Section L Regulation of Transcription in Prokaryotes

Section L Regulation of
Transcription in Prokaryotes
L1 The
lac
operon
L2 The
trp
operon
L3 Transcriptional regulation by alternative
s
factor
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
L1 The lac operon
•
The operon
•
The lactose operon
•
The lac repressor
•
Induction
• cAMP receptor protein
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
Nobelists in Biology in 1965
Francois Jacob
(44y)
Jacques Monod
(55y)
(French)
Lac. Operon Theory
Concept of mRNA
Francois Jacob
Jacques Monod
The operon
Definition : The operon is a unit of gene expression and regulation which typically includes:
Regulator genes Operator sequence Structural genes
P lacI lacI P lac
O lac lacZ lacY lacA regulation information
• Regulator genes : whose products recognize the control-elements, for example a repressor which binds to and regulates an operator sequence.
• Operator sequence : Control elements such as an operator sequence, which is a DNA sequence that regulates transcription of the structural genes.
• Structural genes
: The structural genes for encoding proteins.
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
The lactose operon
Structural genes : The lactose operon consists of 3 structural genes: lacZ, lacY, lacA.
Polycistronic mRNA: The three structural genes are encoded in a single transcription unit lacZYA, which has a single promoter
P lac
, and transcribes a single proteins expressed. polycistronic mRNA, but more
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
The lac repressor
Definition:
The lac I gene encodes the repressor,
which is active as a tetramer of identical subunits.
It has a very strong affinity for the lac operator-binding site, O lac
, and
also has a generally high affinity for DNA.
Structure:
The lac operator-binding site consists of 28 bp
which is palindromic.
This inverted symmetry of the operator matches the inherent symmetry of the lac repressor.
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
D N A
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
The lac repressor
Binding:
In the absence of lactose , the repressor occupies the operator-binding site.
The lac repressor increases the binding of the RNA polymerase to the lac promoter by two order of magnitude.
This means that when lac repressor is bound to the O lac
, the RNA plo is also likely to be bound to adjacent P lac promoter sequence without move.
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
Induction process
1. No lactose : In the absence of lactose, the lac repressor blocks all but a very low level of transcription of lacZYA.
2. Uptake : When lactose is added to cell, the low level of permease allows its uptake, and bgalactosidases catalyzes some lactose to allo-lactose .
3. Induction : Allo-lactose acts as an inducer and binds to the lac represser. This causes a change in the conformation of the repressor tetramer, reducing its affinity for lac operator.
P lacI
Low
Lac.
lacI
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
P lac
O lac
5. Re-Inhibition : lacZ lacY lacA mRNA
4. Transcription :
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
cAMP receptor protein-I
Function:
• The P lac promoter is not a strong promoter. P lac and related promoters do not have strong -35 sequences and some even have weak -10 consensus sequences.
• For high level transcription, they require the activity of a specific protein called cAMP receptor protein ( CRP ).
• CRP exists as a dimer which cannot bind to DNA on its own, nor regulate transcription, but which can form CRP-cAMP
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
CRP-cAMP ( c AMP r eceptor p rotein ) binding site
IR IR
-70 -50 -40 site I site II
● site I
: IR is CRP-cAMP strong binding site ( -70 ~ -50 )
● site II: is CRP-cAMP weak bingding site ( -50 ~ -40 )
●
CRP-cAMP binds site I cooperative effect Promote site II binding
●
CRP-cAMP + site II promotion RNApol. into -35 sequence into -10 sequence starting transcription
RNApol
SiteI siteII
GC Island -35 -10
cAMP receptor protein-II
• Normal Condition : The glucose is present in E. coli .
1. Inactivated operon: The E. coli does not require alternative carbon sources such as lactose. Therefore lactose operon is normally inactivated.
2. Inactivated CRP : The glucose can reduce the level of cAMP, therefor the cAMP is not enough for binding CRP .
• Special Condition
: When glucose is absent in E. coli culture.
1. Activated CRP : The levels of cAMP increased, and CRP binds to cAMP to form the CRP-cAMP complex which is the activated CRP .
2. Activated operon : The CRPcAMP complex binds to the P lac just upstream from the site for
RNA pol. CRP binding induces a
90º bend in DNA, and to enhance
RNA pol binding to the promoter, enhancing transcription by 50-fold.
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
L2 The trp operon
• The tryptophan operon
• The try repressor
• The attenuator
• Leader RNA structure
• Attenuation
• Importance of attenuation
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
trp
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
The tryptophan operon
Structural genes : The trp operon encodes five structural genes whose activity is required for tryptophan synthesis.
Transcript : The operon encodes a single transcription unit which produces a 7 kb transcript which is synthesized downstream from the trp promoter P try and trp operator sites O trp
.
Expression : Like many of the operons involved in amino acid biosynthesis, the trp operon has evolved systems for coordinated expression of these genes when tryptophan is in short supply in the cell.
Regulation speed : As with the lac operon, the RNA product of this transcription unit is very unstable, enabling bacteria to respond rapidly to changing needs for tryptophan.
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
trpR P O E D C B A operon on
Mechanism
Repressor (inactive ) can not bind on the O site
(trp absent) trpR P O E D C B A operon off repressor + trp active repressor
Operator tryptophan
The trp repressor
Trp repressor: A gene product of the trpR operon. It is a dimer of two subunits.
Operator structure : P trp is between -21 and +3. The core binding site is a palindrome of 18bp .
Mechanism:
The trp repressor can only bind to the operator when it is complexed with tryptophan.
The repressor dimer has a structure with a central core and two DNA-reading heads.
When tryptophan is bound to the repressor the reading heads are the correct distance apart, and the side chains in the correct conformation , to interact with major grooves of the DNA at P trp
.
Tryptophan: is the end-product of the enzymes encoded by the trp operon, it acts as a corepressor and inhibits its own synthesis by endproduct inhibition . The repressor reduces transcription initiation by around 70-fold.
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
trp
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
The attenuator
Background : At first, it was thought the repressor was responsible for all of the transcriptional regulation of the trp operon. And then, it was observed that the deletion of a sequence between the operator and the trpE resulted in an increase in both the basal and the activated (de-repressed) levels of transcription.
Attenuator : This site is termed the attenuator and it lies towards the end of the transcribed leader sequence of 162 nt that precedes the trpE initiator codon.
Structure : The attenuator is a
-independent terminator site which has a short GC-rich palindrome followed by eight successive U residues in RNA sequence.
Function : If this sequence is able to form a 3
-
4 hairpin structure in the RNA transcript, then it acts as a highly efficient transcription terminator and only a 140 nt transcript is synthesized.
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
S3 S4
A
A • U
U G
C A
C • G
G • C
C • G
C • G
C • G
G • C
A • U
……NNNN UUUUUUU-OH
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Rho-independent T.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
Attenuation
Reason of attenuation : Attenuation effect depends on the fact that transcription and translation are tightly coupled in E. coli ; translation can occur as an mRNA is being transcribed.
Sequence 1 :
The 3’OH-end of the trp leader peptide coding sequence overlaps complementary sequence 1;
the two trp codons are within sequence 1.
Stop codon : The stop codon in the leader sequence is between sequence 1 and sequence 2.
3:4 hairpin : It is a conditional terminator ( attenuator ). When the tryptophan is non-starved, the 3:4 hairpin forms in the mRNA.
Coordination : As transcription of the trp operon proceeds, the
RNA polymerase pauses at the end of sequence 2 until a ribosome begins to translate the leader peptide.
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
Importance of attenuation
700-fold regulatory effect:
• Attenuation : The presence of tryptophan gives rise to a 10-fold repression of trp operon transcription through the process of attenuation alone.
• Trp repressor : Combined with control by the trp repressor ( 70fold ), this means that tryptophan levels exert a 700-fold regulatory effect on expression from the trp operon.
His operon : For example
• Histidine codons : The His operon has a leader sequence which encodes a peptide with seven successive histidine codons.
• Only mechanism
: The His operon has no repressor-operator regulation, and attenuation forms the only mechanism of feedback control.
Other operons : Attenuation occurs in at least six operons that encode enzymes concerned with amino acid bio-synthesis.
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
L3 Trans. regulation by alternative
s
factor
• Sigma factor
• Heat shock
• Bateriophage
s
factor
groel hsp47
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Regulation patterns and
s
factors
Transcription regulation patterns :
• By transcriptional repressors: such as the lac repressor;
• By transcriptional activators : such as the CRP;
• By different s to direct RNApol binding different promoter:
Functions of s factors :
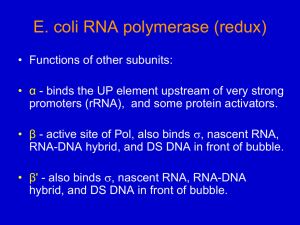
The abb ’ w core enzyme of RNA polymerase is unable to start transcription at promoter sites.
In order to specifically recognize the consensus -35 and -10 elements of the promoters, it requires the s factor subunit.
This subunit is only required for transcription initiation,
being released from the core enzyme after initiation and before
RNA elongation takes place.
Features : Many bacteria, including E.coli, produce a set of s factors that recognize different sets of promoters.
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences
Heat shock gene
Transcriptional regulation by alternative s factor in E. coli for stress condition (an example for the use of different s )
----- When 37 ℃ ; genes expressed in E.coli by RNApol with s 70
----- When > 37 ℃ ; (42 ℃ : very soon; 50 ℃ : the only products)
More then 17 heat-shock proteins are expressed in E.coli through transcription by RNApol using an alternative s 32 , which have own specific promoter consensus sequence
Responsive Promoter -35 -10
Standard s 70 ---TTGACA ----16-18--------TATAAT ------
Heat shock s 32 ---TTGAA----13-15--CCCCAT-T---------
Bateriophage
s
factor
Some phages provide new s subunits to the host RNA polymerase with a different promoter specificity and hence to selectively express their own phage genes.
This strategy is an effective alternative to the need for the phage to encode its own complete polymerase. This pattern allows its own genes to be transcribed at specific stages during virus infection.
Early gene middle genes late genes host s 70 phage s 28 phage s -late
T4 in E.coli proteins
That’s all for Section L
Section L: Regulation of transcrip. in Prok.
Yang Xu, College of Life Sciences