Novel Mutation GcReceptor
advertisement

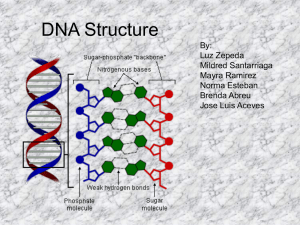
Gluco-corticoid Receptor Protein 9.22.11 Case Study • What is generalized glucocorticoid resistance syndrome? • Go through the case report. Pg 2 • HTA axis cortisone • Through the DBD and LBD of ER, and AP-2 sites • Binding of estrogen dislodges the HSP90 complex, allows binding to AP-2 site Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR) (blue) binds to DNA (in orange and tan) upon cortisone (in purple) binding • Cortisone found in both cytoplasm and nucleus of many different kinds of cells • Shown here as a dimer (vertical line separates) • Two major types, α and β, both act as dimers • LBD is the C-terminal Ligand Binding domain • H helix is rearranged when cortisone binds • cortisone’s binding affect s dimerization and binding to additional transcriptional elements by exposing hydrophobic surfaces •Agonists and antagonists show differential rearrangements of the H helix •DBD is the N-terminal DNA binding domain • binds to glucocorticoid responsive element (GRE) on DNA •Initiatives downstream activation of transcription •Assisted in transcriptional activation by other transcriptional elements H helix in GR modulates function of GR H helix • position is sensitive to chemical nature of ligand and type of GR (alpha or beta) cortisone • normally closed when GR binds at LBD (top image) •Cannot close, when antagonists bind- this blocks the action of the receptor (bottom image) Cortisone antagonist DNA binding domain in GR finds specific region Recognition of GRE on DBD mediated through recognition helix, and Zn(II) finger domains Dimer binds to DNA Palindromic recognition sequence on DNA PDB code 1hcq Properties of GRα • 96% sequence homology in DBD • 58% sequence homology in LBD • Size (RNA splicing isoforms) – GRα- Chromosome 6 (6q25.1) Protein Structure α-HELIX • Human glucocorticoid receptor – pdbID 1M2Z glucocortisone dexamethasone Protein Structure α-HELIX • Human glucocorticoid receptor – pdbID 1M2Z glucocortisone dexamethasone Homodimer 12 alpha helices, 4 beta sheets Secondary Structure Homodimer 12 helices only 10 found by program 4 beta sheets; two on outside and two at interface Secondary Structure N C Rainbow shows for each molecule the N (blue) terminus to the C (red) terminus N termini (helix 1) on A and D connected to the DNA binding domain C termini (helix 12) in A and D involved in binding to GRIP and others. Helix 12, on GE binds the AF helix in antiparallel +4+3 packing • Mutation is R714 to N in of helix 10, wt R ion pairs w E662 of helix 8 • R mutated to N , E662 binds w. R704 of helix 9 (moves 0.4 nm) • This switch releases helix 10, • Mutation is R714 to N in of helix 10 released, causes Y735 rotamer and disrupts bind AF-2 through helix 12 Ligand Binding Domain Switch • • • • 1NHZ Glucocorticoid with antagonist 1P93 Glucocorticoid with agonist 3H52 active/passive forms with antagonist Mouse glucocorticoid receptor – 3MNE (single mutant) – 3MNO (double mutant) – 3MNP (triple mutant)