Presenting: DNA and RNA
advertisement

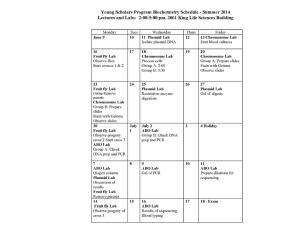
Presenting: DNA and RNA 1 DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic acid 1. It belongs to the class of biochemical molecules known as nucleic acids. 2. It is made up of atoms of : Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Phosphorous 2 Importance of DNA 1. It carries genetic information from one generation to the next. 2. DNA sequences create genes which then determine inherited traits. 3. DNA can be easily copied during the creation of new cells. 3 Where is DNA located? Chromosome DNA double helix Histones 4 Regents Practice Question #1 The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multi-cellular organism. The level represented by X is composed of (1) four types of base subunits (2) folded chains of glucose molecules (3) twenty different kinds of amino acids (4) complex, energy-rich inorganic molecules 5 Regents Practice Question #1(Answer) The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multi-cellular organism. The level represented by X is composed of (1) four types of base subunits (2) folded chains of glucose molecules (3) twenty different kinds of amino acids (4) complex, energy-rich inorganic molecules 6 Regents Practice Question # 2 Which model best represents the relationship between a cell, a nucleus, a gene, and a chromosome? 7 Regents Practice Question # 2 (Answer) Which model best represents the relationship between a cell, a nucleus, a gene, and a chromosome? Correct Answer 8 Regents Practice Question # 3 Which diagram represents the relative sizes of the structures listed below? 9 Regents Practice Question # 3 (Answer) Which diagram represents the relative sizes of the structures listed below? Correct Answer 10 Structure of DNA 1. DNA is a long molecule made up of units called nucleotides. 2. Each nucleotide is made up of three basic parts: • • • 5-carbon sugar (deoxyribose) phosphate group nitrogenous base 11 N U C L E O T I D E 12 There are 4 kinds of Nitrogenous bases Adenine phosphate Guanine Cytosine 5 carbon sugar Thymine 13 DNA is a double helix in which two strands are wound around each other. Nucleotide Hydrogen bonds Sugar-phosphate backbone Key Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) 14 Complimentary Base Pairing 1. The two DNA strands are held together at the nitrogenous bases by weak hydrogen bonds. The bases will always pair up in the following way: •Adenine bonds to Thymine A-T •Cytosine bonds to Guanine C-G 2. Francis Crick and James Watson published the structure of the DNA molecule in 1953. 15 Check for Understanding of DNA Structure 1. What is the name of the sugar? 2. What is the symbol used to represent the sugar? 3. Name the 4 nitrogenous bases. 4. Name the complimentary base pairs. 5. What type of bonds hold the bases together? 16 Check for Understanding of DNA Structure (Answers) 1.What is the name of the sugar? deoxyribose 1. What is the symbol used to represent the sugar? 3. Name the 4 nitrogenous bases. adenine, thymine cytosine, guanine 4. Name the complimentary base pairs. adenine – thymine cytosine - guanine 5. What type of bonds hold the bases together? hydrogen bonds 17 When will DNA replication occur? •DNA replication is the process of copying a DNA molecule •DNA must replicate during cell division so that the genetic information can be passed to the daughter cells. •In order to direct cell functions DNA must replicate itself and send the information out of the nucleus because the DNA is not permitted to leave the nucleus. 18 DNA Replication 1. The DNA separates into 2 strands. It unzips itself with Process the help of an enzyme called DNA polymerase. 2. Each parent (old) strand serves as a template (model) for making a new DNA strand complimentary to itself. 3. Replication results in 2 daughter strands each consisting of an old DNA strand and a new DNA 19 strand. Your Turn! DNA Replication Following base pairing rules, create a new DNA molecule A T A T A T T A T A T A CG C G GC G C Parent New DNA Polymerase Unzips the DNA + C G G C New Parent 20 21 Regents Practice Question # 4 Several structures are labeled in the diagram of a puppy shown below. Every cell in each of these structures contains (1) equal amounts of ATP (2) identical genetic information (3) proteins that are all identical (4) organelles for the synthesis of glucose 22 Regents Practice Question # 4 (Answer) Several structures are labeled in the diagram of a puppy shown below. Every cell in each of these structures contains (1) equal amounts of ATP (2) identical genetic information (3) proteins that are all identical (4) organelles for the synthesis of glucose 23 Regents Review Question # 5 Mustard gas removes guanine (G) from DNA. For developing embryos, exposure to mustard gas can cause serious deformities because guanine (1) stores the building blocks of proteins (2) supports the structure of ribosomes (3) produces energy for genetic transfer (4) is part of the genetic code 24 Regents Review Question # 5 (Answer) Mustard gas removes guanine (G) from DNA. For developing embryos, exposure to mustard gas can cause serious deformities because guanine (1) stores the building blocks of proteins (2) supports the structure of ribosomes (3) produces energy for genetic transfer (4) is part of the genetic code 25 26 Importance of Protein 1. Protein is found everywhere in your body. 2. Every single cell, tissue, muscle and bone contains protein. Protein is essential for providing bone and muscle strength, endurance and immunity. 3. It is estimated that the human body may contain over two million proteins. Sickle Cell Disease 27 Protein Synthesis 1. Genes control the production of proteins which occurs on the ribosomes. 2. Each gene directs the production of a specific protein or special proteins such as hormones and enzymes. 3. The DNA can’t leave the nucleus but it needs to send instructions to the ribosome so proteins can be made. 4. The DNA sends a messenger out to the ribosome that carries the instructions for making the proteins. 28 What is RNA ? 1. RNA is the messenger that carries the instructions to the ribosome so proteins can be made. 2. It is very similar to a DNA molecule but yet different enough that it can cross the nuclear membrane without being recognized as DNA. 29 Structure of RNA 1. The sugar in the nucleotide is ribose. 2. It is single-stranded. 3. It has uracil for a nitrogenous base instead of thymine. 4. Complimentary base pairs are: Cytosine – Guanine C-G Adenine – Uracil A-U 30 Making a Protein starts with Transcription Transcription is the name given to the process where a DNA molecule makes the messenger RNA molecule in the nucleus. Adenine (DNA and RNA) Cystosine (DNA and RNA) Guanine(DNA and RNA) Thymine (DNA only) Uracil (RNA only) 31 Translation happens when mRNA arrives at the ribosome 1. During translation, the cell uses information from mRNA to produce proteins that are built from amino acids. 2. Two other types of RNA are involved: • • Transfer RNA ( tRNA) brings amino acids to the ribosome Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) makes up the ribosome 32 Translation from RNA into Protein Nucleus Transcription of Messenger RNA Phenylalanine tRNA Methionine Lysine mRNA Translation by Transfer RNA Ribosome mRNA Start codon 33 The Genetic Code 1. Codons are located on the mRNA 2. A codon consists of three nitrogenous bases that code for a single amino acid that is to be added to the growing protein chain. 3.There are just 22 different amino acids that exist. . Example of codons: AUG is the start codon that gets the process going UUC codes for Phenylalanine AAA codes for Lysine 34 35 36 Regents Practice Question # 6 The diagram below shows some of the steps in protein synthesis. The section of DNA being used to make the strand of mRNA is known as a (1) carbohydrate (2) ribosome (3) gene (4) chromosome 37 Regents Practice Question # 6 (Answer) The diagram below shows some of the steps in protein synthesis. The section of DNA being used to make the strand of mRNA is known as a (1) carbohydrate (2) ribosome (3) gene (4) chromosome 38 39 40 What are Mutations? 1. Mutations are changes in the genetic material of the cell. (DNA) 2. Mutations can be good, bad or neutral. 3. There are 3 different types of mutations: •substitutions •insertions •deletions 41 Substitutions Substitutions occur when one nitrogenous base is substituted in place of another one. Result: 1.Most likely there will be no change in the protein made. 2.This mutation only affects one amino acid in the long sequence of a protein. 3. It is the least harmful. 42 Example of a Substitution: THECATSAWTHEDOG THE CAT SAW THE DOG THE BAT SAW THE DOG THE CAT SAW THE HOG THE CAT SAT THE DOG 43 Sickle Cell Anemia is a result of a Substitution Mutation 44 Insertions Insertions occur when one extra nitrogenous base is added into the DNA Result: sequence. 1. BAD 2. All the nitrogenous bases after the insertion will be regrouped into different codons. 3. The protein made will be nonfunctional. 45 Example of an insertion: THECATSAWTHEDOG THECCATSAWTHEDOG The letter C was inserted THE CCA TSA WTH EDO G 46 Deletions Deletions occur when one nitrogenous base is missing from the sequence. Result: 1. BAD 2. All the nitrogenous bases after the deletion will be regrouped into different codons. 3. The protein made will be nonfunctional. 47 Example of a Deletion THECATSAWTHEDOG THCATSAWTHEDOG The letter E was missing THC ATS AWT HED OG 48 Regents Practice Question # 7 The diagram below shows a normal gene sequence and three mutated sequences of a segment of DNA. Which row in the chart below correctly identifies the cause of each type of mutation? 49 Regents Practice Question # 7 The diagram below shows a normal gene sequence and three mutated sequences of a segment of DNA. Which row in the chart below correctly identifies the cause of each type of mutation? Correct 50 . Regents Practice Question # 8 The shape of a protein is most directly determined by the (1) amount of energy available for synthesis of the protein (2) kind and sequence of amino acids in the protein (3) type and number of DNA molecules in a cell (4) mistakes made when the DNA is copied 51 Regents Practice Question # 8(Answer) The shape of a protein is most directly determined by the (1) amount of energy available for synthesis of the protein (2) kind and sequence of amino acids in the protein (3) type and number of DNA molecules in a cell (4) mistakes made when the DNA is copied 52 Regents Review Question # 9 Which row in the chart below best describes what happens when some DNA bases are deleted from genes ? 53 Regents Review Question # 9 (Answer) Which row in the chart below best describes what happens when some DNA bases are deleted from gene? Correct 54 Regents Review Question # 10 Which sequence best represents the relationship between DNA and the traits of an organism? 55 Regents Review Question # 10 (Answer) Which sequence best represents the relationship between DNA and the traits of an organism? Correct 56 57 What causes mutations? There are two ways in which DNA can become mutated: 1. Mutations can be inherited. • Parent to child 2. Mutations can be acquired • Environmental damage • Mistakes when DNA is copied 58 What are Mutagens? Mutagens are environmental factors that cause mutations. They include but are not limited to: 1.High temperatures 2.Toxic chemicals (pesticides) 3.Radiation ( nuclear and solar) 59 Regents Review Question # 11 A chemical known as 5-bromouracil causes a mutation that results in the mismatching of molecular bases in DNA. The offspring of organisms exposed to 5-bromouracil can have mismatched DNA if the mutation occurs in (1) the skin cells of the mother (2) the gametes of either parent (3) all the body cells of both parents (4) only the nerve cells of the father 60 Regents Review Question # 11 (Answer) A chemical known as 5-bromouracil causes a mutation that results in the mismatching of molecular bases in DNA. The offspring of organisms exposed to 5-bromouracil can have mismatched DNA if the mutation occurs in (1) the skin cells of the mother (2) the gametes of either parent (3) all the body cells of both parents (4) only the nerve cells of the father 61 Regents Review Question # 12 Researchers have found that formaldehyde and asbestos can alter DNA base sequences. Based on this research, the use of these chemicals has been greatly reduced because they (1) may act as fertilizers, increasing the growth of algae in ponds (2) have been replaced by more toxic compounds (3) are capable of causing mutations in humans (4) interfere with the production of antibiotics by white blood cells 62 Regents Review Question # 12 (Answer) Researchers have found that formaldehyde and asbestos can alter DNA base sequences. Based on this research, the use of these chemicals has been greatly reduced because they (1) may act as fertilizers, increasing the growth of algae in ponds (2) have been replaced by more toxic compounds (3) are capable of causing mutations in humans (4) interfere with the production of antibiotics by white blood cells 63 Regents Review Question # 13 A boy inherits genes for tallness, but his growth is limited as a result of poor nutrition. This is an example of (1) an inherited disorder (2) environmental influence on gene expression (3) expression of a hidden trait (4) a characteristic controlled by more than one pair of genes 64 Regents Review Question # 13 (Answer) A boy inherits genes for tallness, but his growth is limited as a result of poor nutrition. This is an example of (1) an inherited disorder (2) environmental influence on gene expression (3) expression of a hidden trait (4) a characteristic controlled by more than one pair of genes 65 Regents Review Question # 14 The sickle-cell trait is an inherited condition resulting from the presence of abnormal molecules of the protein hemoglobin in red blood cells. A person with the sicklecell trait may have a child with the same condition because the child receives from the parent (1) abnormal red blood cells (2) abnormal hemoglobin molecules (3) a code for the production of abnormal hemoglobin (4) a code for the production of abnormal amino acids 66 Regents Review Question # 14 (Answer) The sickle-cell trait is an inherited condition resulting from the presence of abnormal molecules of the protein hemoglobin in red blood cells. A person with the sicklecell trait may have a child with the same condition because the child receives from the parent (1) abnormal red blood cells (2) abnormal hemoglobin molecules (3) a code for the production of abnormal hemoglobin (4) a code for the production of abnormal amino acids 67 Regents Review Question # 15 Which situation would most likely produce a gene mutation in a squirrel? (1) The squirrel stops using its claws for digging. (2) The squirrel is exposed to radiation for several days. (3) Oak trees gradually become less common. (4) The weather becomes wetter for a short period of time. 68 Regents Review Question # 15 (Answer) Which situation would most likely produce a gene mutation in a squirrel? (1) The squirrel stops using its claws for digging. (2) The squirrel is exposed to radiation for several days. (3) Oak trees gradually become less common. (4) The weather becomes wetter for a short period of time. 69 70