Slides on inteins
advertisement

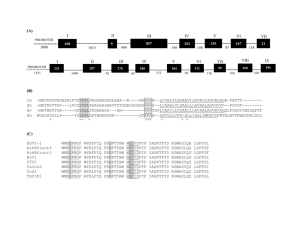
Mural at NASA Ames Research Center Homing Endonucleases Sequence nearly identical to the carrot vma1 gene – except for central region of about 1200 nucleotides. Homing Ribonucleotide Reductase Intein Group I Introns Group II Introns Inteins Group I Introns Group II Introns Homing cycle of a parasitic genetic element (modified from [3, 13]). Recent findings suggest that due to complex population structure the cycle might not operate in synchrony in different subpopulations. The red arrows indicate the trajectory of the functioning HE and the black arrows the fate of the host gene. The precise loss can occur through recombination with an intein or intron free allele, or, in case of introns, through recombination with a reverse transcript of the spliced mRNA [39, 40]. From: Gogarten et al., Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002. 56:263–87 X Alleles with empty Target Site Y Alleles harboring a dysfunctional Homing Endonuclease Y>Z (II) Carriers of the Y-allele are more fit than carriers of the Z allele. The presence of a dysfunctional homing endonuclease provides immunity to invasion by Z Z Alleles invaded by a functional Homing Endonuclease Long term persistence of the HE containing allele is possible within a single well mixed population. Different trajectories result depending on the size of the selective disadvantage caused by the functioning HE and the frequency of efficient homing. Collaboration with Adi Barzel, Uri Obolski, Martin Kupiec, Lilach Hadany from Tel Aviv University