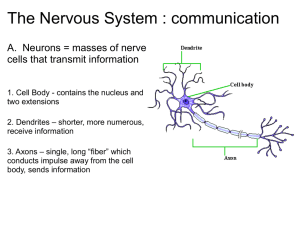
背腹軸の決定と普遍性
advertisement

Brain Development and Evolution Genetic Factors Underlie Human Behaviors Genes Neurons Networks Behaviors Neuroscience The goal of neural science is to understand the mind – how we perceive, move, think, and remember. Eric Kandel Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2000 Behavior can be examined at the level of individual nerve cells by answering five basic questions. 1. How does the brain develop? 2. How do nerve cells in the brain communicate with one another? 3. How do different patterns of interconnections give rise to different perceptions and motor acts? 4. How is communication between neurons modified by experience? 5. How is that communication altered by diseases? Development of Vertebrate Neural Tube Neural plate Ectoderm Mesoderm Endoderm Neural groove Paraxial mesoderm Neural tube Paraxial mesoderm Lateral plate mesoderm Somite Endoderm Notochord Early Development of the Vertebrate Central Nervous System Hox Genes are Expressed in the Developing Neural Tube Hox b2 Hox b4 The HOM/Hox Gene Clusters Hindbrain is Segmented by Hox Genes r1 r2 r2 Segmental Expression of Hindbrain Patterning Genes Hox genes Hoxb-1 Hoxb-2 Hoxb-3 Hoxb4 Other transcription factors Kreisler Krox20 Eph kinases Ephrins EphA4 EphA2 EphB2 EphB3 Ephrin B1 Ephrin B2 Ephrin B3 r3 r3 r4 r5 r6 r7 r4 r5 r6 Somatic motor nuclei Oculomotor nerve (III) Visceral motor nuclei Midbrain Trochlear Nerve (iV) Segmental Development of the Hindbrain Motor Neurons Hindbrain r1 r2 Trigeminal Nerve (V) r3 r4 Abducens Nerve (VI) Facial Nerve (VII) r5 r6 Grossopharyngeal Nerve (IX) r7 Hypoglossal Nerve (VII) r8 Vegus, spinal accessory Nerve (X, XI) Mutation of Hoxb-1 Causes Homeotic Transformation of the Hindbrain Motor Neurons r2 v.s. r4 neurons Wild type Trigeminal nerve exit point Trigeminal motor neurons Trigeminal motor neurons r2 r2 Facial nerve exit point Hoxb-1 Mutant r3 r4 r5 r6 Facial motor neurons r2 Trigeminal-like motor neurons r4 Hoxb-1 r4 r2 HOM/Hox Genes Fail to Cover the Most Anterior Region of the Central Nervous System. What Kind of Genes Specify the Brain?? The Drosophila Central Nervous System is Segmented Green dots: cells expressing Engrailed, a segment-polarity gene Confocal micriscopy image of a fly embryo at stage 14 ショウジョウバエ胚における分節遺伝子 engrailedの発現 Fruit Fly Brain at Stage 14 (10 hours) Green: neurons. Red: Brain Specific Homeobox Protein. Blue:major axonal tracts stained with anti-FAS II Homeobox-Containing Genes, otd and ems, Control Segmental Organization of the Embryonic Fly Brain otd/Otx and ems/Emx Genes Control the Formation of the Vertebrate Brain Genetic Programs of Brain Development are Evolutionary Conserved between Flies and Vertebrates Structures of Drosophila, Human and Ascidian otd/Otx Genes タンパク構造の比較 ホメオドメインのアミノ酸配列の比較 Human Otx Gene Restores Brain Patterning in Drosophila otd Mutant The Drosophila otd Genes Restores Brain Patterning in Mouse Otx Mutants Otx-/WT Genetic Rescue with Fly otd gene WT Otx-/- Rescue with Fly otd gene Cross-Phylum Conservation of Major Axonal Tracts between Flies and Vertebrates Drosophila Zebrafish Inversion of Dorso-Ventral Patterns between Protostomes and Deuterostomes Arthoropods Vertebrates Despite the Apparent Inversion, Genetic Programs of Brain Development is Evolutionary Conserved Common Origin of the Animal Brain Neuroscience Text Books • Principles of Neuroscience, 5th ed. 2012, Kandel, E. R., Schwartz, J. H., Jessel, T. M., Siegelbaum, S. A., and Hudspeth, A. J., McGrae Hill. • Physiology of Behavior, 10th ed, 2009, Carlson, N. R. , Allyn & Bacon. カールソン 神経科学テキスト 脳と行動、 2010、丸善。 • Fundamental Neuroscience, 3rd ed, 2008, Squire L.R et al., Academic Press. Neuroscience Focuses on Molecular Genetic and Behavioral Problems Fundamental Neuroscience 53 Chapters Electrophysiology 3 Genes and Molecules 51 Behavior and Cognition 10 シリーズ脳科学 東京大学出版会 • • • • • • 第1巻 第2巻 第3巻 第4巻 第5巻 第6巻 脳の計算論 認識と行動の脳科学 言語と思考を生む脳 脳の発生と発達 分子・細胞・シナプスからみる脳 精神の脳科学 • 新・脳の探検、上下、ブルーバックス. • 記憶と情動の脳科学、ブルーバックス. • 私の脳科学講義、利根川進、岩波新書. ショウジョウバエ胚の脳(レーザ共焦点顕微鏡画像) Eyeless &Twin of Eyeless