Jay_21Mar2013

Functional Neuro-anatomy of the Visual System:
A Coarse Course
Jay Hegdé
How to Learn (Visual) Neuroanatomy
I. Distinguish 3-D structure from connectivity
II. Keep in mind that not all structures have
(known) functions – biological structures are evolved, not designed.
III. Mind your Greek/Latin
Section I. Anatomy of Various Visual Structures
Developmental Bases of Neuroanatomy
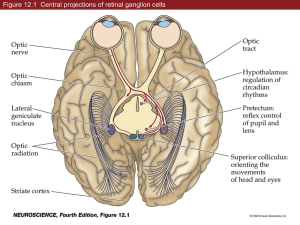
Since the early visual system is anatomically highly ordered, visual field mapping can be highly useful in neuro-ophthalmological diagnosis.
Early Visual Pathway Closer view of the Optic Chiasm
Clinically Important:
Anatomy of Visual System Can be Highly Variable!
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) of Two Healthy Adults
Optic Nerve is Fundamentally Similar to Most Other Sensory Cranial Nerves
In humans, the optic nerve contains 38% of all the axons connecting to the brain.
Mnemonic:
“ O n O ld O lympus' T owering T op, A F riendly V iking G rew V ines A nd H ops”
Human Brain: Ventral View
L ateral G eniculate N ucleus ( LGN )
(Tortured) Mnemonic:
C-I-I-C-I-C
“ S ee I ? I S ee, I S ee”
C = contralateral
I = ipsilateral
Functional Organization of Macaque Visual Cortex
Van Essen et al (1992)
Cortex has a laminar, canonical structure
Courtesy of David Hubel
A closer look at the laminae
Neocortical Layers (Total thickness ~1mm)
Opercular V1
Nissl stained
Courtesy of
David Hubel
Ocular Dominance Columns in V1
Probably a structure without a function
Cytochrome Oxidase ‘Blobs’
Area 17 of the cat / Layers 2 & 3
Scale bar = 2 mm
Arrow: relieving cut
Another structure without a function? (Hmm…)
Some Facts and Figures about Macaque Visual Cortex
• Total cortical surface area: ~100 cm 2
• Total surface area of visual cortex: ~ 50 cm 2
• ~35 visual areas, ~25 primarily visual
• 323 known anatomical pathways; ~33% connectivity
• ~75-85% of visual cortical neurons are pyramidal cells
* Glutamatergic (thought to be always excitatory)
* ~10 4 synapses/cell
• 250,000 neurons/mm 2 in V1;
100,000 neurons/mm 2 elsewhere
• 10 billion axons in the white matter
* ~10-20 million connect with nuclei outside the cortex
* ~ 98.6% of the axons are intra-hemispheric
* Corpus callosum contains ~100 million axons
Molecular Cognitive Science is Here Already !
Molecular pathways of plasticity in the visual cortex
Daw (2004)
Section II. Connectivity
Functional Organization of
Macaque Visual Cortex
How are visual cortical areas distinguished from each other?
F unction
A natomy
C onnectivity
T opography
Felleman and Van Essen (1991)
Hegdé & Felleman (2007)
Marr (1982) Model of Visual Processing
3D
Sketch
Object-level representation
2.5D
Sketch
Primal
Sketch
Image
Surface-level representation
Local primitives (e.g., edges)
Early ‘Feed-forward’ Visual Pathways
Pyramidal Cell: The Workhorse of the Cerebral Cortex (‘Relay’ Neuron)
Stellate Cell: Most Common Interneuron (‘Crosstalk’ Neuron)
Inputs and Outputs of Sensory (Especially Visual) Cortex
From Crick (1995) [still largely current]
How known cortical connections join the layer 6→4 and layer 2/3 building blocks to form the entire V1/V2 laminar model.
Raizada R D S , and Grossberg S Cereb. Cortex
2003;13:100-113
Development of Visual Connectivity in the Macaque
Feed-forward Connections Develop Earlier Than Feedback Pathways
Kennedy and Burkhalter (2004)
Section III. Functional Organization
What Happens to the Visual Information Once It Gets to the Cerebral Cortex?
MST
MT
7a
Area V1
Area V4
Area AIT
Macaque visual system
(Human visual system is fundamentally similar)
Visual Pathways in the Monkey
• A popular urban myth : The dorsal and ventral pathways are the magnocellular and parvocellular pathways, respectively. NOT TRUE!
There is Much that We Don’t Know
Olshausen & Field, 2006
This is even more true of other visual areas.