DNA REPAIR
advertisement

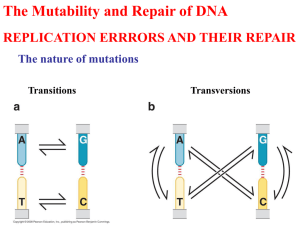
DNA REPAIR DNA REPAIR DNA is the only biological molecule that is repaired DNA damage Alteration to the chemical structure of DNA Mutation Change in the sequence of DNA NATURE OF DNA DAMAGE Loss of bases Modification of bases Inter/intra-strand crosslinks DNA strand breakage (single and double strand) CAUSES OF DNA DAMAGE Endogenous factors Spontaneous - Errors in proofreading - Deamination of bases - Depurination/Depyrimidination Induced - Byproducts of normal cellular processes (reactive oxygen species etc ) Exogenous factors - UV irradiation (sunlight) - High energy irradiation (x-rays) - Mutagenic chemicals (Mustard gas, cigarette smoke, food additives) ERRORS IN PROOFREADING Incorporation of the wrong base/s resulting in mismatches Approximate error rate = 10-9 DEAMINATION May be spontaneous or induced by chemicals Cytosine Adenine Guanine Thymine Uracil Hypoxanthine Xanthine ?? DEAMINATION • Deamination leads to unusual base pairing in DNA - Uracil pairs with adenine - Hypoxanthine pairs with cytosine FAILURE TO REPAIR A DEAMINATED BASE = A POINT MUTATION Parental strand C T U T C Mutation Deamination GA A AG New strand C T U C T C DNA Replication GAGAG New strand C T C T C Unchanged GAGAG Parental strand DEPURINATION/ DEPYRIMIDINATION • Cleavage of the glycosidic bond removes bases C T C T C GAG G – Abasic (Apurinic/apyrimidinic, AP sites) – ~2000-10,000 purines lost per mammalian cell/24 hr FAILURE TO REPAIR ABASIC SITES = DELETIONS Parental strand C T C T C Unchanged GAGAG New strand C T C T C DNA Replication GAG G New strand C T C C AP site Mutation GAG G Parental strand REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES Generated during normal aerobic respiration – Superoxides, O2-, . – Hydroxyl ions (OH ) – H2O2 Most biological damage by OH. Guanine 8-oxodG Exogenous – UV IRRADIATION Dimerizes adjacent thymine residues. The dimer creates a kink in the DNA that blocks the progression DNA polymerase HIGH-ENERGY RADIATION X-rays and gamma rays may directly break DNA strands and/or generate reactive oxygen species Exogenous – CHEMICALS • Alkylating agents (e.g., mustard gas) – Add CH3/CH2CH3 groups to N and O groups of bases. – O6 of guanine particularly susceptible. 6-ethyl guanine acts as an analogue of adenine and pairs with thymine. • Polycyclic Hydrocarbons (cigarette smoke, exhaust fumes etc) Exogenous – CHEMICALS • Food Additives – Nitrates and Nitrites – Metabolized to Nitronium ion/Nitrous acid • Chemotherapeutic drugs – Base Analogues (e.g. 5-bromouracil, 5BU) • Intercalating Agents – Acridine dyes (e.g., proflavin) – Interfere with DNA replication THE CELL CYCLE ☺ METHODS OF REPAIR ☺ Excision repair - Base excision - Nucleotide excision ☺ Mismatch repair ☺ Recombination repair EXCISION REPAIR Recognition of damage Removal of damage Resynthesis of gap Ligation EXCISION REPAIR Two types of excision repairs • Base Excision Repair Repair of methylated, deaminated, oxidized bases and AP sites. • Nucleotide Excision Repair Repair of large adducts or distortion in the double helical structure of DNA (pyrimidine dimers, benzo(a)pyrene) BASE EXCISION REPAIR Glycosylase AP Lyase endonuclease DNA polymerase DNA ligase NUCLEOTIDE EXCISION REPAIR Thymine dimer urvAB excinuclease A B A urvC excinuclease A B A DNA polymerase DNA ligase No thymine dimer NER ASSOCIATED DISEASES • Xeroderma pigmentosum • Cockayne Syndrome • PIBIDS (photosensitivity, ichthyosis, brittle hair, impaired intelligence, decreased fertility, short stature) - Characterized by an increased sensitivity to sunlight Vignette 12 A 3-year-old boy, was referred to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of severe sun sensitivity and freckling. On physical examination, he was photophobic and had conjunctivitis and prominent freckled hyperpigmentation in sun-exposed areas; his development and physical examination were otherwise normal. The parents of the child revealed that they were first cousins; no one else in the family was similarly affected. The dermatologist explained that the boy had classic features of xeroderma pigmentosum (XP), that is, "parchment-like pigmented skin". To confirm the diagnosis, he had a skin biopsy to evaluate DNA repair and ultraviolet (UV) radiation sensitivity in his skin fibroblasts. The results of this testing confirmed the diagnosis of XP. Despite appropriate preventive measures, the boy developed metastatic melanoma at 15 years of age and died 2 years later. His parents had two other children; neither was affected with XP. XERODERMA PIGMENTOSUM • Can be caused by defects in any one of seven different NER genes – Predisposition to skin cancer – Pigmentation abnormalities – Premalignant lesions – Degeneration of the nervous system ☺ EXCISION REPAIR • Base excision repair • Nucleotide excision repair – Repair of modified bases – Glycosylase removes base, leaves backbone intact – AP endonuclease cut backbone, AP lyase removes sugar – Repair of adducts and large distortions in DNA double helix – Double excision removes damage as an oligonucleotide (12-13 nt in E. Coli, 27-29 nt in humans) DNA polymerase fills gap DNA ligase seals nick ☺ Mismatch repair • Repair of replication (proofreading) errors • Recognition of bases that do not form normal Watson-Crick pairs ☺ Mismatch repair • How do the repair enzymes recognize which strand to fix??? CH3 ? CH3 AGA T C T C T T CGA T C x T C T AGAG C AGC T AG ? ☺ Mismatch repair CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 MutS/MutL MutH DNA Polymerase CH3 CH3 DNA Ligase CH3 CH3 HEREDITARY NONPOLYPOSIS COLORECTAL CANCER (HNPCC) • Lynch syndrome • Accounts for 2 -10% of all colon cancers • Caused by defects in mismatch repair genes MSH2, MSH6, MLH1, PMS1 or PMS2 DNA STRAND BREAKS DNA STRAND BREAKS • 10 -100 naturally occurring double-strand breaks per cell per day • Two mechanisms for repair – Homologous recombination repair (HRR) – Nonhomologous recombination repair (NHRR) Homologous recombination repair (HRR) Nonhomologous recombination repair (NHRR) HRR Vs. NHRR HRR • Identical copies made NHRR • Small deletions occur • Only possible in the • Any time in the S and G2 phase of cell cycle the cell cycle Defects in DNA-repair systems associated with certain cancers The End!