselves. The MATRIX gives the tissue its properties. White fibrous tissue: collagen fibrils secreted by fibroblasts. Makes up the tendons and ligaments. Bone: Extremely hard with calcium salts in matrix. Cells are called osteocytes arranged is Haversian system. Adipose: Fat storage. Large storage structure with nucleus moved to side. Blood: Matrix is liquid (plasma) and is NOT formed by the blood cells themselves. Various cells: erythrocytes, various types of leucocytes, and platelets or thrombocytes. White Fibrous Tissue Bone Bone Tissue Blood (Plasma is on top) Adipose Tissue Muscle Tissue Function: specialized for contraction. Have elongated shape containing proteins that undergo changes in shape to cause shortening. Smooth muscle: controlled by autonomic nervous system, involuntary control. Skeletal muscle: striated muscle moved under voluntary control. Cells are multinucleated. Cardiac muscle: Found only in the heart. Striated, branched, with one nucleus. Under autonomic nervous control. Nervous Tissue Function: Receives stimulus from internal and external environment which is converted into action potentials which evoke appropriate responses. Picture Organs Multiple tissue or tissue layers form organs… What type of tissue do you think make up the following organs/structuresIntestines Heart Skin Bones Organ Systems Organs that work together make up organ systems… Do you think all organs belong to only one organ system? Do you think that all organ systems operate independently of one another? Guess that Organ System What organ system do you think the following organs belong to? Heart Skin Liver Lung Kidney Intestine Blood cells What is/are the function(s) of the various organ systems…how do they fit together? Integunmunintary Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Excretory System Immune System Nervous System Endocrine System Reproductive System A few relationships… Circulatory and respiratory systems – the blood carries oxygen to the cells… Circulatory and digestive systems – the blood carries nutrients to the cells… Endocrine and reproductive systems – hormones in the endocrine system help the reproductive system function Integunmunintary and immune system – our skin is our first line of defense against germs Nervous and all systems – the brain and nervous system help control them all!