2. An Overview of the Cell
advertisement

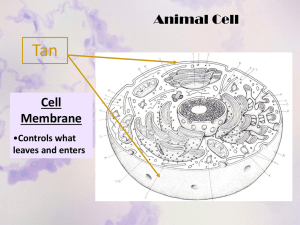
An Overview of the Cell With a focus on Plant and Animal Cell Structures Types of Cells O There are two categories all cells can be divided into: O Prokaryotic cells do not have a membrane-bound nucleus and the genetic material is scattered throughout the rest of the cell. (doesn’t have a true nucleus) O Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane to contain all genetic material. (has a true nucleus) O Cells vary in size, shape and function. Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells The Nucleus O Is the cell’s control center and coordinates all cell activities. O The nucleus contains chromosomes which are threadlike structures that contain our genetic code. These chromosomes are made of proteins and deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA) O Chromatin: The complex of DNA and proteins that make up a eukaryotic chromosome. When the cell is not dividing, chromatin exists as a mass of long thin fibres that are not visible with a light microscope. O Chromosomes: As the cell prepares to divide (reproduce), the stringy, entangled chromatin coils up and becomes thick enough to be seen as separate structures called chromosomes. The Nucleus (and Rough Endoplamic Reticulum) The Nuclear Membrane • Separated from the rest of the cytoplasm by a double membrane. Pores in the nuclear envelope allows RNA and other chemicals to pass through but keeps the DNA inside Nucleolus O A small spherical structure located inside the nucleus. O It is believed that the nucleolus creates ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) which directs the formation of ribosomes. The Cell Membrane O The cell membrane (plasma membrane) surrounds the cell, giving it a definite shape and boundary. It is selectively permeable, so it controls what enters and exits the cell. Cell Wall O In many organisms the plasma membrane is not the outermost boundary. O In plants, most algae, fungi and bacteria, there is a cell wall that lies outside the plasma membrane. O In plants it is made of cellulose and has spaces for water, ions and particles to pass through. O It is NOT selectively permeable but does offer protection and support for the cell. • Some plant cells have an additional secondary wall with a middle lamella in between that contains a sticky pectin to hold cells together. The Cytoplasm O The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance inside the cell. O Cytoplasm - 70% water - 30% proteins, fats, carbohydrates and other ions. O Composition is always changing due to osmosis and diffusion. O The cytoplasm houses the working “organs” of the cell called organelles. Mitochondria O Mitochondrion (singular) Mitochondria (plural) O Are oval-shaped organelles and are the “powerhouses” of the cell. O Mitochondria contain their own DNA O They provide the body with needed energy in a process called cellular respiration. O Sugar molecules are combined with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water with a release of energy. O Energy is not made in the mitochondrion rather the breakdown of glucose sugar releases energy. O Energy is available for processes such as: O Muscle contraction O Synthesis of new molecules O Cellular transport O Two separate membranes – a smooth outer membrane and a folder inner membrane. O Cristae – fingerlike projections of the folded inner membrane. Each contains special enzymes to help breakdown glucose. Ribosomes O Smallest organelle in the cell. O Site of protein synthesis. O Proteins are the molecules that makes up cell structure. O Cell growth and reproduction require constant synthesis of proteins. O In the nucleus, DNA sends messenger molecule to produce protein in ribosomes of the cell. O Location: found both scattered throughout the cytoplasm and attached to endoplasmic reticulum. Endoplasmic reticulum A series of canals that carry materials throughout the cytoplasm. Composed of parallel membranes. 2 types: O O O 1. 2. Rough endoplasmic reticulum Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum O Organelle with a double membrane and ribosomes attached. O Extends from the nuclear membrane to the cell membrane. O Transports proteins made by the ribosomes to the Golgi apparatus. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum O Double membrane bound organelle without ribosomes. O Also extends throughout the cell. O Produces lipids for the cell. Golgi Apparatus O Appears like a stack of pancakes. O They are membranous sacs piled on top of each other. O Function: O To package , modify and store proteins produced by ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum. O To release large molecules (hormones, enzymes) by exocytosis. O Golgi apparatus migrates towards the plasma membrane where small packets (called vesicles) are released and pass through plasma membrane by exocytosis. O The golgi apparatus will also form lysosomes Lysosomes O Formed by exocytosis of vesicles from Golgi apparatus and are smaller than mitochondria. O They are sac-like structures that contain digestive enzymes to break down large molecules and cell parts within the cytoplasm. O Only found in animal cells O Purpose: O The break down cell “food” to use as an energy source. O As a defense mechanism for the immune system. O The Immune Response O Lysosomes destroy harmful substances that find their way into the cell. O Example: White blood cells phagocytise foreign particles. Lysosomes then release digestive enzymes to destroy the invader. O Lysosomes are also known as “suicide sacs”. O Body cells have a certain lifespan after which they die and must be cleaned up. Digestive enzymes in lysosomes clean up cell parts after body cells die. Vacuoles O Vacuoles are fluid-filled, membrane-bound structures that store substances produced by the cell for future use. O They are reservoirs for sugars, minerals, proteins, water and wastes. O Gives plant cells physical support. O Plant cells have large, central vacuoles. O Animal cells have many smaller vacuoles. Cytoskeleton O Microfilaments are threadlike structures in the cytoplasm that help provide shape & movement. O Microtubules are tube-like fibres (made of protein) that transport materials through the cytoplasm – also found in flagella & cilia. Cilia and Flagella O A flagellum is a whip like tail O that aids in movement O Flagella spin like a propeller O Cilia (cilium)are shorter, hair like structures that aid in movement and moving materials. Centrioles O Composed of nine bundles of three microtubules. O Found only in animal cells. O Play a key role in cell division. Plastids O Plastids are “chemical factories” and O O O O “storehouses” for food and other pigments in plant cells Only found in plant cells! Chloroplasts are plastids that contain the green pigment chlorophyll that is used for photosynthesis. Chromoplasts- store orange and yellow pigments Amyloplasts- colourless plastids that store starch O Plastid structure: O Made of a double membrane O Packets of chlorophyll inside which taps into the Sun’s energy to make sugar.