cell
advertisement

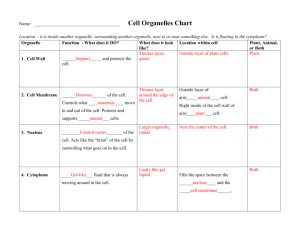
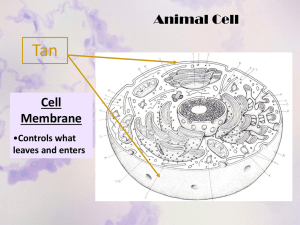
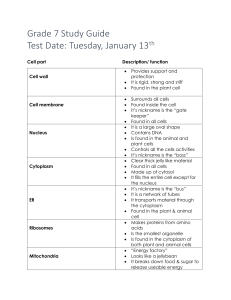
7th Grade 3/12 Do Now: Finish Cell Theory TimeLine Cell Theory: Hooke – first person to discover and name cells Schleiden – discovers plants are made of cells Schwann – discovers animals are made of cells Virchow – discovers cells come from other cells Cell Theory How does Cell Theory answer these questions: – – – What makes something alive? What do cells do? Where do cells come from? THE CELL COMMON CELL TRAITS A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. COMPARING CELLS The size & shape of a cell relates to its function. (job it does) Prokaryotic Cells (proh KAYR ee yah tihk) cells without membranebound structures EX: bacteria pond scum 7th Grade 3/13 Do Now Color and label the picture of the animal cell and plant cell for the following parts of the cell: – – – Cell membrane – orange Cytoplasm – sky (light) blue Cell wall – yellow green Eukaryotic Cells (yew KAYR ee yah tihk) cells with membranebound structures EX: animals, plants, fungi and protists CELL WALL protects the cell gives shape is made of cellulose A cell wall is found in plants, algae, fungi, & most bacteria. CELL MEMBRANE Outer covering, protective layer around ALL cells For cells with cell walls,the cell membrane is inside the cell wall Allows food, oxygen, & water into the cell & waste products out of the cell. CYTOPLASM gelatin-like inside cell membrane constantly flows aka protoplasm CYTOSKELETON scaffolding-like structure in cytoplasm helps the cell maintain or change its shape made of protein Organelle Foldable Take a piece of paper and fold it lengthwise (hot dog). At the top label: Cell Organelles On the same side cut the paper into 7 flaps (approximately 4 lines) Label the 7 flaps: ribosome, chloroplast, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi bodies, vacuole and lysosome. On the inside, define and draw the organelle. Organelle Foldable Take a piece of paper and fold it lengthwise (hot dog). At the top label: Cell Organelles On the same side cut the paper into 7 flaps (approximately 4 lines) Label the 7 flaps: ribosome, chloroplast, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi bodies, vacuole and lysosome. On the inside, define and draw the organelle. NUCLEUS Directs all cell activities Contains instructions for everything the cell does These instructions are found on a hereditary material called DNA Usually the largest organelle NUCLEAR MEMBRANE separates nucleus from cytoplasm controls movement of materials in & out of nucleus NUCLEOLUS Aka “little nucleus” Found in the nucleus CHROMATIN contains genetic code that controls cell made of DNA & proteins NUCLEUS Directs all cell activities Contains instructions for everything the cell does These instructions are found on a hereditary material called DNA Usually the largest organelle NUCLEAR MEMBRANE separates nucleus from cytoplasm controls movement of materials in & out of nucleus NUCLEOLUS Aka “little nucleus” Found in the nucleus CHROMATIN contains genetic code that controls cell made of DNA & proteins ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM A series of folded membranes that move materials (proteins) around in a cell like a conveyor belt Smooth ER – ribosomes not attached to ER Rough ER – ribosomes attached to ER RIBOSOMES Make proteins Float freely or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ribosomes are made in the nucleolus GOLGI BODIES (GAWL jee) Stacked flattened membranes Sort and package proteins VACUOLES Temporary storage spaces Store food, water, waste LYSOSOMES (LI suh sohmz) The word "lysosome" is Latin for "kill body." The purpose of the lysosome is to digest things. They might be used to digest food or break down the cell when it dies. Break down food molecules, cell wastes & worn out cell parts CHLOROPLASTS Green organelles that make food found only in plant cells CHLOROPHYLL A green pigment that gives leaves & stems their color Captures sunlight energy that is used to produce food called glucose Glucose is a type of sugar MITOCHONDRIA Organelles that release energy from food This energy is released by breaking down food into carbon dioxide AKA the powerhouse b/c they release energy from food Some muscle cells have 20,000 mitochondria