Future of Industrial Biotechnology
advertisement

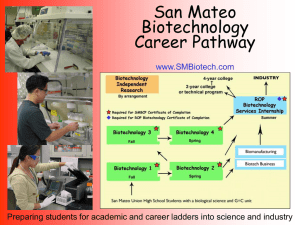
Future of Industrial Biotechnology dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D.,UCSF 1. Biotechnology consists of Traditional and Modern Biotech: Medical, Agro, Environmental, Chemical, and Food Biotechnology 2. Third Generation Biotech= Functional Genomics and Proteomics 3. Targeted Medicine, Tissue Engineering and Stem cells, should be the Focus for Asia 4. BINASIA should become the Information Hub for Biotech Asia 5. Governments must stimulate Innovation in R&D through various Incentives dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 1 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 2 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 3 The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 4 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 5 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 6 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 7 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 8 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 9 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 10 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 11 • Legend: Amino acids specified by each codon sequence on mRNA. Key for the above table: Ala: Alanine Cys: Cysteine Asp: Aspartic acid Glu: Glutamic acidPhe: Phenylalanine Gly: GlycineHis: Histidine Ile: Isoleucine Lys: LysineLeu: Leucine Met: MethionineAsn: AsparaginePro: ProlineGln: GlutamineArg: ArginineSer: SerineThr: ThreonineVal: ValineTrp: TryptophaneTyr: TyrosisneA = adenine G = guanine C = cytosine T = thymine U = uracil DNA transfers information to mRNA in the form of a code defined by a sequence of nucleotides bases. During protein synthesis, ribosomes move along the mRNA molecule and "read" its sequence three nucleotides at a time (codon) from the 5' end to the 3' end. Each amino acid is specified by the mRNA's codon, and then pairs with a sequence of three complementary nucleotides carried by a particular tRNA (anticodon). • Since RNA is constructed from four types of nucleotides, there are 64 possible triplet sequences or codons (4x4x4). Three of these possible codons specify the termination of the polypeptide chain. They are called "stop codons". That leaves 61 codons to specify only 20 different amino acids. Therefore, most of the amino acids are represented by more than one codon. The genetic code is said to be degenerate dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 12 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 13 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 14 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 15 Functional Genomics Definition Functional genomics is a field of molecular biology that is attempting to make use of the vast wealth of data produced by genome sequencing projects to describe genome function. Functional genomics uses high-throuput techniques like DNA microarrays, proteomics, metabolomics and mutation analysis to describe the function and interactions of genes. Because of the large quantity of data and the desire to be able to find patterns and predict gene functions and interactions bioinformatics is crucial to this type of analysis. Comparative genomic Ph.D. analyses can alsodr.Boenjamin held Setiawan, determine gene function.16 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 17 HUPO Brain Proteome Project • HUPO BPP is an open international project under the patronage of the Human Proteome Organisation (HUPO) that aims: • . to analyze the brain proteome of human as well as mouse models in healthy, neurodiseased and aged status with focus on Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease · to perform quantitative proteomics as well as complemantary gene expression profiling on disease-related brain areas and bodily fluids · to advance knowledge of neurodiseases and aging in order to push new diagnostic approaches and medications · to exchange knowledge and data with other HUPO projects and national / international initiatives in the neuroproteomic field · to make neuroproteomic research and its results available in the scientific community and society • dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. http://www.hbpp.org/ 18 The Scientific Development of Biotechnology and Its Industrial Applications dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 19 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 20 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 21 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 22 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 23 Biotechnology Based Drugs Biomanufacturing, the commercial production of biotechnological products, is poised for tremendous growth in the next decade as a number of new biotechnology products enter the marketplace. To date, 130 biotechnology drugs and vaccines have already been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in the United States. There are currently 350 biotechnology-derived drugs in clinical trials and more than 1,200 biotechnologybased drugs in preclinical development. http://www.ncsu.edu/BulletinOnline/06_03/guestcolumn620.htm dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 24 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 25 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 26 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 27 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 28 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 29 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 30 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 31 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 32 • U.S. Leads World in R&D Spending, China Moves to 3rd Place The United States continues to lead the world in R&D witb 38 percent of world R&D spending in 2003 according to data from the OECD. U.S. industry, government and other sectors spend more on R&D than the entire EU combined. The U.S. share has declined only slightly from 40 percent during most of the 1990s, but other nations' shares have changed dramatically. China has increased its R&D investments dramatically in recent years and is now the 3rd largest investor in R&D (adjusted for purchasing power), behind only Japan and the U.S. dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. http://www.aaas.org/spp/rd/06pch4.htm 33 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 34 • United States: Over the past ten years, a new informal innovation system evolved in the U.S., with support from government and industry for basic research in universities, nurtured by rapid growth in venture capital, and implemented by industrial firms through strong investments in R&D, capital equipment, and information technology. This highly complex system of innovation is also based on close collaborations and increasing alliances among industry players, universities, and government labs. There are now stresses in this proven formula that must be addressed. dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 35 • Asia: The Chinese government views 2005 as a vital year to build its country’s innovation capacity to support a harmonious, well-rounded, and prosperous society. A National Science and Technology Plan for 2006-2020 will be promulgated to: produce proprietary intellectual property by scanning the leading science and technology developments; strengthen national competitiveness by developing key technologies; focus on strategic high-tech products and projects; and build sustainable innovation capacity. • To support the Plan’s goals, the government will play an active policy role, drastically increasing public expenditure on R&D. It will improve infrastructure and streamline the innovation system. A comprehensive set of national programs has been developed to manage various aspects of the Plan. Implementation of the Plan and supporting programs will be led by the Ministry of Science and Technology. dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 36 • The economy of Japan is holding steady, supported by satisfactory exports and increasing domestic consumption. Deflation is a continuing concern. Recovery is being led by digital consumer products and the materials industries, especially steel. Although the National Budget of 2005 fiscal year will show decreased expenditures, the allocation for promoting science and technology will by increased by 2.6 percent to 1.3 trillion yen. This is aligned with the Japanese Government strategy to realize “an advanced science- and technology-oriented nation”. dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 37 • In spite of a blurry economic picture, Korean R&D expenditure will increase 22.2 percent in 2005, focusing on telecommunications, electronics, computers, machinery, chemicals, metals, and food & medicines. Over 80 percent of the companies surveyed will increase R&D expenditures in 2005 The National Innovation System will be reworked to improve university research, seek globalization and to concentrate national S&T resources on the development of 10 new growth industries. To facilitate commercialization of public R&D results, the technology transfer budget was more than tripled dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 38 The Future of Regenerative Medicine/Stem Cells dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 39 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 40 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 41 Nucleus of patient transferred to enucleated human oocyte. Inner cell mass from blastocyst cultured and stimulated to form specific cell types required for THERAPY---Diabetes, Parkinson, Cancer, Stroke etc, dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 42 The Chemoattractive homing hypothesis of circulating STEM CELLS, attracted to injury, in the infarcted area dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 43 Biotechnology: Present and Future dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 44 "Biotech's best days are still to come, It is a fundamentally sound and innovative industry creating essential products for improving the health and quality of life of everyone on the planet." http://wistechnology.com/article.php?id=533 dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 45 Recommendations 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Considering the limited financial and human resources Indonesia must focus its R&D on MEDICAL BIOTECHNOLOGY (Functional Genomics/Proteomics Targeted Therapeutics)and STEM CELL/Regenerative Medicine The Government must STIMULATE INNOVATION by giving TAX INCENTIVES to industries doing R&D Efforts must be made to Facilitate GovernmentUniversity-Industry cooperation Applied Research in Universities and Government institutions should be done in close cooperation with industries BINASIA should become the communication hub for International Cooperation and Technology Transfer dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 46 THANK YOU dr.Boenjamin Setiawan, Ph.D. 47