MICROBIOLOGY
advertisement

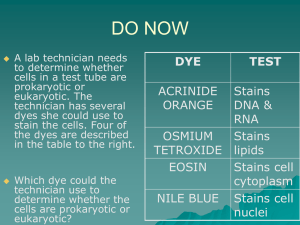
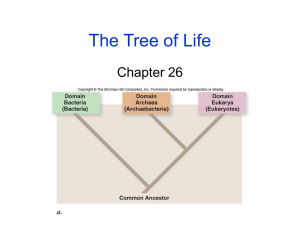
MICROBIOLOGY Nur Hidayat http://nurhidayat.lecture.ub.ac.id Microbiology The branch of biology concerned with the study of microorganisms and their activities Microorganisms can be: unicellular multicellular acellular – viruses – viroids – prions-proteinaceous infectious particle Occurrence of Microorganisms air we breathe food we eat on the human body – Only 1 in 10 cells of the body is human, the rest are microbial – A square centimeter of skin holds about 100,000 microbes – Humans are free of microbes until they pass through the birth canal environments – extreme Activities of microorganisms Destructive – Disease-EIDs (emerging infectious diseases) – Food spoilage – Eutrophication Beneficial Activities – Foods - SCP (single cell protein) – C, N, S, P cycles – Decomposition – Genetic engineering (recombinant DNA technology) – Bioremediation Bioremediation - use of microbes to remove an environmental pollutant Eutrophication - the nutrient enrichment of large aquatic habitats caused directly or indirectly by human activities Haeckel’s 3 Kingdoms Plant Animal Protista Eucaryotes vs Procaryotes Eucaryotes True nucleus – nuclear membrane – more than 1 chromosome – chromosome replicated by mitosis – membrane-bound organelles ex. algae, fungi, protozoa, plants, animals Eucaryotic Cell Procaryotes Nuclear area (nucleoid) – no nuclear membrane – 1 chromosome – no mitosis – ribosomes are the only membranebound organelles ex. bacteria (rickettsia, blue-green algae), archaea Procaryotic Cell Major Groups of Microorganisms Algae Fungi Protozoa Bacteria Archaea Viruses Description of Each Eucaryotes or procaryotes? Unicellular, multicellular or acellular? Importance Field of study Algae Eucaryotes Unicellular & Multicellular Producers Phycology Unicellular Alga Multicellular Alga Kelp Fungi Eucaryotes Multicellular except yeasts Decomposers Mycology Multicellular Fungi Amanita muscaria Unicellular Fungi Protozoa Eucaryotes Unicellular Free-living or parasitic Protozoology and Parasitology – protozoology - study of protozoa – parasitology - study of pathogenic protozoa & multicellular parasites (worms) Protozoa classified by means of motility Amoeba - pseudopods ex. Entamoeba histolytica - amebic dysentery Flagellates - flagella ex. Giardia lamblia - giardiasis Ciliates - cilia ex. Paramecium Sporozoa - nonmotile ex. Toxoplasma gondii - toxoplasmosis ex. Plasmodium - malaria Amoebas Amoeba Entamoeba histolytica Amebic dysentery Flagellate Giardia lamblia Giardiasis Ciliate Balantidium coli Sporozoa At least one million deaths per year worldwide http://www.cdc.gov/Malaria/impact/index.htm Sporozoa Toxoplasma gondii Toxoplasmosis http://www.cdc.gov/toxoplasmosis/epi.html Bacteria Procaryotes Unicellular Photosynthesis, decomposition, parasites, biogeochemical cycles Bacteriology Gram Positive Staphylococcus Gram Negative Escherichia coli Archaea Procaryotes Unicellular Lack typical bacterial cell wall Live in extreme environments – methanogens - produce methane – extreme thermophiles – extreme halophiles Importance - geochemical cycles Bacteriology Rickettsia Procaryotes Unicellular Obligate intracellular parasites Transmitted by insects & ticks ex. Rickettsia rickettsii - Rocky Mtn. Spotted fever Bacteriology Viruses Composed of nucleic acid + protein coat Obligate intracellular parasites Latency Virology Adenovirus Bacteriophage Immunology The study of the resistance of the living body to disease producing organisms and the reactions of living tissues to foreign substances •Resistance to disease •Vaccines •Allergies •Transplantation