Sex Linkage and Polygenic
Inheritance
Higher Human Biology
Lesson Aims
• To revise sex chromosomes
• To examine effects of sex-linked genes
• To look at polygenic inheritance
Normal Body Cells
• In the nucleus of every
body cell there are 46
chromosomes
• 22 homologous pair
and one pair of sex
chromosomes
Female and Male Sex Chromosomes
Red Green Colour Blindness
• Inability to distinguish
between red and green
• A red green colour
blind person does not
see the number 29 on
the right
• In humans normal
vision is completely
dominant to red-green
colour blindness
Genetics of Colour Blindness
•
•
•
•
Normal vision C
Red-green colour blindness c
Heterozygous females are called carriers
Work out the genotypes of the following
family tree
Answers
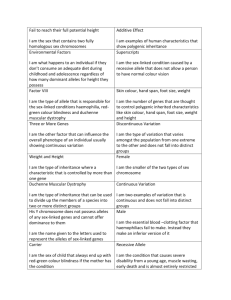
• Carrier mother XCXc
• Nomal father XCY
•
•
•
•
Normal daughter XCXC
Carrier daughter XCXc
Normal son XCY
Colour-blind son XcY
Haemophilia
• Haemophiliacs cannot
make the blood
clotting protein Factor
VIII.
• It caused by a
recessive allele carried
on the X but not the Y
chromosome
• Hence is sex-linked
Family Tree of Haemophilia
Muscular Dystrophy
• Skeletal muscles loose
their normal structure
and fibrous tissue
develops in their place
• Caused by a recessive
allele carried on the X
chromosome and is
sex-linked
Family Tree of Muscular Dystrophy
Polygenic Inheritance
• Polygenic inheritance is a characteristic showing
continuous variation and is controlled by the
alleles of more than one gene
• The more genes involved the more intermediate
phenotypes that can be produced
• The effects of the genes are additive (each
dominant allele of each gene adds a contribution
towards the characteristic controlled by the gene)
Polygenic Inheritance
Polygenic Inheritance in Humans
• Examples include skin
colour, height, weight
Polygenic Inheritance in Humans
Effect of Environment
• Many of these characteristics are influenced
by the environment.
• Polygenic inheritance + environmental
factors = phenotypic characteristic which
shows a wide range of continuous variation
and a normal pattern of distribution.
Facts you need to know
• P6 from “sex-linked genetics problems…”
• to p7 “weight or height or skin colour…”


![[11.1,11.2,11.3] COMPLEX INHERITANCE and HUMAN HEREDITY](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006715925_1-acaa49140d3a16b1dba9cf6c1a80e789-300x300.png)