Inhibition of Matrix-Metallo-proteinases by Garlic Compounds
advertisement
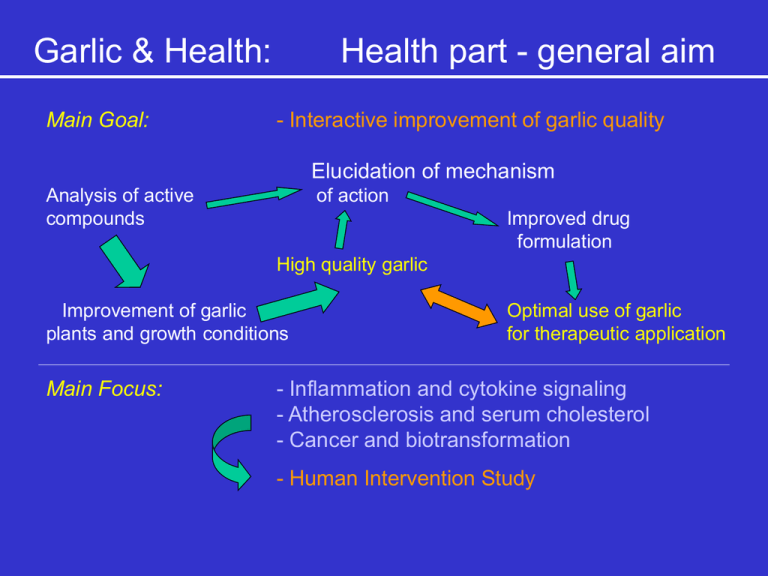
Garlic & Health: Main Goal: Health part - general aim - Interactive improvement of garlic quality Elucidation of mechanism Analysis of active compounds of action Improved drug formulation High quality garlic Improvement of garlic plants and growth conditions Main Focus: Optimal use of garlic for therapeutic application - Inflammation and cytokine signaling - Atherosclerosis and serum cholesterol - Cancer and biotransformation - Human Intervention Study Garlic & Health: Health part Major achievements: • new findings on bioavailability, identification of new metabolites • definition/exclusion of biomolecular mechanisms mainly of single compounds, but also on extracts by using in vitro systems • establishment of a reliable analytics of organosulphur compounds • first evaluation of efficacy of single molecules and extracts in an animal study Garlic & Health: Health part Future focus: • continuation of the work of each workpackage • integration of our new results • efficient and extensive in vivo evaluation • intensification of dissemination of data and major achievements Garlic & Health WP 5.2 Cholesterol and vessel wall WP 5.2 Cholesterol and vessel wall Milestones: Characterization of the interaction of organosulphur compounds (DADS and AM) with cholesterol metabolism Studies on garlic with different sulphur fertilization Interactions of garlic flavonoids with cholesterol biosynthesis and signal transduction pathways Production of matrix metalloproteinases and inhibitors (TIMP) by endothelial cells under the influence of organosulphur compounds. Mechanisms of Arteriosclerosis Serum Cholesterol MMPs + TIMPs Inhibition of Matrix-Metalloproteinases by Garlic Compounds K. Meyer and R. Gebhardt Institute of Biochemistry University of Leipzig Pathological Implications of MMP-TIMP-Imbalance: MMP TIMP Morphogenesis, Differentiation, Wound healing, etc. TIMP MMP Arteriosclerosis Arthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis Inflammation Tumour-Growth -Metastasis -Angiogenesis Ulcers Parodontosis MMP TIMP Fibrosis Diabetic Nephropathy Glomerulosclerosis Scleroderma Spectrum of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMP-1 in cultured HUVEC cells. After 9 h of cultivation. Induction of MMPs and TIMP-1 in HUVEC cells 9 / 24 h after PMA, forskolin and TNF-alpha Spectrum of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMP-1 in cultured HCAEC cells. After 9 h of cultivation. Induction of MMPs and TIMP-1 in HCAEC cells 9 h after PMA, forskolin and TNF-alpha Inhibition of MMP-2 Production in HUVEC by DADS, AM and SAC Activity assay MMP-1 and MMP-3 are not affected by DADS, AM and SAC in HUVEC cells ELISA Inhibition of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 Production by DADS, AM and SAC HUVEC stimulated with PMA, forskolin and TNF-alpha MMP-9 (activity assay) - Unstimulated HUVEC cells do not secrete MMP-9 - In the case of TIMP-1 unstimulated cells respond similarly TIMP-1 (ELISA) Inhibition of MMP-1 Production in HCAEC by DADS, AM and SAC (HCAEC stimulated with TNF-alpha, forskolin and PMA) (HCAEC unstimulated) Inhibition of TIMP-1 Production in HCAEC by DADS, AM and SAC (HCAEC stimulated with TNF-alpha, forskolin and PMA) (HCAEC unstimulated) Influence of MOR-200 on MMP-9 and TIMP-1 Production by HUVEC cells MMP-9 Activity Assay (HUVEC stimulated with TNF-alpha, forskolin and PMA, 24 h) No response of HUVEC to the garlic extract MOR-200 below cytotoxic concentrations TIMP-1 ELISA Cytotoxicity (MTT) Inhibition of MMP-2 Production by different garlic extracts (MOR-200; MES-200; PRI-200; PRI-0) (unstimulated HCAEC cells) RESULTS: - Inhibtion is stronger in HCAEC than in HUVEC cells - only slight differences between garlic extracts with different fertilization Summary: • DADS is able to inhibit the production of several MMPs and of TIMP-1 by endothelial cells • HCAEC cells are more sensitive to DADS than HUVEC cells • AM and SAC are less potent than DADS • Garlic powders do not affect HUVEC cells but exert an inhibition of MMP production in HCAEC cells • so far no significant influence of garlic fertilization Final conclusion: • Garlic preparations may potentially influence the MMP-TIMP balance in certain endothelia