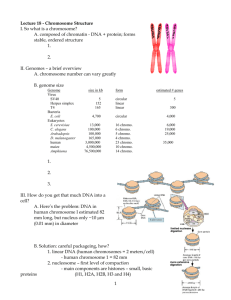
SEX LINKED INHERITANCE
Sex Determination: The human XY system
Nondisjunction: The failure of chromosomes to separate
properly during one of the stages of meiosis (fig. 11-12)
This can produce gametes w/two sex chromosomes or no
sex chromosomes. Results in abnormal # of sex chromo.
Nondisjunction disorders
Turner syndrome- female in appearance, w/o sex organs
45X or 45XO
Klinefelter syndrome- Male in appearance, sterile, 47XXY
Babies are not born without an X chromosome
What can we learn? X chromo. Is essential; gender is
determined by presence/absence of Y
NONDISJUNCTION
DISORDERS
SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE
SEX-LINKED GENETIC DISORDER
Sex-linked: Genes carried on the X or Y Chromo. Which are
expressed more commonly in males. WHY?
COLORBLINDNESS- Most caused by genes located on X chromo.
Red-green is most common, 8% males; 1% females
Carried on X chromo.; dominant allele is XC & recessive is Xc.
Why more common in males?
HEMOPHILIA- Bleeders disea
se, protein AHF is missing.
MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY- Progressive wasting away of muscle.
Caused by defective version of the gene, dystrophin
SEX-INFLUENCED TRAITS: Caused by a gene whose expression
differs in males & females, located on autosomes.
SEX-LINKED DISORDERS