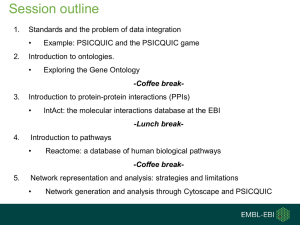
PPT
advertisement

EMBL-EBI MSD database is structured around the fact that Proteins are “sticky” EMBL-EBI A short biography of 1 protein whose very existence depends on being as sticky as possible EMBL-EBI EMBL K02078 ttaacgcgta ccaataaaaa ctacttccgc ataaacgcat gcagttgtcg tgaggctttc cttatcgagc gcctaccaag caaaaatcag tctgccggcg gttaaaaacg ggcaaaaaac cagccggtta gacaccaagc ttaggcctta ccgggcggct taatatatcg aattcaaaaa agtaacgaaa aaaccacacc aaaatttcac caacaaaaaa ccctttcaat tgatgattgt actacaccgc ccgtcaccga tggcatcccc gcgtcgttac tctccctgtg cgcgcaccga acctgccgtc aattttaaat tgtcttttaa at tctcaaattc atcggcacta cacctaaaag ctcaaaacat ccgatggtta taggagtaat gatcgctatc ccgcgcgcaa gtattacctg cccctccgac cgccacaatg ggccaggcgt cgacgacacc aacctgccgc aaatcaagcg gggtttgcaa cgacccaatc aaactgacaa aaaatacaaa aaaatcggca aatacattgc tttatgaata gtcggcattt gtttccgaag aatcacggca atcaaaggca ctttcaagcg gaaaacggtt gttgccgacg gataaggcat gtaagtgatt ggcgggcggg aacacacccg ttttcgacac ataaaaacaa cgaatcttgc atgatgccga cccttcaaaa tggcggcagt ccatcctttt aatggccgga aatatgttaa gcgtaaacaa cggtaaaatg ccaaagacgg ctgatgccaa ttccacccgc gtcgtccgtt ataccccatg tgccgccccc ttatatagag tttataatac tggcaagccc aggctttacc cgcccttccc ggccgaaggt aaacaacact agaggttgaa tgaaatcaaa gttctgcgga caaagaaatc atgaggcaaa ccggatcaac ccggtggaaa EMBL-EBI UniProt P02974 MNTLQKGFTL YQDYTARAQV HGKWPENNTS KNGVVTATML NGSVKWFCGQ TKHLPSTCRD IELMIVIAIV SEAILLAEGQ AGVASPPSDI SSGVNNEIKG PVTRTDDDTV NFDAK GILAAVALPA KSAVTEYYLN KGKYVKEVEV KKLSLWARRE ADAKDGKEID EMBL-EBI PDB 1AY2 MSD DATABASE pentamer MSD DATABASE negatively stained TEM images EMBL-EBI The pili are polar flexible filaments of about 5.4 nm diameter and 2500 nm average length. Neisseria gonorrhoeae expressing pili and interacting with epithelial cells. EMBL-EBI PDB 2PIL / 1AY2 Forest, K.T., Parge, H.E., Tainer, J.A. Nature. 1995 378, 32-8. Forest, K.T., Dunham, S.A., Koomey, M., Tainer, J.A. Mol Microbiol. 1999 31, 743-52. SOURCE: Neisseria gonorrhoeae A fibre forming cell adhesion protein responsible for the virulent attachment Pilin is a subunit of the pilus, a polar flexible filament, which consists of a single polypeptide chain arranged in a helical configuration of five subunits per turn. PDB 1ay2 , 1dzo , 1hpw , 1kb7 , 1nil , 1pan CATH 3.30.700.10 SCOP d.24.1.1 , j.23.1.1 Type IV Pilin Structure and Assembly: X-Ray and EM Analyses of Vibrio cholerae Toxin-Coregulated Pilus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK Pilin L. Craig, R.K. Taylor, M.E. Pique, B.D. Adair, A.S. Arvai, M. Singh, S.J. Lloyd, D.S. Shin, E.D. Getzoff, M. Yeager, K.T. Forest & J.A. Tainer Molecular Cell, 11, 1139–1150, 2003 EM Analysis of TCP Reveals a Three-Start Helix with a 45 Pitch C Bundle of negatively stained TCP filaments D computed Fourier transform of a single filament within the bundle as indicated by the box in (C). E Left-handed representation of a three-start helix with each start shown in a different colour. EMBL-EBI Pili are thin, protein tubes The pilus has a shaft composed pilin. At the end of the shaft is the adhesive tip structure having a shape corresponding to that of specific glycoprotein or glycolipid receptors on a host cell Because both the bacteria and the host cells have a negative charge, pili may enable the bacteria to bind to host cells without initially having to get close enough to be pushed away by electrostatic repulsion. Once attached to the host cell, the pili can depolymerize and enable adhesions in the bacterial cell wall to make more intimate contact. EMBL-EBI Type IV pili are not merely passive sticky fibres but dynamic machines that participate in a surprising number of functions including: Bacterial aggregation Adhesion to host cells Twitching motility Pilus retraction DNA transformation In another bacterial species, motility. Phage receptor in V. cholerae. EMBL-EBI EMBL UniProt PDB Assembly (MSD) Microscopy still not the full story - GENOME EMBL-EBI Pilus gene organisation Many copies of pilin gene throughout chromosome Two are functional, pilE1 and pilE2 All other copies are silent Antigenic variation occurs due to recombination (within mini-cassettes) EMBL-EBI Antigenic variation in N. gonorrhoeae A single cell can give rise to daughter cells expressing structurally and antigenically different pili Gonococcus has the genetic capacity to make as many as a million different pilin variants All able to bind to same host tissues and to cause the same disease symptoms EMBL-EBI PILI are the pathogen’s answer to Mankind's physical defence systems One of the body's innate defences is the ability to physically remove bacteria from the body by: constant shedding of surface epithelial cells coughing, sneezing, vomiting, and diarrhoea removal by bodily fluids such as saliva, blood, mucous, and urine. pili enable adhere N. gonorrhoeae to receptors on target epithelial cells and thus colonize and resist flushing by the body. EMBL-EBI REMEMBER – this all achieved by simple non-covalent forces EMBL-EBI What has all this got to do with MSD? PDB Entries and X-Ray results 1. Crystal Structure 2. Molecular Structure (covalent) 3. Oligomeric Assembly EMBL-EBI MSD Relational Database Exp. Result Assembly Chains Residues assembly_deposition_fk ASSEMBLY assembly_deposition_fk CHAIN chain_assembly_fk DEPOSITION chain_assembly_fk assembly_a_data_fk atd_chain_fk atd_chain_fk COMPONENT ATOM DATA atd_component_fk atd_component_fk assembly_a_data_fk ASSEMBLY DATA atd_model_fk atd_atom_fk ATOM atd_atom_fk assembly_data_model_fk assembly_data_model_fk atd_model_fk atd_alt_fk MODEL ALT atd_alt_fk Atoms EMBL-EBI KEY to MSD DataBase EMBL-EBI Biological Context PDB MSD Oxalate oxidase 1FI2 hexameric EMBL-EBI Protein Stickiness What does this mean? What is the evidence? EMBL-EBI PDB Xray coordinates PDB entry the deposited coordinates usually consist of the contents of the asymmetric unit: The contents of the ASU define a single copy of the macromolecule The contents of the ASU consist of more than one copy of the macromolecule The contents of the ASU require crystallographic symmetry operations to be applied to generate the complete macromolecule(s) A combination of the above, including multiple copies and required symmetry transformations A crystal is a periodic arrangement of a motif in a lattice. The motif can be a single atom, a small molecule, a protein or any combination thereof. Often the motif, also referred to as to the 'asymmetric unit', is subjected to a number of symmetry operations yielding differently oriented copies. EMBL-EBI Space Groups The combination of all available symmetry operations (point groups plus glides and screws) with the Bravais translations leads to exactly 230 combinations, the 230 Space Groups. Kathleen Yardley Lonsdale 19031971. Carried out a profound and systematic study of the theory of space groups , methods for their determination, and the possibilities of molecular symmetry that are involved (1924, 1936). EMBL-EBI benzene C6H6 Covalent bonded EMBL-EBI Benzene crystallised in Space Group P6/m 6-fold rotation axis Mirror plane EMBL-EBI Benzene P6/m in the PDB Entire atomic contents: ATOM C1 x1 y1 z1 occupancy 0.5 ATOM H1 x2 y2 z2 occupancy 0.5 EMBL-EBI HELD TOGETHER BY WEAK FORCES The stronger of the two is the hydrogen bond. The weaker is the van der Waal's forces. Both interactions depend on the same fundamental cause, the charge on electrons, and how that results in attraction and repulsion at an atomic level. EMBL-EBI Johannes D. van der Waals The equation of state for gases and liquids Nobel Prize 1910 The origin of the London van der Waals force lies in the instantaneous dipole generated by the fluctuation of electron cloud surrounding the nucleus of electrically neutral atoms. EMBL-EBI van der Waals forces All intermolecular attractions are known collectively as van der Waals forces. The various different types were first explained by different people at different times. Dispersion forces, for example, were described by London in 1930; dipole-dipole interactions by Keesom in 1912. EMBL-EBI van der Waals EMBL-EBI Hydrogen Bonding Linus Pauling (1901-1994) Nobel Prize 1954 EMBL-EBI Hydrogen Bonds Pauling in 1935 was the first to explain the mysterious stickiness of water molecules. The basic principle behind hydrogen bonding is that the electron deficient hydrogen atom of one polar molecule is attracted to the electron rich side of another polar molecule. Hydrogen bonds are somewhat stronger than van der Waal's forces, and require two components: a donor group and an acceptor group. EMBL-EBI Hydrogen Bonds EMBL-EBI Quaternary Structure Quaternary Structure is defined as that level of form in which units of tertiary structure aggregate to form homo- or hetero-multimers. Consideration of the presence of a quaternary state is important in the understanding of a protein's biological function. Crystal Structure Crystal Structure Oligomeric Assembly Proteins EMBL-EBI don’t do this – pack by translationals EMBL-EBI Symmetry There are three main types of symmetry: symmetry with respect to a plane (mirrors) symmetry with respect to a line (rotations) symmetry with respect to a point (inversions) EMBL-EBI Symmetry symmetry with respect to a line (rotations) symmetry with respect to a plane (mirrors) symmetry with respect to a point (inversions) EMBL-EBI Rotational symmetry 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 -fold rotational symmetry These are the only rotational symmetries that can exist in crystals; all others are disallowed. These five rotational axes are called the five Proper Axes Symmetries showing 5-, 7-, 8-, 9-, 10-, 11-, & 13- fold rotations are known for biological molecules – these are observed in the Asymmetric Unit. 1g8h A’ A Residues of Chain A in interface Applying 1st 3-fold Rotation A’ Residues of Chain A’ in interface A A’ A” A Applying 2nd 3-fold Rotation Also has a 2-fold rotation Final Assembly is a Hexamer from 23 symmetry EMBL-EBI Screw Axes If you add translations to rotation axes, you form what are call screw axes. For an nm screw axis, the rotational component is 360/n degrees, and the translations is m/n of the unit translation along the axis. In Biological Crystallography --> Polymers Helices are improper Screw axes – e.g. DNA EMBL-EBI Screw Axes YopM is a strongly acidic protein containing 13–20 repeats of a 19-residue leucine-rich-repeated motif (LRR). YopM has a crescent shape, formed from parallel β-sheets,with a loose amino terminus95. Four YopM monomers form a hollow cylinder with an inner diameter of 35 Å . YopM is an important virulence factor in Yersinia infection EMBL-EBI 1jl5 YOPM 4-fold screw axis EMBL-EBI Also has a 2-fold rotation – infinite cylinder in crystal Screw Axis EMBL-EBI Screw Axes example tubulins EMBL-EBI Bacteriophage T4 Molecular Machine EMBL-EBI Bacteriophage T4 Identified Gene products Bacteriophage T4 1N7Z Gp8 Baseplate Structural Protein 1QEX Gp9 1EL6 Gp11 Baseplate-tail tube complex 1CZD Gp45 Processivity Clamp 1G31 Gp31 Co-Chaperonin 1OCY Receptor-Binding Domain 1RFO Phagehead Fibritin - whisker antigen control 1C1K Gp59 Helicase Assembly Connector Protein From Bacteriophage Phi29 1FOU EMBL-EBI Bacteriophage T4 24 Genes give proteins in the Head+Whiskers/Neck 22 Genes give proteins for the Tail+Base Plate 7 Genes give proteins in the Tail Fibres 1 Gene gives the fin attachment protein e.g. in the Head scaffold there are 576 copies of gp22 ALL HELD TOGETHER BY WEAK FORCES EMBL-EBI Bacteriophage T4 Identify genes Identify structures Identify location Becomes Mechanics – just balls and springs EMBL-EBI Bacteriophage T4 Important Hinge Proteins EMBL-EBI Hinge-Bending, Swiveling Motions Most large proteins are built from assemblies of domains that for the most part consist of regions of nearly rigid motions jointed by flexible regions. The activity of many proteins induces conformational transitions by hinge bending, which involves the movement of relatively rigid parts of a protein about flexible joints The conformational switch from open to closed of the flexible loop-6 of triosephosphate isomerase (TIM) The hinge region on the Fc fragment of human immunoglobulin G EMBL-EBI Hinge-Bending, Swiveling Motions Hinge mechanism that occurs when there is no continuously maintained interface constraining the motion. Hinge motions usually occur in proteins with two domains with one domain rotating about the hinge as a rigid body. The rotation is caused by a few large torsion angle changes within the hinge region. shear mechanism that occurs when two interfaces slide across each other in order to maintain a wellpacked interface. Shear motions are typically small so a large shear motion will be composed of a number of individual shear motions. EMBL-EBI Genes Proteins Structure Function Genes Proteins Structure Function Some Proteins have No predicted structure or regions predicted not to fold Genes Proteins Structure DYNAMICS Function http://www.BioSimGrid.org/ EMBL-EBI http://bioportal.weizmann.ac.il/fldbin/findex FoldIndex© tries to answer to the question: Will this protein fold? It's a dynamic and interactive process that estimates the local and general probability for the provided sequence, under specified conditions, to fold. EMBL-EBI Bacteriophage T4 EMBL-EBI Bacteriophage T4 baseplate Kostyuchenko et al., Nat. Struct. Biol.,2003 10, 688 Emd Entry 1048 EMBL-EBI gp5/gp27 hexamer of the tube makes up the hypodermic needle at the tip EMBL-EBI gp5/gp27 hexamer Bacteriophage T4 PDB Entry 1K28 BACTERIOPHAGE T4 CELL-PUNCTURING DEVICE KANAMARU, et.al., EMBL-EBI gp5/gp27 hexamer PDB: ASU 3-fold Rotation MSD: Assembly EMBL-EBI PDB Example EMBL-EBI Observed Asymmetric Unit 1e94 M.Bochtler et al, Nature, 403, 800 (2000) EMBL-EBI 1e94 - 3 separate molecules (?) 2 dodecamers 1 hexamer EMBL-EBI 1e94 M.Bochtler et al, Nature, 403, 800 (2000) EMBL-EBI hexamer EMBL-EBI hexamer Grapple EMBL-EBI 1e94 M.Bochtler et al, Nature, 403, 800 (2000) EMBL-EBI dodecamer EMBL-EBI dodecamer EMBL-EBI Heat shock proteins HslV and HslU that form a new ATP-dependent protease in Escherichia coli - ATP-dependent protease complexes rid cells of misfolded or damaged proteins and control the level of certain regulatory proteins. M. Bochtler, C. Hartmann, H.K.Song, G.P.Bourenkov, H.D.Bartunik, and R.Huber (2000) The structures of HSLU and the ATP-dependent protease HSLU-HSLV. Nature 403, 800 Couvreur B. , Wattiez R. , Bollen A. , Falmagne P. , Le ray D. , Dujardin J.C. (2002). Eubacterial HslV and HslU subunits homologs in primordial eukaryotes.Mol. Biol. Evol. 19, 21102117 Easter Island Complex with topknot P31059 HSLV (P31059) caps HSLU (P32168) P32168 EMBL-EBI STATS on PDB Oligomers ~ 24,000 entries Oligomer type Num Monomer 7490 dimer 9179(8169) 7215(6261) 1958(1908) trimer 1659(1628) 815( 786) 844( 842) tetramer 2963(2930) 1852(1828) 1111(1102) pentamer 178( 178) hexamer 898( 883) heptamer octamer 53( Homo 52) 421( 418) 91( Hetero 91) 534( 521) 29( 29) 209( 208) 87( 87) 364( 362) 24( 23) 212( 210) nonamer 62( 62) 6( 6) 56( 56) decamer 72( 72) 43( 43) 29( 29) undecamer 10( 10) 8( 8) 2( 2) 230( 230) 96( 96) dodecamer 134( 134) EMBL-EBI Windscreen bug splat examples 1fmd EMBL-EBI SYMMETRY Rules –BUT What about - What happened to symmetry? 2:1 hetero-complex The Ribosome – the champion Heterocomplex proteins tossed around the RNA protein aggregates complicate the lives of people who study proteins in vitro Protein Aggregation and Amyloid Diseases - Converting the protein from a soluble to a fibrillar structure EMBL-EBI ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I have taken from the WWW most of the pictures used here The list of sources is available separately.