Higher Biology
advertisement

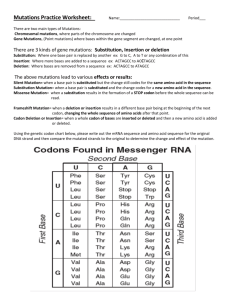
Higher Biology Chapter 16 Gene Mutations Gene Mutations • This type of mutation involves a change in one or more of the nucleotides in a strand of DNA. • There are four types of gene mutation: • 1. Substitution of a nucleotide. • 2. Inversion of two or more nucleotides. • 3. Deletion of a nucleotide. • 4. Insertion of a nucleotide. • In all of these cases one or more codons for one or more particular amino acids have become altered. • This in turn leads to a change in the protein which is synthesised. • For a protein to work properly it must have the correct sequence of amino acids. Gene Mutations • This type of mutation involves a change in one or more of the nucleotides in a strand of DNA. • There are four types of gene mutation: • 1. Substitution of a nucleotide. • 2. Inversion of two or more nucleotides. • 3. Deletion of a nucleotide. • 4. Insertion of a nucleotide. Substitution Gene Mutations • This type of mutation involves a change in one or more of the nucleotides in a strand of DNA. • There are four types of gene mutation: • 1. Substitution of a nucleotide. • 2. Inversion of two or more nucleotides. • 3. Deletion of a nucleotide. • 4. Insertion of a nucleotide. Inversion of Two or More Nucleotides “Point” Mutations • Substitution and inversion are known as “point” mutations. • These bring about minor changes as only one amino acid is affected. • Sometimes the organism is affected slightly or not at all. • However when the substituted amino acid occurs at a critical position in the protein then a major defect may arise. (Sickle cell anaemia) Gene Mutations • This type of mutation involves a change in one or more of the nucleotides in a strand of DNA. • There are four types of gene mutation: • 1. Substitution of a nucleotide. • 2. Inversion of two or more nucleotides. • 3. Deletion of a nucleotide. • 4. Insertion of a nucleotide. Deletion of a Nucleotide Gene Mutations • This type of mutation involves a change in one or more of the nucleotides in a strand of DNA. • There are four types of gene mutation: • 1. Substitution of a nucleotide. • 2. Inversion of two or more nucleotides. • 3. Deletion of a nucleotide. • 4. Insertion of a nucleotide. Insertion of a Nucleotide ‘Frameshift’ Mutations • Insertion and deletion gene mutations are known as ‘frameshift’ mutations. • These mutations lead to major changes as they cause a large portion of the gene’s DNA to be misread. • The proteins produced differ from the normal proteins by many amino acids and tend to be nonfunctional. • If these proteins are enzymes which catalyse essential steps in the metabolic pathway, the pathway will become disrupted. (PKU) Gene Mutations • Since most proteins are indispensible to the organism, most gene mutations produce an inferior version of the phenotype. • If these changes result in death (eg. albino plants) then the altered gene is said to be lethal.