Punnet Square Notes
Phenotype & Genotype
• Phenotype – the physical
characteristics of an organism (example:
blue eye color)
Phenotype & Genotype
• Genotype – the alleles possessed by an
organism (example: inheriting two blues
alleles on from each parent)
Dominant & Recessive Allele
Dominant Allele – An allele that
dominants over a recessive allele.
Represented in genetics with a capital
letter (example the capital letter B could
represent the dominant allele for brown
eyes).
Dominant & Recessive Allele
Recessive Allele - An allele that does NOT
dominate over other traits. Represented
in genetic by a lower case letter (example
the lower case letter b could represent the
allele for blue eyes)
Types of Genotypes
• Homozygous Dominant: An organism
having two identical dominant alleles.
Represented in genetic by having two
upper case letters. (example: BB
represents a person that has two alleles for
brown eyes)
Types of Genotypes
• Homozygous Recessive: An organism
having two identical recessive alleles.
Represented in genetic by having two
lower case letters. (example: bb
represents a person that has two alleles for
blue eyes)
Types of Genotypes
Heterozygous: An organism having two
different alleles for a trait, one recessive
and one dominant. Represented in
genetic by having one upper case and one
lower case letters. (example: Bb
represents a person that has a dominant
alleles for brown eyes and a recessive allele
for blue eyes).
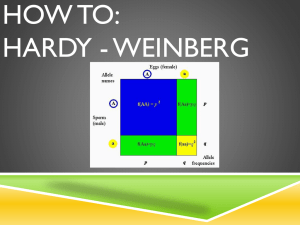
Punnet Square/ Grid
Punnet Square / Grid is a grid or table that
shows all the possible outcomes between
a cross between a male in female
organisms
Example
Cross a Heterozygous pea plant with smooth seeds with a
homozygous recessive plant with wrinkled seeds.
1.
2.
3.
Select Symbols the alleles:
Write the cross (alleles parents can give):
Make a punnet square.
–
–
–
What percent are heterozygous?
What percent are smooth?
What percent are wrinkled?
Example
Cross a Heterozygous pea plant with smooth seeds with a homozygous recessive plant with wrinkled seeds.
1.
Select Symbols the alleles: S = Smooth; s= wrinkled
:Ss X ss
2.
Write the cross (alleles parents can give)
3.
S; s
1.
Write down what each parent can give, also called Gamete or sex cell
x s ;s
Make a punnet square.
–
–
–
s
s
S
Ss
Ss
s
ss
ss
What percent are heterozygous? 50%
What percent are smooth? 50%
What percent are wrinkled? 50%
P-square Practice Question #1
Let's say that in seals, the gene for the length of the whiskers has two
alleles. The dominant allele (W) codes long whiskers & the recessive allele
(w) codes for short whiskers. Cross two long-whiskered seals, one that is
homozygous dominant and one that is heterozygous?
– The Symbols (letters you will use) ______________________
– The Cross (the parent’s genotypes)_________________________
– The Punnett square:
P-square Practice Question #2
In purple people eaters, one-horn is dominant and no horns is recessive. Draw
a Punnet Square showing the cross of a purple people eater that is
heterozygous for horns with a purple people eater that does not have
horns.
–
–
–
The Symbols (letters you will use) ______________________
The Cross (the parent’s genotypes)_________________________
The Punnett square:
Test Crosses
Problem:
• When an organism has a shows a
dominant phenotype (example: Brown
Eyes) it is not always possible to know if
this organism is has a heterozygote
genotype (Bb) or Homozygote dominant
genotype (BB) because the phenotype
(physical appearance) it the same for both
genotypes.
Test Cross
Solution:
• To determine the genotype of an
organism showing a dominant phenotype
a test cross is used.
What is a test cross?:
In a test cross an individual that might be
heterozygous or homozygous dominant is
crossed with an individual that is
homozygous recessive.
How it works?
If you cross a homozygous recessive
organism with a homozygous dominant
organism all (100%) the offspring will
have the dominant phenotype.
Example: Black fur color is dominant to white fur color in sheep. A
homozygous dominant black sheep is cross with a homozygous
recessive white sheep.
• The Symbols (letters you will use) ______________________
• The Cross (the parent’s genotypes)_________________________
• The Punnett square:
If you cross a homozygous recessive
organism with a heterozygote 50% of the
offspring will have the dominant
phenotype and 50% will have the
recessive phenotype.
Example: Black fur color is dominant to white fur color in sheep. A
heterozygous black sheep is cross with a homozygous recessive
white sheep.
•
The Symbols (letters you will use) ______________________
•
The Cross (the parent’s
genotypes)_________________________
•
The Punnett square:
Practice 3 problem.
• First try this problem on your own then
check your answer with the next slide.
•
•
P-square practice Question #3
A green-leafed luboplant (I made this plant up) is crossed with a luboplant
with yellow-striped leaves. The cross produces 185 green-leafed
luboplants.
•
Summarize the genotypes & phenotypes of the offspring that would be
produced by crossing two of the green-leafed luboplants obtained from the
initial parent plants.
•
A green-leafed luboplant (I made this plant up) is crossed with a luboplant with yellow-striped leaves. The cross
produces 185 green-leafed luboplants. Summarize the genotypes & phenotypes of the offspring that would be
produced by crossing two of the green-leafed luboplants obtained from the initial parent plants.
Note: Green plant is crossed with yellow plant results in all green plants. THUS, green is dominant, and initial
green parent’s genotype homozygous dominant (GG). Initial yellow parent is homozygous recessive (gg),
because the only way you can show the recessive phenotype is if you are homozygous recessive.
Cross of initial parents:
GG x gg
ALL offspring from the initial parents are green and heterozygous (Gg).
This question asks you to cross the offspring from the initial parents. Thus you will cross brother and sister
produced from initial parents (Gg x Gg)
•
The Symbols (letters you will use) G= green g = yellow
•
The Cross (the parent’s) genotype: Gg x Gg
•
The Punnett square:
•
Summary of offspring phenotypes
– Percentage that will have yellow-striped leaves: 25%
– Percentage that will have green-leaves: 75%
Problem 4
• First try this problem on your own then
check your answer with the next slide
Mendel found that crossing wrinkle-seeded plants with pure roundseeded plants produced only round-seeded plants. What
genotypic & phenotypic ratios can be expected from a cross of a
wrinkle-seeded plant & a plant heterozygous for this trait (seed
appearance)?
•
•
•
Mendel found that crossing wrinkle-seeded plants with pure round-seeded plants
produced only round-seeded plants. What genotypic & phenotypic ratios can be
expected from a cross of a wrinkle-seeded plant & a plant heterozygous for this trait
(seed appearance)?
NOTE: Crossing a wrinkled seed plant with a round seed plant produced all
round seeds. Thus you can assume that round is dominant to wrinkled.
Remember the only way the recessive phenotype will show is if the organism is
homozygous recessive for that trait.
–
–
–
•
The Symbols (letters you will use) R = round; r = wrinkled
The Cross (the parent’s genotype): Rr x rr
The Punnett square:
Summary of offspring
– Percentage that will have heterozygous: 50%
– Percentage that will have rounded-seeds: 50%
– Percentage that will have wrinkled-seeds: 50%
Problem 5 & 6
• Do these problems on your own.