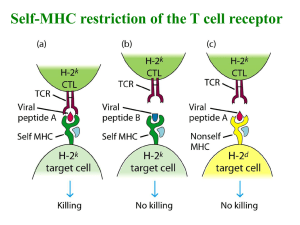
CD8 - Molecular and Cell Biology
advertisement

How T cells recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Lecture 11, MCB 150 Laurent Coscoy 1 Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do? •By the early 1980s, much about T cell function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified •Recall that Ig was purified as soluble myeloma protein •There is no soluble form of T Cell Receptor 2 Monoclonal antibody approach (Allison and colleagues 1982) 3 Liver cells B cell lymphoma Hedrick & Davis strategy: Subtractive cDNA cloning T cell clones Probed with cDNA clone 1 Probed with cDNA clone 2 4 TCR: An ab heterodimer 5 A second type of TCR • Hetero dimer of g and d chains (like a and b chains) • Expressed on a rare subset of T cells with fascinating properties (more later) ab T cells CD4 T cells CD8 T cells gd T cells 6 Comparison of TCR and BCR (Ig) 7 T cell receptor loci Analogous to B cell receptor loci 8 Generation of the T cell receptor 9 TCR structure 10 TCR: Peptide/MHC I Interaction Binding groove Peptide Va CDR3’s Vb Variable domains Cb Ca Constant domains 11 Peptide Binding Grooves of MHC Molecules Class I Class II 12 Soluble peptide/MHC complexes: a probe to detect specific T cells MHC I Made by genetic engineering; does not exist in nature Ig HC Fc Region 13 HTLV-I and tropical spastic paraparesis HTLV-I: - human retrovirus, persistent infection - 20 millions people are infected worldwide - encodes the oncogene Tax TSP: - progressive inflamatory disease of the CNS - pathogenesis not fully understood 14 Following Antigen-Specific T Cells CD8 15 CD4 and CD8: Co-receptors for the TCR 16 What’s with these “CD” names? • “CD” stands for cluster of differentiation • Many labs generated monoclonal antibodies against cellsurface proteins --> naming of antibodies and their targets was a mess • Conference was called to “clean up” the naming business • Target of monoclonal ab directed against the same surface protein or complex was given a number, as in CD3, CD4, etc. 17 Co-receptors bind to non-polymorphic regions of MHC I (CD8) or II (CD4) 18 19 CD4 and CD8 mark mutually exclusive subsets of mature T cells Anti-CD4 & Anti-CD8 Anti-CD4 Anti-B220 Flow cytometry of spleen Anti-CD3 Anti-CD8 Anti-gd TCR 20 Contrast how B and T cells see antigen B Cell T Cell APC 21 TCR affinity is quite low 22 Mysteries in T cell antigen recognition • About 105 copies of each MHC molecule on cell surface • Frequency of any particular Peptide:MHC complex may be as low as 0.01% • How does the TCR sort through all those incorrect complexes and find ones with which to trigger? 23 Co-receptor and adhesion molecules improve avidity CD2 T cell TCR LFA-3 MHC target cell CD4 or CD8 LFA-1 ICAM-1 24 Immunological Synapse: A model Red: adhesion Green: Antigen T cell T cell APC APC T cell APC 25 Immunological “synapse” Peptide-MHC complexes Adhesion molecules (ICAM-1) 26 The synapse in real-time B-Cell (Peptide-pulsed ) QuickTime™ and a Vid eo d eco mp re ss or a re nee de d to s ee th is picture. T-Cell 8 minutes in 20 seconds of video 27 The synapse in real-time QuickTime™ and a Vid eo d eco mp re ss or a re nee de d to s ee th is picture. 28 TCR Signal Transduction Why do we care? It helps us understand T cell function It gives us molecular targets for immunotherapy It is an amazing example of biological complexity 29 Consequences of T cell activation Proliferation Cell cycle entry and cell division Clonal expansion Differentiation Secretion of cytokines (helper cells) Activation of killer functions (cytotoxic cells) Acquisition of effector function Memory Death Important for down-regulation of immune response How is TCR:peptide:MHC binding linked to these events? TCR signaling induces changes in gene expression 30 Example of T cell activation TCR binds peptide:MHC Induces expression of genes T cells divides many times creating more T cells with the same TCR T cells differentiate and acquire new characteristics 31 Signal Transduction Transmission of external signals across the membrane and conversion of these signals into intracellular biochemical events Peptide:MHC TCR ? Changes in gene expression 32 TCR signaling: Big Picture RECEPTOR ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Alterations in 33 Gene expression How does the TCR transduce signals with such a little tail? 34 TCR associates with the CD3 Complex Analogous to the Iga and Igb proteins that associate with BCR on B cells 35