Incomplete & Codominance Powerpoint

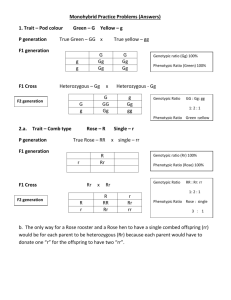
Incomplete & Codominance
Genetics
Biology 30
Mrs. S. Pipke-Painchaud
Reviewing
All photos from: http://www.naturalselectionreptiles.com/Genetics.html
Incomplete Dominance
• (a.k.a. partial dominance or blending)
• occurs when both alleles contribute to a trait that is not like either parent.
• this condition is only seen in the heterozygous individual
– ex.. Snap Dragons or Four O’Clocks or Morning Glory or Primrose (Flowers)
– Curly (homozygous) or straight (homozygous), but if you are heterozygous you have wavy hair.
Example: Snap Dragons
Parents: Red X White http://www.usask.ca/biology/genetics/extensions/ snapdragon.jpg
W = red w = white
Parents are both true breeding red and white.
WW X ww
W W
Genotype: All Ww w Ww Ww
Phenotype: All Pink w Ww Ww
http://www.visionle
arning.com/library/ modules/mid129/Im age/VLObject-
3228-
050216120240.jpg
F1 x F1 Cross
Ww X Ww
Remember:
W = red w = white Ww = pink
W w
Genotypic Ratio:
1WW: 2 Ww: 1ww
W WW Ww w Ww ww
Phenotypic ratio:
1 Red: 2 Pink: 1 White
***NOTE: Because there is no dominance in the heterozygote the phenotypic ratio is identical to the genotypic ratio****
• http://courses.bio.psu.edu/fall2
005/biol110/tutorials/tutorial5_f iles/figure_14_9.gif
http://library.thinkquest.org/2046
5/media/flowers.gif
How the coloring works . . .
• WW – have enough pigment to be red
• ww - flowers don’t have any pigment
= no color
• Ww – only have enough pigment to be pink
Codominance
• the two dominant genes are expressed at the same time
• both traits appear in the heterozygous individual at the same time
– ex.. Roan (Red or Blue) coat color in horses and cattle
– Chestnut and White color in horses are both dominant traits; the heterozygous individual is a palomino
(golden).
Blue Roan Example: http://www.virginiacowboy.com/sitebuilder/images
/DSC_0040-803x536.jpg
Red Roan Example: http://www.naturalselectionreptiles.com/G enetics/exCodominance.jpg
Coat Color in Horses
• C= Color gene
• C R C R = Red C W C W = White
C R C W = Red Roan
If you cross a true breeding Red horse with a true breeding white horse, what ratios will you get?
Genotypic Ratio:
All C R C W
Phenotypic Ratio:
All Red Roan
C R C R
C W C R C W C R C W
C W C R C W C R C W
Example: MN Blood Group
• MN blood group – is characterized by a certain type of glycoprotein on the surface of the RBCs.
• There are two forms: M and N
• Designate is L
• L M L M = M
• L N L N = N
• L M L N = MN type
MN Blood Group
• L M L M = M
•
L N L N = N
• L M L N = MN type
What types of offspring would be produced from a cross of a homozygous M type with an MN type?
Parents: L M L M X L M L N
Genotypic Ratio: L M L M
1 L M L M : 1 L M L N
Phenotypic Ratio:
L M L M L M L M L M
1 M blood type: 1 MN blood type
L N L M L N L M L N