Structure Function
advertisement
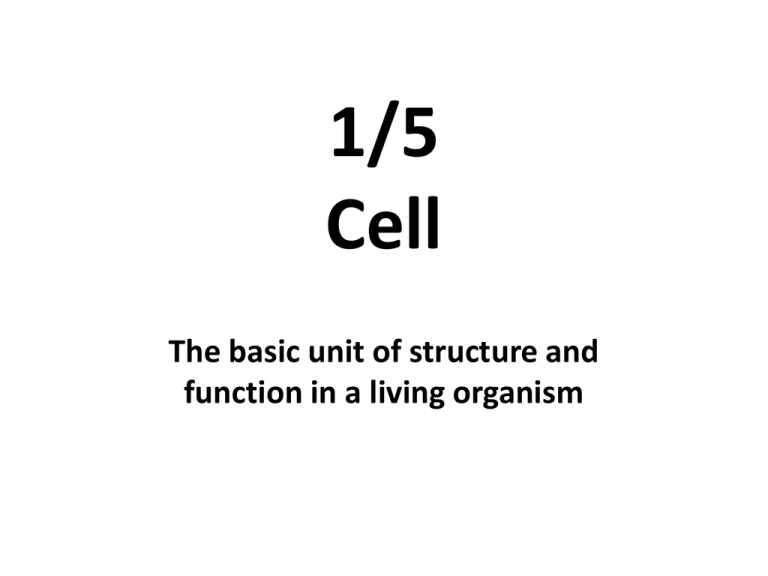
1/5 Cell The basic unit of structure and function in a living organism 1/6 Tissue A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. Example: The heart is an organ made of cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and blood tissue. 1/9 Organ A structure made of two or more tissues working together to perform a specific function in an organism Example: The heart is an organ that pumps blood throughout the body. 1/10 Organ System A group of organs that are interdependent and work together to perform body functions. Human organ systems include: circulatory, digestive, endocrine, excretory, immune, integumentary, lymphatic, muscular, nervous, reproductive, respiratory, and skeletal. 1/11 Organism Any living thing composed of ONE or more cells. *An organism is able to independently carry out all life processes. 1/12 Organelle A specialized structure found inside cells that carries out a specific life process . Example: ribosomes, vacuoles, nucleus, mitochondria 1/13 *Count 20 pages from the BACK of your CJ and start this section Practice Test Question The food that you eat travels from your mouth, down your esophagus, into your stomach, and through your small and large intestines before your body rids itself of solid waste. As the food passes through your body, it is digested, and you get important nutrients from the food. Which of the following is the correct term used to describe a group of body parts working together to perform a specific function? *Write the underlined part of the question and correct answer Choice! A. an organism B. a tissue C. an organ system D. an organ 1/17 Write Both Words Structure Function The shape and The specific job performed composition of a part of by a part of an organism or an organism or system system Example: An organism’s structure determines its function. Example: The function of muscle cells is to assist in movement. 1/18 Nucleus Cell Structure that contains genetic material. Acts as the “Brain” of the cell. 1/6 Structure The shape and composition of a part of an organism or system Example: An organism’s structure determines its function. 1/7 Function The specific job performed by a part of an organism or system Example: The function of muscle cells is to assist in movement. 1/19 2 Words Today Nucleus • In biology it is the cell structure that contains genetic material Chromosome • A structure in the nucleus that contains genetic material Example: Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes. 1/19 2 Words Today Nucleus • In biology it is the cell structure that contains genetic material Chromosome • A structure in the nucleus that contains genetic material Example: Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes. 1/20 Cell Membrane The protective outer covering of all cells. Example: The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing some materials to enter and leave the cell. 1/21 Cell Wall The stiff outer covering of plant cells that provides structure and protection. Example: The cell wall is composed mostly of a tough, fibrous material called cellulose. 1/13 Multicellular Organisms that consist of more than one cell, and have differentiated cells that perform specialized functions in the organism. Example: Plants, Animals, Vegetables, Humans 1/14 Unicellular An organism consisting of only one cell. Example: Bacteria, any microorganism 1/19 ( 2 Separate Words) Cell Wall Cell Membrane The stiff outer covering The protective outer of plant cells that covering of all cells. provides structure and protection Example: The cell Example: The cell wall is composed mostly of a tough, fibrous material called cellulose. membrane is semipermeable, allowing some materials to enter and leave the cell 1/20 Mitochondria Structures in a cell that produce energy for the cell. “Powerhouse” of the cell. 1/23 ( 2 Separate Words) Unicellular Multicellular Organisms that consist of more than one cell, and have differentiated cells that perform specialized functions in the organism. Example: Plants, Example: Bacteria, Animals, Vegetables, any microorganism Humans An organism consisting of only one cell. 1/24 ( 2 Separate Words) Vacuole Cytoplasm A fluid-filled storage sac found within a cell. The gel-like fluid within a cell that contains cell structures Ex. Vacuoles can store food, water, or waste products in a cell. 2/6 Cell Theory Theory that ALL living things are made of cells, that ALL cells come from other cells, and that the cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 1/24 Write both in your SHOES & Prefix, Suffix & Root Word Section in your CJ. ( 2 Separate Words) Re - Trans- Again Across Example: Replicate, Repeat Example: Transcription, Transport 1/26 Cytoplasm The gel-like fluid within a cell that contains cell structures 1/27 Vacuole A fluid-filled storage sac found within a cell. Ex. Vacuoles can store food, water, or waste products in a cell. 1/28 NO WORD 1. Pick up a “clicker” hold power button in top left corner to turn on, then arrow down and “find class” select-Graham. 2. “login” in with student ID and WAIT! 3. Study for cell structure and function quiz! CJ check will be after 1/25 Endoplasmic Reticulum A tube-like network of membranes within the cytoplasm of cells, where proteins and lipids are synthesized 1/26 Golgi Body/Complex A series (stack) of flattened membrane-bound sacs in the cytoplasm that packages proteins and carbohydrates into vesicles for export from the cell. 1/27 Practice Test Questions *Pick up Hand-out in the tray!* Answer test questions and put hand-out the back of your CJ where your other practice test questions are. 1/30 Ribosomes Small structures in the cytoplasm of cells that make the proteins needed by the cell. 1/31 Lysosome A membrane-bound organelle that contains digestive enzymes that help break down large molecules. 2/1 Mitosis The division of genetic material in a cell nucleus, producing two nuclei with the identical genetic makeup as the parent cell. Also called Cell division Chloroplast • Structure only found in plant cells that contain chlorophyll to enable the plants to make sugars through photosynthesis • Chromosomes: structures in the nucleus that contain genetic material. 2/2 Meiosis A type of cell division that produces egg and sperm cells used in reproduction Ex. Cells formed though meiosis have half the number of chromosomes of the original cell. 2/7 Write both in your SHOES & Prefix, Suffix & Root Word Section in your CJ. ( 2 Separate Words) Anthro- Corp- (Prefix) (Prefix) Means human Example: Anthropology, Anthropologist Means body Example: Corporate, Corporation Spontaneous Generation The theory, now discredited, that living organisms can arise from nonliving matter independently 2/6 Cell Theory Theory that says: 1.ALL living things are made of cells 2.ALL cells come from other cells. 3. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 2/7 Cytokinesis A process of cell division in mitosis and meiosis when the nucleus is finished dividing. 2/8 System A group of structures, cycles, and processes that interact and relate to each other. Example: In the human body, the circulatory system and the respiratory system work together to carry oxygen to all cells of the body. 2/9 Practice Test Questions *Pick up Hand-out in the tray!* Answer test questions and put hand-out the back of your CJ where your other practice test questions are. 2/10 No Word Unit 8 Post-Test Today! Come in, make sure you have a sharpened pencil, start studying quietly by yourself and wait until test is handed out.