Viruses & Bacteria
advertisement

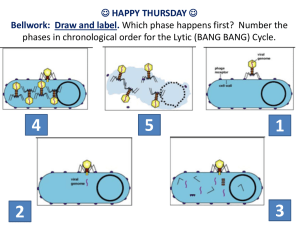
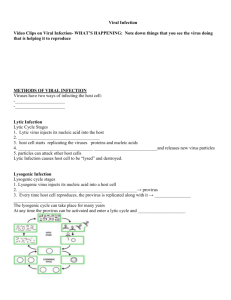
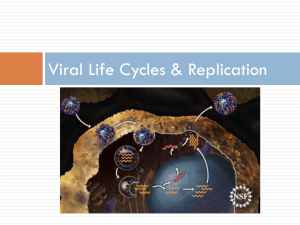
Viruses Chapter 18 Pg 489-499 This Powerpoint is hosted on www.worldofteaching.com Please visit for 1000+ free powerpoints What are Viruses A virus is a non-cellular particle made up of genetic material and protein that can invade living cells. Non-living= doesn’t carry out respiration, grow, develop, or reproduce on its own Living cells used in replication = host cells Naming Viruses Viruses are not named like living organisms, i.e. using binomial nomenclature. Named after: the disease it causes (ex. Rabies, polio) named after the person(s) who discovered them after tissue they infect (ex. Adenovirus infects adenoid tissue…common cold) Some given a genus and species name or code number T4 Bacteriophage Bacteriophage a virus that infects bacteria. The Structure Of a Virus a core of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) Nucleic acid core is surrounded by a protein coat (capsid) Some viruses have additional envelope (made of cell membrane parts) ex. Human flu THE END Viruses come in many shapes and sizes •Protein arrangement determines shape • Shape determines cells that can be infected (page 491) The Influenza Virus! 1918 Influenza or Spanish flu Protein. Common flu structure Spanish Flu continued http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/sciencenow /video/3318/q02-220.html What does all this mean…? Viruses use Host Cell to Replicate Virus recognizes and attaches to host cell Each virus has specifically shaped proteins that interlock with receptor sites on host cell Viruses are mostly species specific or cell type specific • Smallpox is said to be eradicated because it is human specific • Flu is not human specific Viral Replication Virus inject nucleic acid into cell A virus can have two different cycles of replication: lytic and lysogenic Viral Replication Cycles: Lytic Cycle Lytic Cycle Analogy A. Virus attaches to cell B. Nucleic Acid is injected into cell C. Host cell makes viral nucleic acid and proteins D. New virus particles are assembled E. Host cell breaks open to release new virus particles 1. An army tank (virus) filled with enemy troops (nucleic acid) 2. Crashes through the wall of an automobile factory (host cell) 3. Troops take over factory’s machinery (nucleus) and adapt them to make new tanks (viruses) instead of cars (cell parts) Viral Replication Cycles 2: Lysogenic Lysogenic Cycle A. Virus attachment and entry into cell B. Viral nucleic acid becomes part of host’s chromosomes (provirus - viral DNA that is part of the host cell’s chromosomes) C. Viral nucleic acids are replicated during chromosome replication At some point it will enter lytic cycle Lytic vs. Lysogenic Examples Lytic = Measles, cold viruses Lysogenic = shingles, warts, HIV Disease Symptoms of provirus's Cold sores – herpes simplex I virus - virus remains in cells as provirus, when enters lytic cycle, new cold sore erupts • Possible triggers for activating lytic cycle = physical stress (ex. Sunburn), emotional stress (ex. Anxiety) • Chicken pox…later becomes shingles Release of viruses Lysis – bursting of cell Exocytosis Cycle of Lytic and Lysogenic Flu viruses are spread mainly from person to person through: coughing, sneezing or talking by people with influenza. Sometimes people may become infected by touching something – such as a surface or object – with flu viruses on it and then touching their mouth or nose. Vaccines Viruses grown on chicken embryos are attenuated vaccines Another type of vaccine is made by heat “killing” the virus These non-harmful forms of virus are injected into body so that the body can learn how to defend itself Retrovirus Nucleic Acid is RNA (not DNA) Once RNA is injected into host cell, it will make viral DNA with help from an enyzme (reverse transcriptase) Viral DNA becomes a provirus (page 495) HIV = infection of white blood cells Infected host cells function normally – provirus No symptoms – can still transmit virus in body fluids White blood cells will be lost when provirus enters lytic cycle Immune system is compromised HIV Info HIV becomes AIDS when the number of immune cells drops below a predetermined number No one dies from HIV or AIDS; people die from secondary infections (ranging from the common cold to cancer) More than 3 million people (size of Chicago) die each year There are approx. 14,000 new cases of HIV worldwide every day Viruses and Cancer Retroviruses may cause cancer - Normal cells become tumor cells DNA viruses, papilloma virus (HPV) and hepatitis B virus may cause cancer