B1510_module4-8_Gene_regulation_questions_2011
advertisement

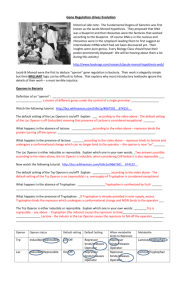
preQ: Under which conditions will E. coli cells express (transcribe and translate) lots of beta-galactosidase? A) B) C) D) E) In medium with glucose as the only sugar In medium with glucose and lactose In medium with lactose as the only sugar In medium with galactose All of the above preQ: If the repressor gene is mutated, so that no repressor protein is made, then a) The lac operon will never be induced b) The lac operon will always be induced c) The lac operon will be induced whenever lactose is present d) The lac operon will be induced whenever glucose is absent e) The lac operon will be induced only when both lactose and glucose are present preQ: What causes induction of the lac operon? A) When repressor binds to the operator, regardless of CAP B) When CAP binds to the promoter, regardless of Repressor C) When Repressor binds to inducer D) When both A) and B) occur E) When CAP binds to the promoter and Repressor is not bound to the operator preQ: In wild-type E. coli cells in medium with glucose, and no lactose: A. CAP binds to promoter B. Repressor binds to operator C. Both CAP and Repressor bind to promoter and operator, respectively D. Neither bind preQ: If a mutation eliminates binding of inducer to the repressor, but the repressor still binds to DNA; A) The lac operon will be always induced B) The lac operon will never be induced C) The lac operon will be induced whenever glucose is absent, regardless of the presence or absence of lactose D) The lac operon will be induced only when both glucose and lactose are present E) The lac operon will be induced only when glucose is present and lactose is absent Lac operon demonstration • Need volunteers for – RNA polymerase – Repressor protein – CAP protein postQ: Under which conditions will E. coli cells express (transcribe and translate) lots of beta-galactosidase? A) B) C) D) E) In medium with glucose as the only sugar In medium with glucose and lactose In medium with lactose as the only sugar In medium with galactose All of the above postQ: If the repressor gene is mutated, so that no repressor protein is made, then a) The lac operon will never be induced b) The lac operon will always be induced c) The lac operon will be induced whenever lactose is present d) The lac operon will be induced whenever glucose is absent e) The lac operon will be induced only when both lactose and glucose are present postQ: What causes induction of the lac operon? A) When repressor binds to the operator, regardless of CAP B) When CAP binds to the promoter, regardless of Repressor C) When Repressor binds to inducer D) When both A) and B) occur E) When CAP binds to the promoter and Repressor is not bound to the operator postQ: In wild-type E. coli cells in medium with glucose, and no lactose: A. CAP binds to promoter B. Repressor binds to operator C. Both CAP and Repressor bind to promoter and operator, respectively D. Neither bind postQ: If a mutation eliminates binding of inducer to the repressor, but the repressor still binds to DNA; A) The lac operon will be always induced B) The lac operon will never be induced C) The lac operon will be induced whenever glucose is absent, regardless of the presence or absence of lactose D) The lac operon will be induced only when both glucose and lactose are present E) The lac operon will be induced only when glucose is present and lactose is absent