WP5.1 - Vollmar
advertisement

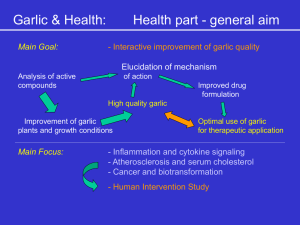
The Interaction of Garlic With Mediators of Inflammation Prof. A. M. Vollmar Dr. V. M. Dirsch H - P Keiß Overview 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Interaction of garlic powders and constituents with activation of NF-B Interaction of garlic powders and constituents with expression of adhesion molecules ICAM-1 & E-selectin Interaction of garlic powders and constituents with cytokine production Additional targets Outlook Interaction of garlic powders and constituents with NF-B No inhibitory effect on TNF- induced NF-B activation was found for: – – – – – – – – – – Diallyl disulfide Allyl mercaptane S-allylcysteine -glutamylcysteine Allyl-methyl sulfoxide Allicin French garlic powders 2000 French garlic powders 2001 Spanish garlic powders 2000 Spanish garlic powders 2001 Interaction of garlic powders and constituents with ICAM-1 & E-selectin No inhibitory effect on TNF- induced expression of adhesion molecules was found for: – Diallyl disulfide – Allyl mercaptane – S-allylcysteine Summary Tested garlic compounds do not interact with NFB and expression of adhesion molecules Garlic metabolites fail to inhibit the activation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB and subsequent expression of the adhesion molecule E-selectin in human endothelial cells Verena M. Dirsch*, Hans-Peter Keiss, and Angelika M. Vollmar Reviewer 1: I would like to suggest that the authors submit a new manuscript providing additional experimental data on the effects of DADS and AM on NF-B activity and E-selectin expression choosing longer incubation periods. Furthermore, cytotoxicity data for DADS and AM seem to be crucial. Editor: ....“but I also would like to encourage you to submit a new mansucript when new experimental findings have been added“ Eur. J. Nutrition Interaction of garlic powders and constituents with cytokine production in whole blood Allicin, DADS, AMSO2, -glutamyl-cysteine, lipophilic and hydrophilic garlic extracts were tested. Conflicting data between individual experiments – Summer 2001: Il-1, TNF reduced, Il-10 increased – Winter 2001/2002: Il-1, TNF and Il-10 increased – Summer 2002: Il-1 reduced, TNF and Il-10 increased Possible explanation All sets represent self-contained observations and are conclusive. Garlic powders used – Summer 2001: French powders of year 2000 – Winter 2001/2002: French powders of year 2001 (cave contaminated) – Summer 2002: Mixed garlic powders from France and Spain 2000 & 2001 For our publication we chose the data from summer 2001, because data are conclusive (and we have performed the luciferase assay) Summary Tested garlic compounds do interact with LPS-induced cytokine liberation in human whole blood Garlic (Allium sativum) modulates cytokine expression in LPSactivated human blood leading to an overall inhibitory effect on NF-κB activity. Hans-Peter Keiss, Verena M. Dirsch, Thomas Hartung, Thomas Haffner ?? and Angelika M. Vollmar Submitted to Journal of Nutrition Additional targets Garlic induced NO-liberation NO - re le as e x -fo ld 1 .5 S -allylc ys te ine D iallyl d is ulfid e A llylm e thyl-S O 2 A llic in A llylm e thyl-s ulfid e A llyl-m e rc ap tan 1 .0 0 .5 0 .0 CN 10 µM 100 µM G arlic c o ns titue nts NO - re le as e 1 .2 5 x-fold 1 .0 0 S pain 2000 0 .7 5 F ranc e 2000 S pain 2001 0 .5 0 F ranc e 2001 0 .2 5 0 .0 0 CN 50 µg/ml P rintanor 500 µg/ml DADS increased NO liberation in HUVEC “1.2” fold. All other tested garlic constituents and metabolites had no effect on NO-liberation Some Garlic extracts even reduced NO-liberation. Garlic and PAI-1 and tPA P rintano r S p ain 2 0 0 1 3000 2000 1000 All garlic extracts – France 2000 0 CN 50 500 TNF 50 µg/m l 500 µg/m l wo . T N F- 5 ng/m l T N F- – France 2001 – Spain 2000 – Spain 2001 P rintano r s p ain 2 0 0 1 * 15 tPA [ng/m l] P A I-1 [ng/m l] *** showed no effect on PAI-1 and tPA liberation in HUVEC 10 5 0 CN 50 500 µg/m l wo . T N F- TNF 50 500 µg/m l 5 ng/m l T N F- Garlic induced cytotoxicity 125 100 * *** *** ** *** A MS O 2 75 A MS O DADS A c t. *** 50 *** 25 . ct A M 10 10 0µ µM M 1µ M 10 0µ µM M 10 1µ M 10 0µ µM 10 1µ C M N 0 125 100 *** *** *** *** 75 F 2000 S 2000 50 S 2001 *** 25 ct A /m µg . l l 0 50 µg /m µg 50 50 µg 0 50 /m l l /m l /m µg 50 0 µg C /m N l 0 50 P ercent P ercent ** *** Only DADS showed a noteworthy effect on cell viability AMSO, AMSO2 and garlic extracts had no cytotoxic effects. Outlook Looking at vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and hypertrophy as a target for antiatherogenic compounds The blood vessel Endothelium Smooth muscle cells Connective tissue Physiological function: Intima Media Adventitia vasoconstriction vasorelaxation Robbins pathologic basis of disease 1999 Vascular smooth muscle cells and their response to injury Endothelium Smooth Migration of smooth muscle cell muscle cells to the mitosis intima Elaboration of extracellular matrix Intima Media Robbins pathologic basis of disease 1999 C: core of lipid; F: fibrous cap; L: llumen, moderately narrowed Robbins pathologic basis of disease 1999 Primary rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) + Serum ? VSMC proliferation DADS Cell cycle, cell signaling Angiotensin II - long-term effects Ang II AT1-Receptor Cell growth Cell migration ECM deposition Growth factor and cytokine production Intimal thickening, vascular remodeling, inflammation Primary rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) + Ang II Hypertrophy ? DADS Cell signaling Relevant publications Haider UGB, Sorescu D, Griendling KK, Vollmar AM, Dirsch VM. Resveratrol suppresses angiotensin II-induced Akt/Protein kinase B as well as p70 S8 kinase phosphorylation and subsequent hypertrophy in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Mol Pharmacol 62: 772-777, 2002 Haider UGB, Sorescu D, Griendling KK, Vollmar AM, Dirsch VM. Resveratrol increases serine15-phosphorylated but transcriptionally impaired p53 and induces a reversible DNA replication block in serum-activated vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Pharmacol, in press