Lecture
advertisement

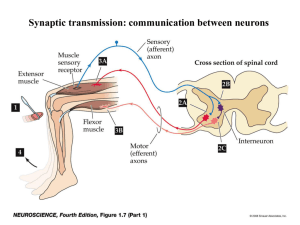
Laboratory course: Model organism C. elegans Week 4: 1. 2. 3. 4. What is trafficking? How is cargo transported? Motor-cargo specificities Studying trafficking using kymograph analysis 王歐力 助理教授 Oliver I. Wagner, PhD Assistant Professor National Tsing Hua University Institute of Molecular & Cellular Biology College of Life Science Trafficking in C. elegans neurons Vesicles and mitochondria move along actin or microtubule tracks attached to molecular motors as myosins, kinesins and dynein v20-02-vesicle_transport.mov + - -+ Axonal transport of vesicles • Synaptic vesicles and mitochondria are transported via kinesins from the cell body of the neuron to the termini (growth cone) • The molecular motor dynein transports them back Mitochondria synaptic vesicle + (growth cone) Mitochondria are the energy factories of the cell 3D EM image of a mitochondrion (computer-generated from series of 2D EM images) Model of kinesin-based vesicle transport • Kinesins bind via their motor domain to microtubules while the tail (cargo) domain is connected to the vesicle • The vesicle connection is mediated by kinesin receptor proteins (linker proteins) Kinesin receptor control cargo attachments Axon Dendrites Hirokawa and Takemura, 2005, Nat Rev Neurosci. Kinesin superfamily proteins (KIF) • KIF1A is a monomeric kinesin: in C. elegans it is called UNC-104 • It is the main synaptic vesicle transporter in neurons The mechanisms of kinesin I movement on microtubules is well known Cargo-binding Motor 16_7.mov KIF1A knockout mice: defect in synaptic precursor transport and neuronal cell death • Reduction in the density of synaptic vesicles in nerve terminals, accumulation of vesicles in the cell body • KIF1A plays a critical role in the development of neuropathies resulting from impaired axonal transport WT (Yonekawa, JCB, 1998) wt/kif1a kif1a/kif1a Dynein alone cannot attach to vesicles or mitochondria: it needs another “helper” named dynactin DYNACTIN DYNEIN MT binding HC contains AAA domains Dynein moves cargo backwards Dynactin is an adaptor to connect dynein to the vesicle and the microtubule + Vesicle Joseph Roland 2002 The motor toolbox for intracellular transport • Motor domains = blue • Cargo binding domains = purple Dendritic vesicles Axonal vesicles Backward transport Vale, 2003, Cell Synaptic vesicles move bidirectional: coordinated activity of antagonistic motors? Taken from: Cell Biology, Pollard & Earnshaw … or tug-of-war between antagonistic motors? Determination of motor activity by analyzing motility of UNC-104::GFP particles • bidirectional • velocity of 1 μm/s • fast axonal cargo transport - movie length about 5 min. - width of neuron about 150 nm Living worm A Kymograph is the translation of a moving spot, on a line in one direction, into a two dimensional projection area with time and distance. movie Kymograph The „paper“ is continuously moving. A stable spot in the axon remains as a line on the “paper”. t x A moving spot will leave an individual trace on the „paper“. => with time and distance we can calculate velocity, pausing, run length etc. Translation of a particle movement from a movie-sequence into a kymograph Example of data evaluation using the kymograph technique All Particles unc104(ok217) cells Velo. w/o pauses (µm/s) Total run length (µm) Change direction per 100 s Change direction per 10 µm Pausing per 100 s Pausing per 10 µm Pausing duration (s) Persis. of mov. at uni. velo.(s) # Events # Anterograde movements # Retrograde movements # Unidentified movements # Axons # Dendrites # Commissures # Unidentified # Particles # Movies Pause Calibration Ave. (s) Velocity due to particle size Counts: 7 Large STDEV+/- Medium Aver. 0,39 0,13 L versus M L vers. S T-Tests 0,19 0,43 5,47 4,12 2,06 2,19 1,44 16,45 9,00 490 25 30 7 25 0 0 0 62 25 0,062 21 STDEV+/- Antero STDEV+/0,19 0,32 0,13 3,56 5,19 3,00 2,53 4,37 2,37 1,26 2,34 1,18 1,16 1,98 0,73 1,03 1,36 0,87 7,16 19,37 9,78 3,37 7,85 2,56 245 Events neither antero nor retro: 45 % antero 57 55 % retro 43 Retro STDEV+/0,47 0,17 5,94 3,84 4,09 2,79 1,94 1,37 2,54 1,61 1,68 1,31 14,68 7,90 9,62 3,69 186 59 % antero events % retro events 32 STDEV+/- Small STDEV+/0,30 0,14 0,48 0,22 M vers. S 0,18 0,001 Velos of particles with no CD and one event only (linear and directed movements) Aver. 0,62 STDEV+/0,26 Aver. 0,34 STDEV+/T-Test 0,0017 0,12 In living worms In primary C. elegans neurons Current research example Isolated primary C. elegans neurons