Personalized Breast Cancer Care
advertisement

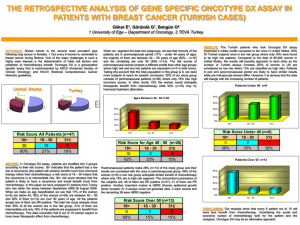
Personalized Breast Cancer Care Sunil Patel, MD Medical Oncology and Hematology Collom and Carney Clinic. No financial disclosure Personalized Breast Cancer Care Topics • Role of genetic/familial high risk assessment • Role of specific markers on breast tissue in decision making of treatment. • For some patients, more(=chemo) is not better. - Role of genetic profiling of the tumor in decision making. Breast Cancer Progress Report • Breast Cancer mortality rates have decreased by 2.3% annually since 1990 • The decline in mortality is primarily due to early detection and new treatment methods Source: Breast Cancer Facts and Figures 2005-2006 National Center for Health Statistics data as analyzed by NCI The Stages of Breast Cancer Breast Cancer is diagnosed according to stages (stages 0 through IV) under the TNM classification. Factors used in staging of Breast Cancer: • Tumor Size Size of primary tumor • Nodal status Indicates presence or absence of cancer cells in lymph nodes • Metastasis Indicates if cancer cells have spread from the affected breast to other areas of the body (i.e. skin, liver, lungs, bone) Source: National Cancer Institute Genetics Help us Identify Patients at High Risk of Developing Breast Cancer Genetics – Genetics is the study of heredity • While genetics influence genomics, genetics is responsible for only 5-10% of breast cancer • Genetics focuses primarily on the likelihood of developing cancer • Genetic tests find mutations, not disease Source: Understanding Cancer Series: Gene Testing, National Cancer Institute Genomics Help us Look at the Patients Individual Tumor Biology Genomics Genomics is the study of how genes interact and are expressed as a whole • Genomics and gene expression profiling tools focus on the cancer itself and can help determine How aggressive is the cancer (prognosis) What is the likely benefit from treatment (prediction) Examples of Genetic and Genomic Tests Genetic Test • BRCA1 and BRCA2 • The genetic make up of patients is tested for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. Patients with those mutations have higher chances of developing breast cancer. Genomic Test • Oncotype DX® Breast Cancer Assay • The expression level of 21 genes is measured in tumor tissue from patients that have already been diagnosed with breast cancer. This assay evaluates if a patient is going to recur (prognostic) and predicts benefit from chemotherapy and hormonal therapy (predictive) •Mammaprint assay Genetic Risk Factor Assessment • NX 42 year old white female with no family history of breast cancer, now has 4 cm right breast cancer. • Biopsy confirmed IDC,ER+, HER2/neu + • What’s next? – Surgery- ipsilateral or bilateral mastectomy, chemo, hormonal therapy? Or more? Breast & Ovarian Cancer Risk Assessment – for patients - Age 50 y or younger Triple negative breast cancer ( ER-PR-Her2/Neu-) Two breast cancer primaries Breast cancer at any age - 1 or more close relative with breast or ovarian cancer at age 50 or younger -2 or more close relatives with breast and/or pancreatic cancer -women of Ashkenazi Jewish descent at any age breast/ovarian cancer. - Other cancer history – Thyroid, sarcoma, adrenal , endometrial, pancreatic, brain cancer - Ovarian cancer - Male breast cancer. Patient NX • NX 42 year old white female with no family history of breast cancer, now has 4 cm right breast cancer. • Biopsy confirmed IDC,ER+, HER2/neu + • What’s next? – Surgery- ipsilateral or bilateral mastectomy, chemo, hormonal therapy? Or more? Patient NX • Should go I go for surgery first? Then chemo? • Blood for BRCA 1 and 2 mutation. Patient MB • MB is a 53 year old white male with right sided breast cancer, stage I. BReastCAncer Genes BReast CAncer • Women have about a 1 in 7 chance of getting breast cancer in their lifetime. • Most cancer is sporadic, about 5-10% of cases are genetically linked • Women inheriting mutation of BRCA gene have increased chance of disease • Also can lead to ovarian cancer The Numbers Frequency of BRCA Mutations in the U.S. U.S. citizens 1 in 500 Ashkenazi Jews 1 in 40 Women with breast cancer under age 50 Approx. 1 in 13 Women with breast cancer under age 40 1 in 10 Ashkenazi Jews with breast cancer under age 50 Approx. 1 in 8 BRCA Genes • BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 • Roles they play Life is all about the right balance. What are they? • BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 – Known as breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility genes – Tumor suppressor genes • regulate the cycle of cell division by keeping cells from growing and dividing too rapidly or in an uncontrolled way • inhibit the growth of cells that line the milk ducts in the breast – Involved in many other functions including control of DNA replication and damage repair BRCA 1 • Cloned in 1994 (Miki et al) –Mapped to chromosome 17q21 –5,592kb long –24 exons BRCA 2 • • • • Cloned in 1995 (Wooster et al.) Mapped to chromosome 13q12-13 10,254 kb (3,418 aa) 27 exons More Numbers Type of Cancer General Population That Will Develop Disease People With BRCA1 Mutation Who Will Develop Disease People With BRCA2 Mutation Who Will Develop Disease Breast 12.5% 55 – 85% 33 – 86% Ovarian 1.43% 28 – 44% 10 – 30% Prostate 4 – 6% 12 – 18% Male breast cancer Less than 1% 6% 4 – 14% Pancreatic 0.6% not applicable 6 – 7% 12 – 18% Patient NX • BRCA 1 mutation positive • Neo-adjuvant chemotherapy then bilateral skin sparing mastectomy. • Hormonal therapy • Prophylactic bilateral salpingo-oopherectomy • Genetic counseling for family members. Patient MB • • • • BRCA 2 mutation positive Chemotherapy Contra-lateral mastectomy PSA screening test. Topics • Role of genetic/familial high risk assessment • Role of specific markers on breast tissue in decision making of treatment. • For some patients, more is not better. - Role of genetic profiling of the tumor in decision making. How Do We Assess Risk in Breast Cancer Patients? Classic Pathological Criteria Lymph Node Status Tumor Size Age Tumor Grade AdjuvantOnline! ER/PR HER2 Computer-based model ER/PR/Her2-Neu • Estrogen receptor • Progesterone receptor • Her2/Neu – Human epidermal growth factor Receptor 2 • ER/PR+ Her2/Neu – • ER/PR – Her2/Neu – (Triple negative) • ER/PR – Her2/Neu + • ER/PR+ Her2/Neu + Triple-Positive Breast Cancer H&E ER-Pos PR-Pos HER2/neu-Pos Triple-Negative Breast Cancer H&E ER-Neg PR-Neg HER2/neu-Neg Treatment options Chemotherapy Endocrine therapy – Tamoxifen or Aromatase inhibitor - Anastrozole (Arimidex) , Letrozole (Femara) , Exemestane (Aromasin) Trastuzumab (Herceptin) HerceptinTM(trastuzumab) Triple negative breast cancer Hormone Receptor - /HER2 • Chemotherapy for tumor more than 0.5 cm. • Nodal involvement. Hormone Receptor Positive, HER2 Positive Breast Cancer • 0.5 cm or less tumor size – Adjuvant endocrine therapy • 0.6 to 1 cm – Adjuvant endocrine +/- chemo with trastuzumab. • > 1 cm tumor size and/or lymph node involvement – adjuvant endocrine therapy, chemotherapy with trastuzumab. Hormone Receptor Negative, HER2 Positive Breast Cancer • 0.5 cm or less tumor size – No chemo. • 0.6 to 1 cm – Consider chemo with trastuzumab. • > 1 cm tumor size and/or lymph node involvement – chemotherapy with trastuzumab. • HORMONAL THERAPY NOT USEFUL. Hormone Receptor Positive, HER2 Positive Breast Cancer • 0.5 cm or less tumor size – Adjuvant endocrine therapy • 0.6 to 1 cm – Adjuvant endocrine +/- chemo with trastuzumab. • > 1 cm tumor size and/or lymph node involvement – adjuvant endocrine therapy, chemotherapy with trastuzumab. Hormone Receptor Positive HER2 Negative Breast Cancer Tumor size • Tumor size < 0.5 Cm and No LN involvement – Adjuvant endocrine therapy. No chemotherapy • T > 0.5 Cm and No LN involvement adjuvant endocrine therapy +/- ?? Chemo. Hormone Receptor Positive HER2 Negative Breast Cancer • Nodal involvement > 2mm focus – adjuvant endocrine therapy + chemotherapy • 1 to 3 Lymph nodes or >3 nodes involved – does every one need chemo? Topics • Role of genetic/familial high risk assessment • Role of specific markers on breast tissue in decision making of treatment. • For some patients, more(=chemotherapy) is not better. - Role of genetic profiling of the tumor in decision making. How Do We Assess Risk in Breast Cancer Patients? Classic Pathological Criteria Lymph Node Status Tumor Size New tools in the Genomic Era… Genetic Profiling of Tumor Age Tumor Grade ER/PR HER2 AdjuvantOnline! Computer-based model Adjuvant Treatment for Early Stage Breast Cancer Today Hormonal Therapy Based on the Landmark NSABP B-14 Study using Tamoxifen If 100 women with ER+, N- disease are treated with hormonal therapy how many will recur within 10 years? 15 Recurrence Disease free 85 Fisher et al. N Engl J Med 1989;320(8):479-84 Chemotherapy and Hormonal Therapy Based on the Landmark NSABP B-20 Study using Tamoxifen + Chemotherapy If all 100 women with ER+, N- disease are treated with chemotherapy and hormonal therapy, how many will benefit from the addition of chemotherapy? 4 11 Benefited from Chemotherapy Relapsed despite Chemotherapy 85 Disease free regardless of Chemotherapy Fisher et al. J Natl Cancer Inst 1997;89:1673-82 Outcomes of Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Walgren et al. JCO 2005;23:7342-7349 Cop yrigh t © A m erican S oc ie t y o f C lin ical O ncolog y How Do We Assess Risk in Breast Cancer Patients? Classic Pathological Criteria Lymph Node Status Tumor Size New tools in the Genomic Era… Genetic Profiling of Tumor Age Tumor Grade ER/PR HER2 AdjuvantOnline! Computer-based model Patient A Patient B Patient C With Genomic Tools We Can Now Analyze Cancer at the Molecular Level 1. Patient’s tumor 2. Oncotype DX® Assay 5. Shared Decision Making 4. Oncotype DX® Report 3. Analyze expression of tumor’s genes Oncotype DX®: A Genomic Assay Oncotype DX® 21-Gene Recurrence Score® (RS) Assay 16 Cancer and 5 Reference Genes From 3 Studies PROLIFERATION Ki-67 STK15 Survivin Cyclin B1 MYBL2 INVASION Stromelysin 3 Cathepsin L2 ESTROGEN ER PR Bcl2 SCUBE2 GSTM1 CD68 BAG1 HER2 GRB7 HER2 REFERENCE Beta-actin GAPDH RPLPO GUS TFRC Paik et al. N Engl J Med. 2004;351: 2817-2826 Oncotype DX® 21-Gene Recurrence Score® (RS) Assay Calculation of the Recurrence Score Result Coefficient x Expression Level RS = + 0.47 x HER2 Group Score - 0.34 x ER Group Score + 1.04 x Proliferation Group Score + 0.10 x Invasion Group Score + 0.05 x CD68 - 0.08 x GSTM1 Category - 0.07 x BAG1 Low risk RS (0-100) RS <18 Int risk RS ≥18 and <31 High risk RS ≥31 Paik et al. N Engl J Med. 2004;351: 2817-2826 The Oncotype DX® Assay mostly used for N-, ER+ Breast Cancer Patients Invasive Breast Cancer Stage I ER- Stage II ER+ N- ER- Stage III N+ ER+ Stage IV Patient A Patient A • Patient was identified as low risk by Oncotype DX® with a Recurrence Score ® result of 4 • Patient received hormonal therapy since she was in a group in which chemotherapy does not provide benefit Patient B Patient B • Patient was identified as high risk by Oncotype DX® with a Recurrence Score® result of 34 • The Recurrence Score helped convince the patient on the likely benefits of taking chemotherapy given the biology of her disease • Patient received chemotherapy and hormonal therapy Patient C Patient C • Patient was identified as intermediate risk by Oncotype DX® with a Recurrence Score® result of 25 • Is there benefit from chemotherapy for this patient? The TAILORx trial evaluates the utility of chemotherapy in the mid-range risk group Outcomes of Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Walgren et al. JCO 2005;23:7342-7349 Cop yrigh t © A m erican S oc ie t y o f C lin ical O ncolog y The Promise of Personalized Medicine in Breast Cancer Tamoxifen Women with HR+ breast Cancer Aromatase Inhibitor Chemotherapy Biologic agents Her2, EGFR, VEGF, Parp Anth, Taxane, Platimun The Molecular Portrait Hypothesis You can recognize the Mona Lisa by her smile and her nose and her eyes and even her hands – if you are really good, but not the sky or the trees Thank you. Questions?