Compounds found in living
things
All contents copyright © 1992-2004 the
Author(s) and The University of Iowa. All
rights reserved.
http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/anatomy/a
tlasofanatomy/plate22/index.html
Inorganic compounds:
Compounds that lack both carbon
and hydrogen together.
Examples:
Organic Compounds:
Compounds that contain both
carbon and hydrogen.
Examples:
What are the 4 groups of organic
compounds?
1. Carbohydrates
2. Lipids (fats)
3. Proteins
4. Nucleic Acids (DNA)
Each group has a monomer,
which is a small building
block or subunit
Monomers are put together to
build the polymer of the group
• Cells link monomers to form polymers by
dehydration synthesis
1
2
3
Short polymer
Unlinked monomer
Removal of
water molecule
1
Figure 3.3A
2
3
Longer polymer
4
• Polymers are broken down to monomers by
the reverse process, hydrolysis
1
2
3
4
Addition of
water molecule
1
2
3
Coating of
capture strand
Figure 3.3B
1. Carbohydrates
- Function: energy storage and
structure
- Foods with carbohydrates:
Pastas, cereals, potatoes
Carbohydrates…..
Pasta
Free-Stock-Photos.com
Cereal
Carbohydrates…..
Bread
Free-Stock-Photos.com
Pasta
Carbohydrates…..
Orange juice
Free-Stock-Photos.com
Carbohydrates
-Monomer: simple sugar called
a monosaccharide
-Ex: glucose, fructose, galactose
Draw a glucose molecule
here! Your teacher will show
you how to draw it!
Carbohydrates…..
molecular structure
Carbohydrates
- Polymer: complex carbohydrate
called polysaccharides
Ex: starches in plants (energy)
cellulose in plants (structure)
glycogen in animals (energy)
Building a complex
carbohydrate…(a polymer)…..
http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookTOC.
html
2. Lipids
- Function:- energy storage
- cell membrane
structure
- chemical messengers
- Characteristics – contain C,H,O
- oils – liquid at room temp.
- fats – solid at room temp.
2. Lipids
- Foods with lipids:
butter, cheese, red meats,
chocolate, ice cream
Lipids……
milk
cheese
hamburger
Free-Stock-Photos.com
2. Lipids
- Monomer: glycerol and 3 fatty
acids
Your teacher will have you
draw these monomers here.
- Polymer: fats and oils
sterols (cholesterols)
phospholipids (part
of cell membrane)
2. Lipids
Lipids can be
saturated – with single
bonds between C’s in fatty
acid tails (red meats, dairy)
unsaturated - with double bonds
between C’s in fatty acid tails
(fish oils, veg. oil)
Saturated = tails w/NO double bonds
Unsaturated = tails w/ double bonds
3. Proteins – A diverse group!
Characteristics: all contain
Nitrogen (N)
- Function: Movement (muscles), help
chemical reactions (enzymes - catalysts),
immunity (antibodies), messengers
(hormones), transporters (in blood)
- Foods with proteins:
meats, fish, cheese, yogurt
Proteins….
cheese
fish … mmm
yogurt
Classroomclipart.com
Free-Stock-Photos.com
hamburger
3. Proteins – A diverse group!
- Monomer: amino acids (20 types)
Your teacher will have you draw
these monomers here.
- Polymer: Polypeptide chain
(protein chain)
Building a complex
carbohydrate…(a polymer)…..
Dipeptide
Peptide Bond
http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookTOC.html
The sequence of amino
acids in the chain will
determine the protein’s
shape and function!!!
Many foods contain more than one
group of organic compound…
tacos
cupcakes
Free-Stock-Photos.com
4. Nucleic Acids
- Characteristics –
made of C,N,O,H,P.
- Monomer: nucleotides
your teacher will have you draw
a nucleotide here.
- Polymer: DNA, RNA (polynucleotides)
- Function: storage of genetic
information
http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookTOC.html
• Polymers are broken down to monomers by
the reverse process, hydrolysis
1
2
3
4
Addition of
water molecule
1
2
3
Coating of
capture strand
Figure 3.3B
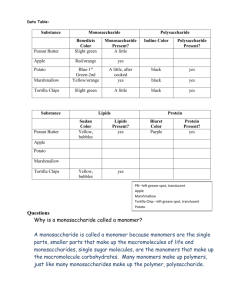
Maltose is ONE type of
dissaccharide (double sugar)
http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookTOC.
html
Double Sugars and their Monomers
• Maltose (malt sugar) is made of 2
glucoses
• Sucrose (table sugar) is made of 1
glucose and 1 fructose
• Lactose (milk sugar) is made of 1
glucose and 1 galactose
• All if these sugars have the same
chemical formula, but their structures
are slightly different from each other.
• This means that they are isomers!