Notes
advertisement

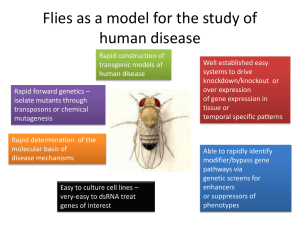
The Life Cycle P Neuroptera Coleoptera Hymenoptera Lepidoptera Mecoptera Siphonoptera Strepsiptera Diptera ~250 Mya Nematocera Brachycera Muscomorpha Cyclorrhapha Schizophora Calyptrata Acalyptrata Camillidae Steganinae Cladocheata etc Zaprionus etc s.g. Drosophila Chymomyza etc s.g. Sophopora Drosophila melanogaster subgroup Drosophila melanogaster - cosmopolitan - 1830 Drosophila simulans - cosmopolitan - 1919 Drosophila mauritiana - Mauritius - 1974 Drosophila sechellia - Seychelles -1981 Drosophila yakuba - Equatorial Africa - 1954 Drosophila santomea - Sao Tome - 2000 Drosophila teissieri - Equatorial Africa - 1979 Drosophila erecta - Central West Africa - 1974 Drosophila orena - Cameroons - 1978 mel f x sim m sim f x mel m Viable, sterile f Viable, sterile m Larval lethal m Embryo lethal f aabb AAbb x aaBB AaBb Hmr allele of melanogaster (transcription factor) Lhr allele of simulans (chromatin binding protein) “Eventually, the story of the chromosomal mechanisms and its evolution will have to be entirely rewritten in molecular terms.” Michael White, 1973, Animal Cytology & Evolution, 2nd edition. Q a r e u ic k T im e ™ a n d d e c o m p r e s s o r n e e d e d t o s e e a t h is p ic t u r e . Paracentric inversions are the most common rearrangement Segregating in 106 out 183 species. - 57% - (Powell 1997). 22000-56000 inversions have become fixed during the evolution of the genus (Clayton & Guest 1986). a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t a b j i h g f e d c k l m n o p q r s t a b j l o n m l k c d e f h i p q r s t a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t a b c d e f g h i o n m l k j p q r s t a b k l m n o i h g f e d c j p q r s t 12 genomes have been sequenced in the genus Drosophila Ectopic recombination between homologous fragments of DNA 1. 2. 3. ( Cáceres et al. Science 1999 ) ~280 Kb ~450 Kb BACs BACR16N15 BACR42I20 BACR08K01 BACR07M14 BACR45A07 3R of D. melanogaster centromere 84F1 telomere 93F6-7 centromere telomere 3R of D. simulans Inversion-mediated duplications can result from staggered isochromatid breaks & repair. A C B D E F G H I J K 5' 3' 3' 5' 5' 3' 3' 5' 3' 5' 5' 3' 5' 3' A 5' 3' B C D I H 5' 3' 5' 3' 5' G F E D C B I 3' 3' J 5' 5'5' K 3' 3' 5' 5' 5' 3' 3' 5' 5' Lemeunier & Ashburner, 1976 BLAST-N of D. mel 3R transcripts against D. yak 3R J. Ranz, C. Bergman & M. Ashburner Flanking duplications are a common by-product of the genome reorganization between D. melanogaster and D. yakuba. 20 9 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 with without Most inversions occurred in the D. yakuba lineage 1 ( 3.4 % ) D. melanogaster 28 ( 96.6 % ) D. yakuba outgroup species 1: A-B A]-----[B A-B 2: A]-----[B A-B A-B Large-scale comparison of the gene order between D. melanogaster and D. yakuba. 55 breakpoints = 12 + 22 + 9 + 12 0.025 0.02 Breakpoints Mb Myr 0.015 0.01 0.005 0 X 2L+2R 3L 3R 29 inversions Comparison of total number of breakpoints that correspond to small and gross inversions between D. melanogaster and other flies' genomes 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 D. Gr i. D. Vi r. D. M oj. D. W il. D. Ps e. . D. Pe r D. An a. . D. Ya k . D. Er e . D. Se c D. Si m . 0 Cluster gram based on the number of breakpoints that correspond to inversions Comparison of total number of breakpoints that correspond to small and gross inversions divided by the square of evolutionary distance 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 0.10 D. G ri. D. Vi r. D. M oj . D. W il. D. Ps e. D. Pe r. D. An a. D. Ya k. D. Er e. D. Se c. . 0.00 D. Si m Number of breakpoints / square of evolutionary distance 0.60 Number of time the pair of genes has been broken Distribution of breakpoints from X chromosome to 3L 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 1 1001 2001 3001 4001 5001 6001 7001 8001 9001 10001 Genes within genes within genes 700 9000 350 4500 0 0 Number of nonoverlapping pairs Number of overlapping pairs Number of antisense/sense overlapping pairs of genes in D. melanogaster 700 2000 350 1000 0 H. Sapiens D. Melanogaster D. melanogaster is different from H. sapiens. 0 RIKEN Group and FANTOM Consortium, Antisense transcription in the mammalian transcriptome. Science 2005 309(5740) 100 Percentage of conserved pairs 90 80 3'-3' Antisense overlap 5'-5' Antisense overlap 70 5'-3' Sense overlap 3'-3' Nonoverlapping pair 60 5'-5' Nonoverlapping pair 5'-3' Nonoverlapping pair 50 40 M el a no g as t er Si m ul an s Se ch el lia Ya ku ba Er ec An ta a na Ps ss eu ae do ob sc ur a Pe rs im ilis W illi st on M oj av i en si s Vi ril G rim is sh aw i 30 Thanks to: Jose Ranz (Cambridge). Casey Bergman (Manchester). Marcin von Grotthuss (Cambridge). Karen Eilbeck & Suzi Lewis (Berkeley). Lincoln Stein (CSGL) & Richard Durbin (WTGC) Hadi Quesneville (Paris). The MRC for 25 years of continuous funding. The BBSRC for a grant to Jose. EMBO for support to Marcin. The Royal Society for a Fellowship to Casey. Depth of knowledge Annotation Detailed analysis (typically biological) of single genes Annotated genome Large-scale analysis (typically computational) of entire genome Breadth of knowledge Assemblies from the 12 ongoing Drosophila sequencing projects are available right now Comparison of number of annotated proteins 16000 GLEANR BlastN/TblastN/PSI(NR70)-TBlastN All Blasts + Syntenic Info 12000 10000 8000 6000 4000 2000 e ct iv Ef fe on Co m m D. G ri. D. Vi r. D. Er e. D. Ya k. D. An a. D. Pe r. D. Ps e. D. W il. D. M oj . D. Se c. . 0 D. Si m Number of orthologs 14000 Comparison of total number of breakpoints that correspond to small and gross inversions divided by evolutionary distance Number of breakpoints / evolutionary distance 30 25 20 15 10 5 D. G ri. D. Vi r. D. M oj . D. W il. D. Ps e. D. Pe r. D. An a. D. Ya k. D. Er e. D. Se c. D. Si m . 0 Number of time the pair of genes has been broken Distribution of breakpoints along the chromosome X (Muller's element A) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 1 201 401 601 801 1001 1201 Number of time the pair of genes has been broken Distribution of breakpoints along the chromosome 3R (first 1283 pairs) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 1 201 401 601 801 1001 1201